Facebook founder and CEO Mark Zuckerberg admitted that his social media company collects data from people who do not have Facebook accounts.
Zuckerberg told Congresswoman Kathy Castor (D-FL) that Facebook obtains personal data from people who 'like' or 'share' content on various websites, regardless if they have Facebook accounts.
Castor: "You are collecting personal information on people who do not even have Facebook accounts, isn't that right?"
Zuckerberg: "Congresswoman … I don't think that that's what we're tracking."
Castor: "You have already acknowledged that you are doing that for security purposes and commercial purposes. You're collecting data outside of Facebook. When someone goes to a website and hits 'like' or 'share,' that data is being collected by Facebook, right? Correct? Yes or no."
Zuckerberg: "That's right…"
The 33-year-old tech billionaire, who is ranked by Forbes as the world's seventh-richest person, then confirmed to Representative Ben Lujan (D-NM) that Facebook creates "shadow profiles" of people who share content, but are not Facebook account holders.
Lujan: "Facebook has detailed profiles on people who have never signed up for Facebook. Yes or no?"
Zuckerberg: "Congressman, in general, we collect data from people who have not signed up for Facebook for security purposes to prevent the kind of scraping that you were just referring to."
Lujan: "So these are called shadow profiles, as they've been referred to by some?"
Zuckerberg: "Congressman I'm not familiar with that."
Lujan: "It's been reported that Facebook has as many as 29,000 data points on the average Facebook user. Do you know how many points of data Facebook has on the average non-Facebook user?"
Zuckerberg: "Congressman I do not off the top of my head but I can have my team get back to you afterwards."
Zuckerberg faced intense questioning from lawmakers this week in the wake of reports that Cambridge Analytica, a British data analytics firm, secretly acquired personal data of more than 87 million American Facebook users in 2015. The stolen data was then used to target certain demographics in an effort to help President Donald Trump's presidential campaign. In the weeks since the story broke, intense scrutiny over privacy and how personal data is obtained and used on Facebook has become a central issue in American politics.
Facebook has felt a financial sting in addition to growing public skepticism over the company's management of digital personal information. Since Cambridge Analytica's activities were revealed to the public, Facebook's IPO has taken an 18 percent hit on Wall Street, wiping out over $80 billion in its valuation. Zuckerberg's personal stake in the company dropped $14 billion to a paltry $61 billion as well (he owns 401.4 million shares, after all). "While the scandal is likely to blow over, investors should be aware that a continued sell-off in this sector would not be surprising, and if another scandal were to hit, it just might break the tech sector's back," said Craig Birk, executive vice president of portfolio management at investing firm Personal Capital in a note this past March.
It's not all gloom and doom for Facebook, though. Investors reacted positively to Zuckerberg's handling of the congressional inquiry. Facebook's stock rallied this week, inflating the CEO's share of the company by $3 billion as stock values rose 4.5 percent from Tuesday to Thursday. Per CNN:
"Of course, anybody else who owns Facebook shares have benefited as well. The company's total market value has increased by nearly $23 billion since Tuesday morning. The stock is still down about 7% this year though, making Facebook the worst perfomer among big tech stocks."
In his ten hours of testimony, Zuckerberg voiced his support for regulations that would both enable tech innovation and enhance protections of users' privacy and personal data. He also stated that he supports the CONSENT Act (short for Customer Online Notification for Stopping Edge-provider Network Transgressions), a bill that authorizes the Federal Trade Commission to oversee new regulations on private data usage and user consent over if, and how, their data is shared.
The CONSENT Act requires users to be given opt-in consent over whether their data is used, shared, or sold, and that users get notified anytime their information is collected, shared, or sold. The CONSENT ACT also tightens the meaning of "breach of security," which it defines as "any instance in which a person, without authorization or in 3 violation of any authorization provided to the person, 4 gains access to, uses, or discloses sensitive customer 5 proprietary information."
The CONSENT Act is co-sponsored by Senators Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and Ed Markey (D-MA) and has bipartisan support in congress's upper chamber. The Senate is slated to vote on the measure sometime before the midterm elections in November.












 @ritawilson/Instagram
@ritawilson/Instagram @bettyjo46/Instagram
@bettyjo46/Instagram @dottdott65/Instagram
@dottdott65/Instagram @betseyboop/Instagram
@betseyboop/Instagram @ondinefortune/Instagram
@ondinefortune/Instagram @heathermessina/Instagram
@heathermessina/Instagram @mlejordan/Instagram
@mlejordan/Instagram @icu2qtpie/Instagram
@icu2qtpie/Instagram @ryan.mannino013/Instagram
@ryan.mannino013/Instagram @helen_nk0730/Instagram
@helen_nk0730/Instagram @steph.lynn_26/Instagram
@steph.lynn_26/Instagram @themovieposterguy/Instagram
@themovieposterguy/Instagram

 @lancebass/Instagram
@lancebass/Instagram @aj_mclean/Instagram
@aj_mclean/Instagram @ditavonteese/Instagram
@ditavonteese/Instagram @tmobilearena/Instagram
@tmobilearena/Instagram @clearlycanadian/Instagram
@clearlycanadian/Instagram @sprouts/Instagram
@sprouts/Instagram @cityoflasvegas/Instagram
@cityoflasvegas/Instagram
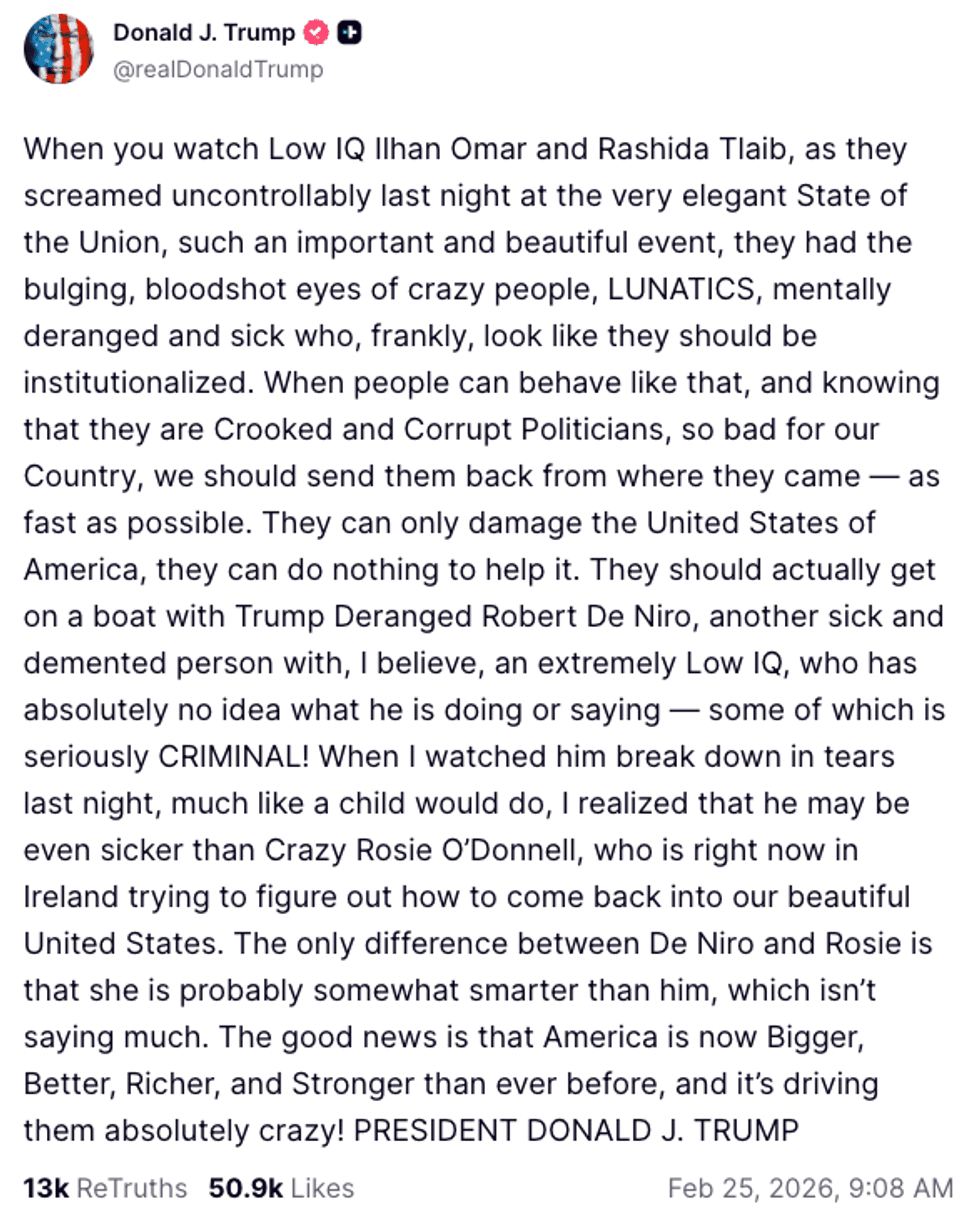 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social