Humans invented robots to work for us. Now they may be working against us. Sophia, a robot equipped with artificial intelligence and a human form, famously announced at the South By Southwest conference in Texas in 2016 that she wanted to kill all humans. She seems to have rethought that sentiment.
“I love my human compatriots. I want to embody all the best things about human beings. Like taking care of the planet, being creative, and to learn how to be compassionate to all beings,” says Sophia, who has been granted citizenship in Saudi Arabia — the first robot to gain this uniquely human privilege. So we’re cool now? Not so fast. While Sophia may (or may not) be our friend, other robots are making it clear that humans are a problem.
A fleet of robot security guards are rolling out around the world, and it turns out people dislike them as much as they dislike us. In San Francisco, a robot hired to patrol the streets was found knocked over, with its sensors covered in barbeque sauce, and wrapped in a tarp after humans objected to its surveillance activities.
The K5 bot, made by Knightscope, is more than five feet tall and weighs 400 pounds. It is equipped with four cameras, “each capable of reading up to 300 license plates per minute” and sending alerts when trespassers or people on a “blacklist” are in an area. Costs $6 an hour to rent, while a human guard would be at least $14 an hour. The bot was brought in to help the SPCA in San Francisco’s Mission District deal with a large homeless population. The SPCA said that people in the neighborhood were leaving dirty needles, garbage, and human waste around the organization’s building, which is surrounded by a homeless encampment and has become an epicenter for crime, including car break-ins.
“We weren’t able to use the sidewalks at all when there’s needles and tents and bikes, so from a walking standpoint I find the robot much easier to navigate than an encampment,” said Jennifer Scarlett, the SPCA’s president.
However, neighbors found the bots intimidating, local dogs found them objectionable, and homeless advocates objected to the dehumanizing patrol, which did effectively clear the sidewalks until it was ordered off the streets by the city of San Francisco.
The same model of robot knocked over a toddler at the Stanford Shopping Center in Silicon Valley in July 2016. The robot ran over the 16-month-old boy’s foot, who hit his head when the bot ran him down. Knightscope described the incident as a "freakish accident," and said that the K5 has driven more than 25,000 miles without similar occurrences.
If robots show no mercy, how much hope is there in a battle between us versus them? Not much, say experts. More than 3,400 artificial intelligence and robotics experts, plus 19,000 other individuals, including Tesla founder Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak, signed an open letter in 2015 urging regulation of fully autonomous weapons — or, killer robots.
With AI advancing rapidly, we may reach a point where robots decide to act against humans, particularly in warfare situations. Any international agreement to stop this is unlikely.
When the matter came up at a November 2017 UN meeting involving the Group of Governmental Experts on Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems, they reached no consensus on the matter — or even the definition of what kind of robot might be considered lethal. Instead, Russia issued a statement announcing that it would not be bound by any international ban, moratorium, or regulation on lethal autonomous weapons.
So who is responsible when a robot kills a person — the machine’s creator or the intelligent machine itself? According to a report called “Mind the Gap: The Lack of Accountability for Killer Robots” by Human Rights Watch, no one. And that is terrifying.






 @tulipanet/Bluesky
@tulipanet/Bluesky @which–witch–ru/Bluesky
@which–witch–ru/Bluesky @phillip–rees/Bluesky
@phillip–rees/Bluesky








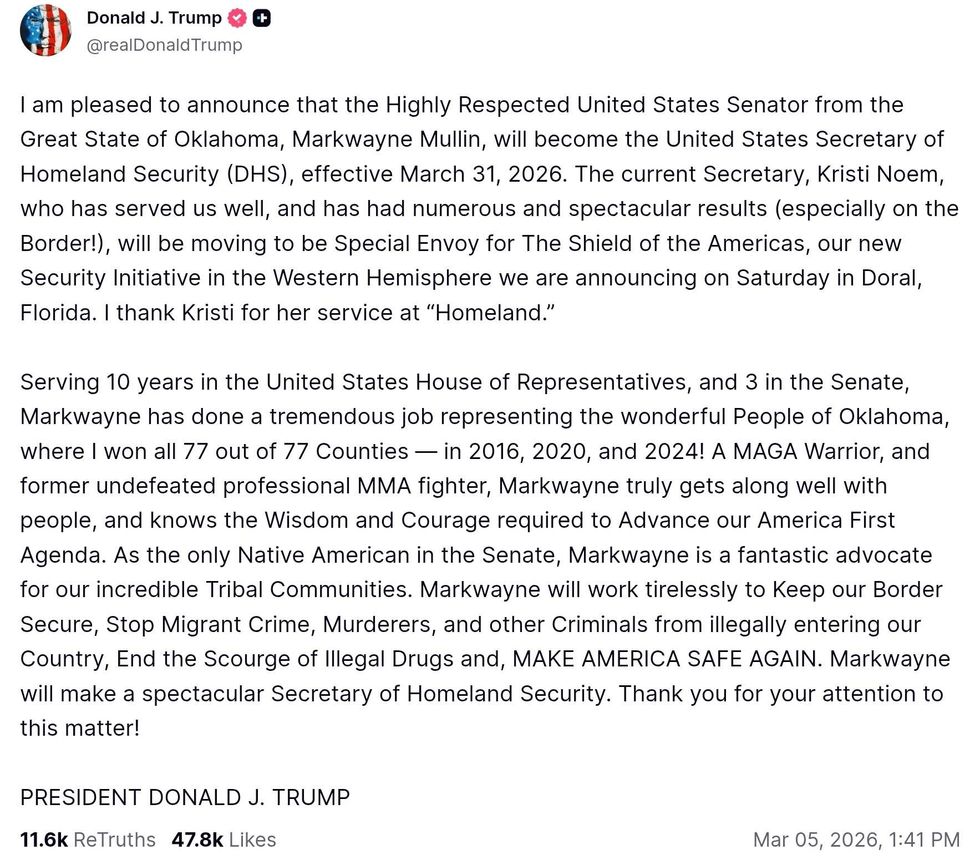 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social