Wannabe business owners, take heed: new research shows “the entrepreneurial spirit” may be a load of poop — literally.
A team of scientists led by a professor from the University of Colorado Boulder has found an association between entrepreneurship and infection by toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan parasite found in cat feces.
Many first hear of toxoplasma gondii and its associated infection, toxoplasmosis, from warnings that pregnant women should stay away from cleaning cat boxes. The parasite is known to cause miscarriages and birth defects, and can pass from mother to baby. For those with healthy immune systems, infection with toxoplasma gondii goes largely unnoticed, with either no or mild symptoms. In fact, in the U.S., approximately 11 percent of people older than age 6 have been infected at some point, and in other parts of the world, the infection rate is closer to 95 percent.
Toxoplasma’s mode of infection is to infiltrate the brain. In mice, this causes a lack of fear — specifically of cats, which allows the felines to more easily catch and eat the infected, unafraid mice, thereby ensuring the parasite’s reproduction.
In people, toxoplasmosis has been associated with an increased risk of “car accidents, mental illness, neuroticism, drug abuse and suicide,” the research team wrote in its study, published in late July in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, a biological-sciences journal. The team couldn’t help but wonder, then, if the same mechanism that toxoplasma worked on mice’s brains — that is, to make them risk-seekers — would work on people. Lead researcher Stefanie Johnson, an associate professor of management, collaborated with her husband, a biology professor, to test their theory on students.
First, they collected saliva from 1,495 individuals, finding that those who tested positive for T. gondii were “1.4 times more likely to major in business and 1.7 times more likely to have an emphasis in ‘management and entrepreneurship’ over other business-related emphases,” the researchers wrote in their report.
Second, they tested 197 people attending “entrepreneurship events.” Those who tested positive for T. gondii were “1.8 times more likely to have started their own business compared with other attendees.”
Third, the group analyzed infection disease databases and the global entrepreneurship data, finding that countries with higher T. gondii infection rates indeed had higher levels of entrepreneurship activity.
“Economics research has historically emphasized the importance of rationality in explaining human decisions, with individuals considering benefits and risks before acting in their self-interest,” the scientists wrote. “T. gondii exposure, however, might nudge individuals toward higher risk, higher reward activities and deviating from economic theory.”
Just how T. gondii reduces fear of risk is not known, but it’s thought to have something to do with neurotransmitters or perhaps even hormones like testosterone. In any case, the thought that a protozoan parasite could be inside a person’s brain, controlling his or her thoughts, isn’t necessarily welcome, even if it could mean owning one’s own business.
“As humans, we like to think that we are in control of our actions,” study lead co-author Pieter Johnson, Stefanie Johnson’s husband, said in a University of Colorado Boulder press release. “But emerging research shows that the microorganisms we encounter in our daily lives have the potential to influence their hosts in significant ways.”












 @maddiemcrojas/Instagram
@maddiemcrojas/Instagram @eeemgeeebeee/Instagram
@eeemgeeebeee/Instagram @chefmelissaking/Instagram
@chefmelissaking/Instagram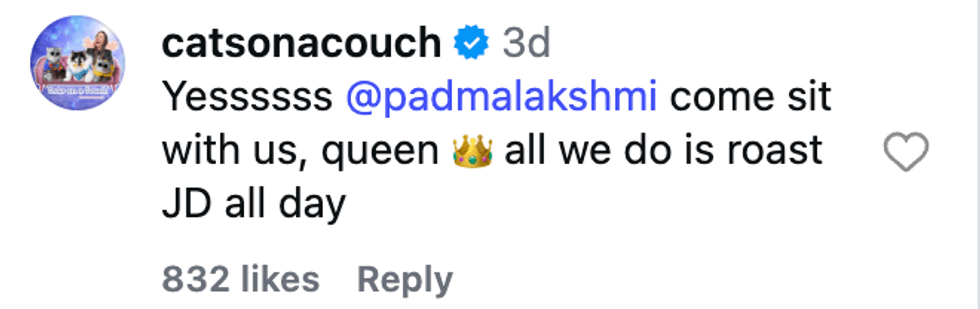 @catsonacouch/Instagram
@catsonacouch/Instagram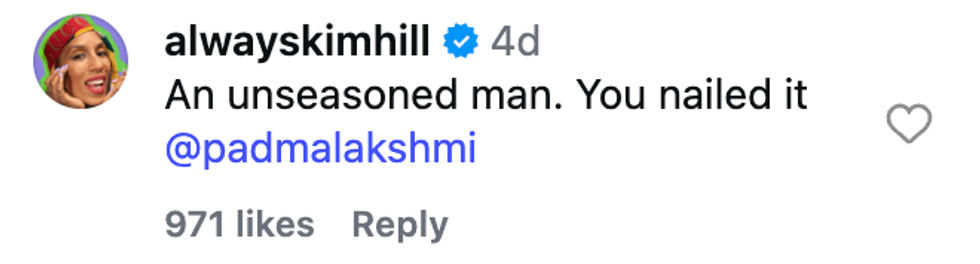 @alwayskimhill/Instagram
@alwayskimhill/Instagram @_completelybooked/Instagram
@_completelybooked/Instagram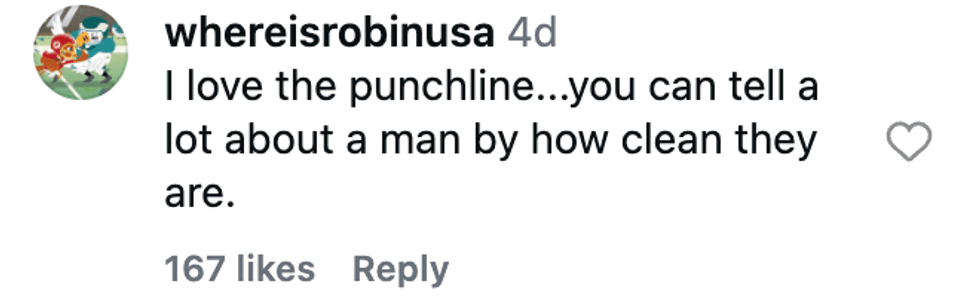 @whereisrobinusa/Instagram
@whereisrobinusa/Instagram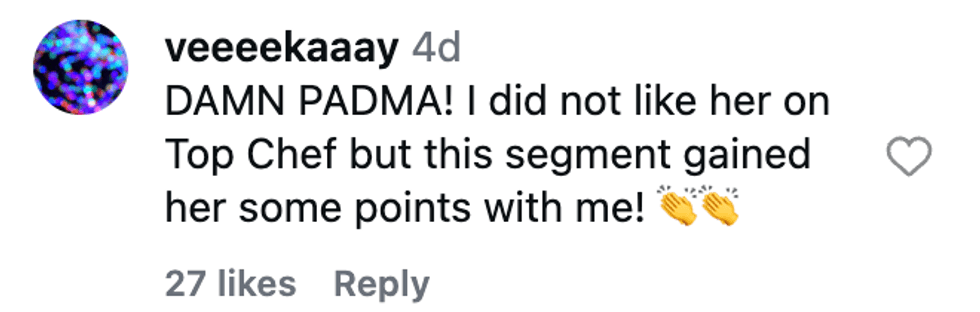 @veeeekaaay/Instagram
@veeeekaaay/Instagram @getlei_d/Instagram
@getlei_d/Instagram @andrebsteele/Instagram
@andrebsteele/Instagram @xxthisiskkxx/Instagram
@xxthisiskkxx/Instagram @ddrobjr/Instagram
@ddrobjr/Instagram
