Please SHARE this with your friends and family.
Source: The British Museum
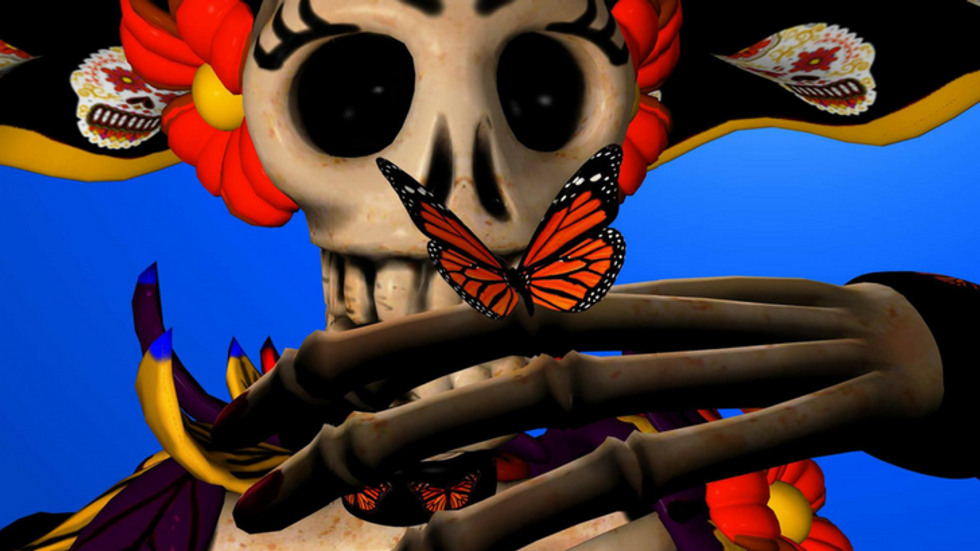
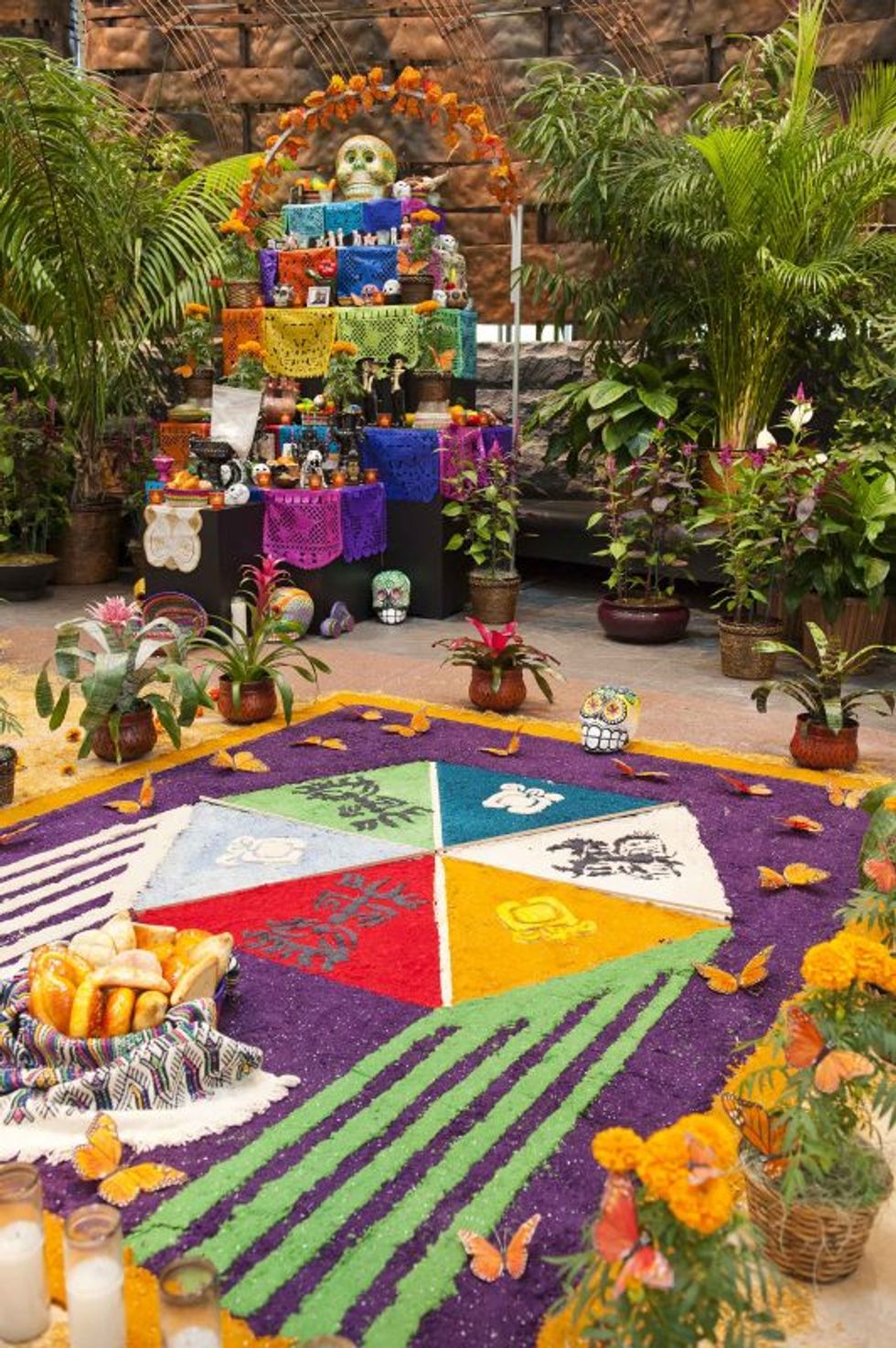
The Day of the Dead celebrations are upon us. Dia de Los Muertos is a time to recount the history and origins of a holiday that playfully picnics with deceased ancestors in cemeteries and at home with colorful altars, sweet treats, marigolds and dancing skeletons. Many Mexicans and Latino families remember times when everybody in town spend full days and nights the cemeteries to celebrate life and have a party with the dead. Nothing to fear in this tradition; it’s a time to smile at death and tell stories of ancestors and their life on earth.
The evolution of this community celebration comes from a mashup of Aztec rituals, Catholic missionaries and 20th century political statements in Mexico.
-
Aztecs believed that death was an integral part of life. Humans were the bridge between heaven and earth.
As long ago as 1500 B.C. Aztecs throughout Mexico believed that death was part of the cycle of nature and their crops. Human bodies were a vessel for the soul, a divine creation that continued into afterlife.
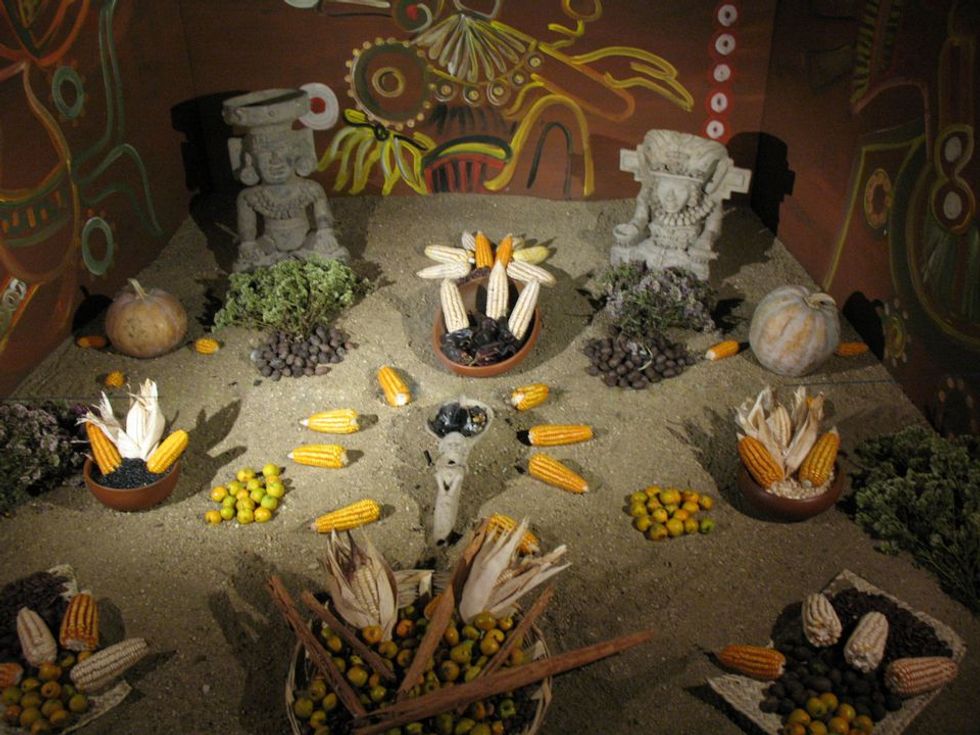
According to the National Hispanic Center, the belief was that Mitclan (the Land of the Dead) was the final destination and souls undertook a four year voyage through dangerous challenges at nine different levels. Families of the deceased were honored to provide tools and feed the souls on their journey. These tools and provisions are the foundations of the altars and ofrendas built by families to guide them to their final place.
2. Catholic and Medieval Spanish traditions become ofrendas and cemetery fiestas.
When the missionaries came to Mexico and Central America territories, the Roman Catholic Church allowed the autumn celebrations of death to occur on All Souls and All Saints Days. The family ceremonies for building bonfires at their ancestors graves, offering food and singing through the night merged with the Catholic ritual of holding mass in the catacombs of Saints and Martyrs. Medieval Spanish traditions added in the soul bread, flowers and oil lamps at the graves and altars for the souls to find their earthly homes and loved ones.
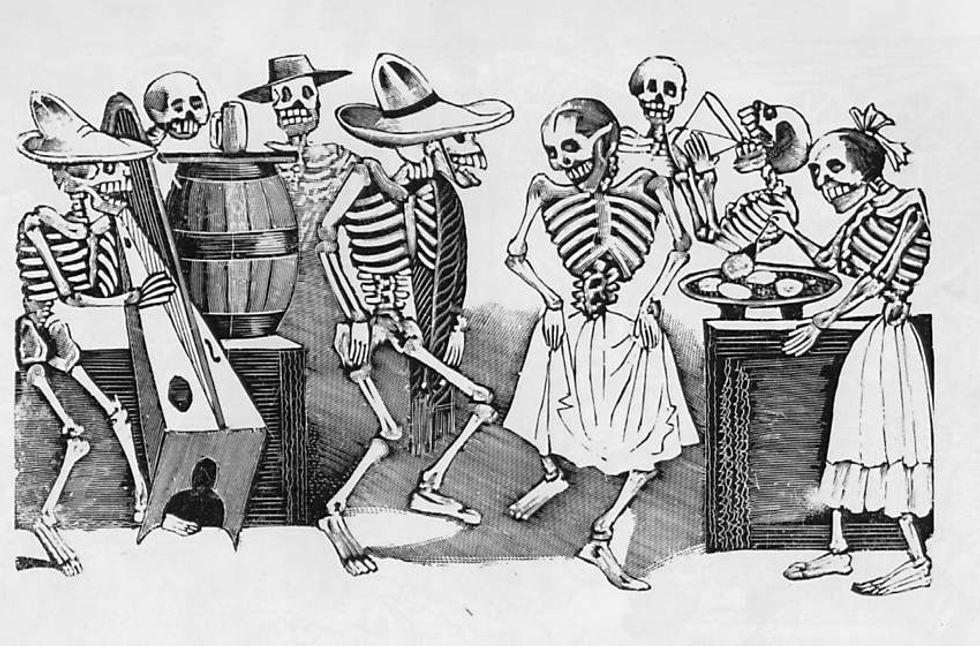
3. Artists mock death in the 20th century
Most people have seen the many images of playful skeletons tied to the Dia de Los Muertos festivities. The brightly colored flowers painted on sugar skulls and jaunty scenes of the dead living happy moments of their former life can be attributed to the illustrations of Jose Guadalupe Posada (1852-1913). He mocked death by showing clothed skeletons doing everyday activities and poked fun at politicians. La Catrina is the most famous and well-dressed skeleton and thought to be a social statement aimed at the ruling president Porfirio Diaz.
















 @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram @CNN/Instagram
@CNN/Instagram
 Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images
Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images