Australia could become the first country to completely eliminate cervical cancer, according to an announcement made by the International Papillomavirus Society.
HPV (human papillomavirus) is a sexually transmitted infection that causes 99.9% of cervical cancers. In the world of infectious diseases and sexually transmitted diseases, HPV poses a tremendous global risk. The sexually communicable virus is also linked to increases risks for other various forms of cancer, including the vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth and throat.
In 2007, the Australian federal government began a pilot program designed to offer the vaccine to girls who were at high risk for contracting HPV. These girls, ages 12-13, were given access to the vaccine for free. Six years later, the program expanded to provide the vaccination to boys. The inoculation process for HPV require a series of two to three vaccinations. Despite the age restrictions on the government sponsored program, boys and girls between the ages of 14-19 are offered access to two doses of the vaccine—an effort to make the preventive measure more accessible and affordable to that vulnerable age range.
According to The Guardian, by 2016, 78.6% of 15-year old girls and 72.9% of 15-year old boys in Australia had been vaccinated. Because of this, by 2015 the rate new HPV infections had dropped to just 1.1 percent for women ages 18-24.
In December 2017, the government also installed a new program that provides a more comprehensive and advanced cervical cancer screening that could identify cancer at an earlier stage. According to Professor Ian Frazer, a co-inventor of the HPV vaccine that Australia is using, the new screening test, coupled with the free vaccination program, will help to potentially eradicate cervical cancer in Australia within a decade or two.
“As long as we continue the screening program, we will continue to pick up those with the virus already, and as long as we keep up the vaccination, we could have no new cases in 10-20 years. Only 50-60% of women participate regularly in the screening program. If that was 100% we would have no cervical cancer in this country even without the vaccine, “ he said.
The advancements towards eradicating cervical cancer is a marked difference from the United States. According to the CDC, 79 million Americans are infected with HPV, many of whom are in their late teens and early 20’s. 14 million new Americans are infected with HPV each year.
Accessibility to the vaccine, thankfully, is not a huge barrier for many Americans, both with private and public medical insurance. Medicaid, Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, Immunization Grant Program (Section 317 of the Public Health Service Act), and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) offers vaccine coverage to many American. For example, Medicaid (as guaranteed by the Affordable Care Act) ensures that all children under 18 have access to the vaccine.
Despite the accessibility, however, cervical cancer is still a huge problem, especially when race becomes a factor. According to the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, “Limited access to treatment and diagnosis at later stages of disease progression, as well as cost, lack of physician referral, and cultural barriers may account for some of the disproportionate impact of cervical cancer on Black women.” Prevention is key to preventing cervical cancer; the HPV vaccine is just one of these tools.
Thankfully, more and more Americans are being vaccinated against HPV, a trend that will hopefully continue to mirror the path taken by Australia. According to Morbidity and Mortality Weekly, an estimated 60% of teenagers in the US are now vaccinated against HPV. This number will need to continue to rise, should a true eradication of cervical cancer ever be possible on American soil.







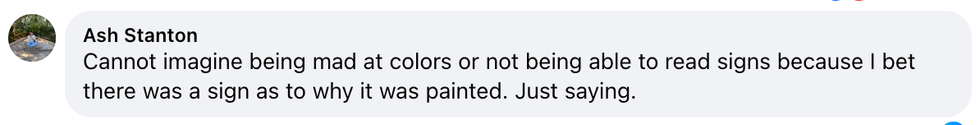 Ash Stanton/Facebook
Ash Stanton/Facebook Laura Sprinkle/Facebook
Laura Sprinkle/Facebook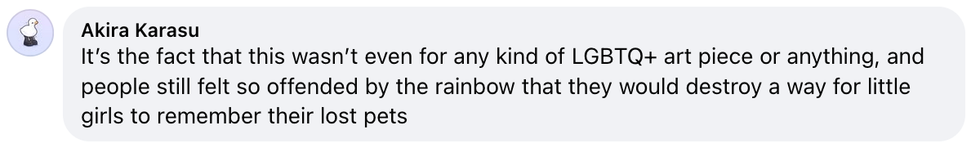 Akira Karasu/Facebook
Akira Karasu/Facebook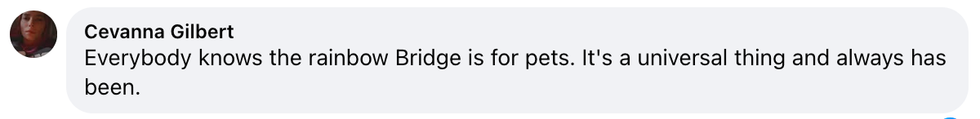 Cevanna Gilbert/Facebook
Cevanna Gilbert/Facebook Troy Adam/Facebook
Troy Adam/Facebook





 @GovPressOffice/X
@GovPressOffice/X
 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social