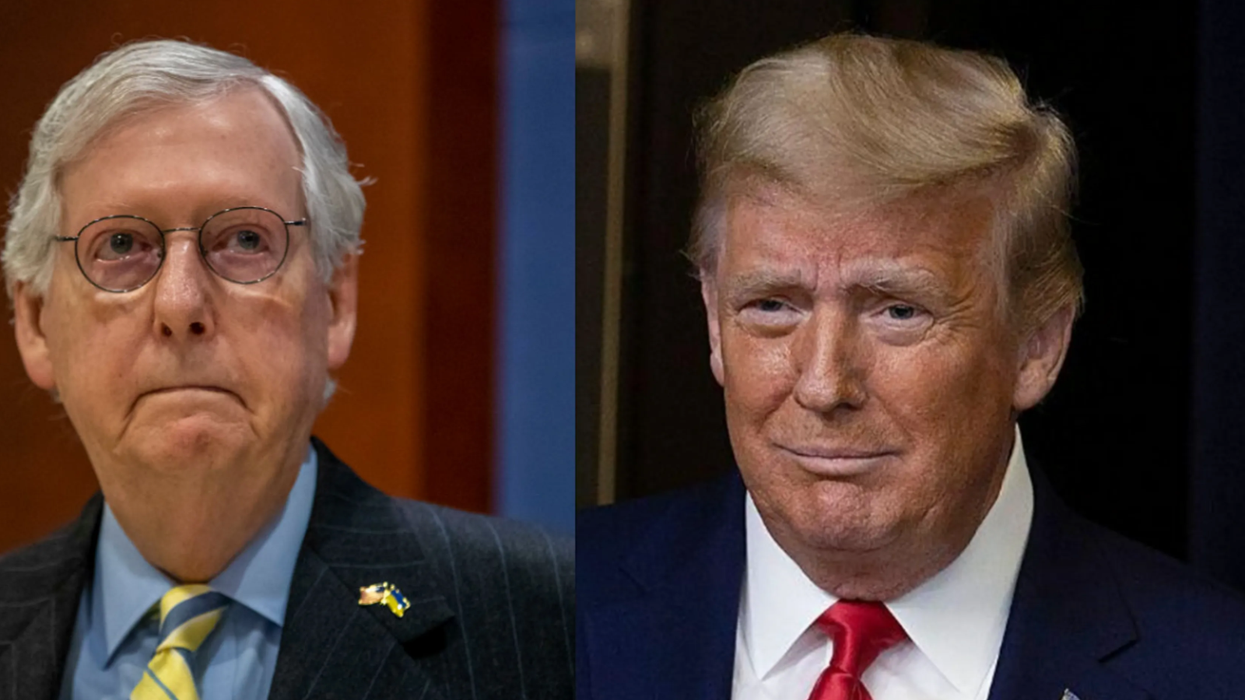
Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell broke with former President Donald Trump's claim over absolute presidential immunity but was criticized by people who were unimpressed with his remarks considering his history.
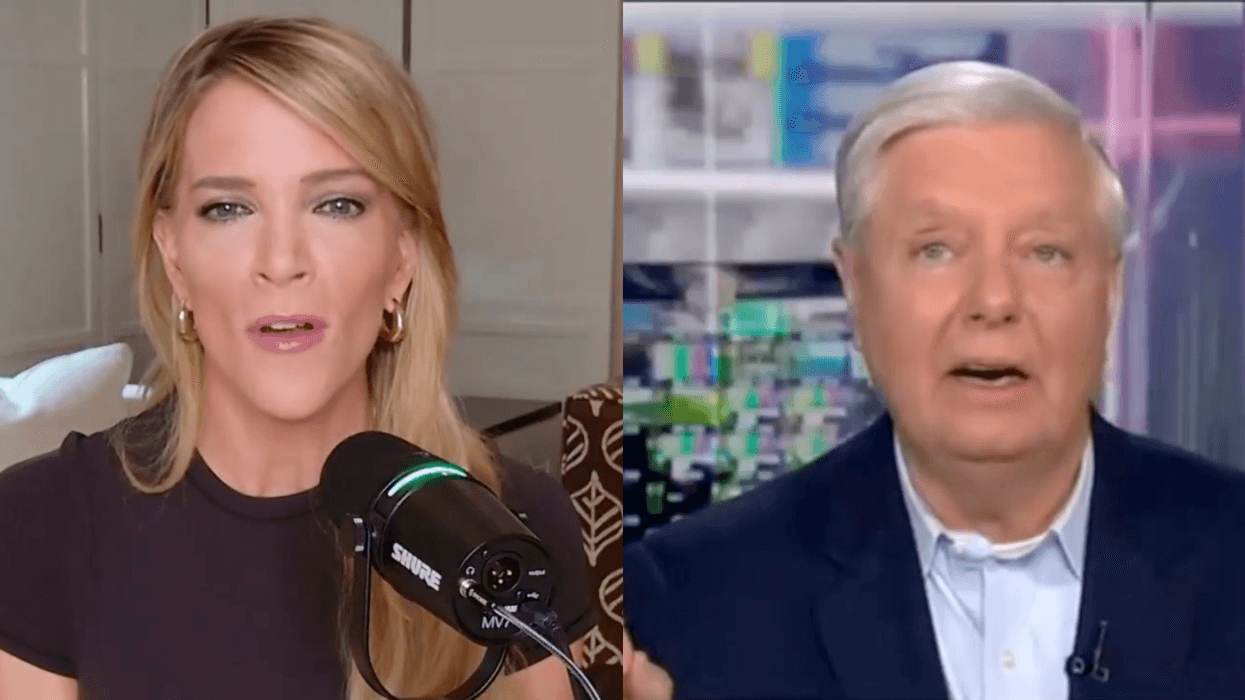
In an interview with Meet the Press moderator Kristen Welker, McConnell said presidents should not be immune from criminal prosecutions for actions taken while in office.
However, McConnell noted that it's ultimately up to the Supreme Court, which is currently hearing oral arguments on Trump's claim, which will determine if federal authorities can charge him over his attempts to overturn the 2020 election result.
He said:
“Obviously, I don’t think that. But it’s not up to me to make that decision. The president clearly needs some kind of immunity, or he’d be in court all the time. So we’ll see how the Supreme Court deals with it.”
"I’m not on the Supreme Court. I don’t get to make the final decision on that."
Welker also asked McConnell if he stands by remarks he made in 2021 when he voted against convicting Trump in a Senate trial after he was impeached by the House of Representatives on charges related to the January 6 insurrection, the day a mob of Trump's supporters attacked the United States Capitol on the false premise the election had been stolen.
At the time, McConnell said Trump "is still liable for everything he did while he was in office," adding that "we have a criminal justice system in this country" and "civil litigation." He stressed that these features signify that "former presidents are not immune from being [held] accountable by either one.”
McConnell said that is "still my view" on the matter though he once again noted that the answer to this question is ultimately up to the nation's highest court:
"But my view is only my view. I mean, the court is going to decide."
“We’re gonna find out, aren’t we? I mean, the Supreme Court is going to deal with that direct issue that I was referring to on Feb. 13, 2021. And I think we’ll find out sometime soon."
The relationship between Trump and McConnell has been largely strained since McConnell acknowledged President Joe Biden as the winner of the 2020 election even as Trump mounted a failed campaign to overturn the election results that culminated in the insurrection.
McConnell rebuked Trump in the days following the attack, saying that the mob of Trump supporters who attacked the Capitol "were provoked by the president and other powerful people, and they tried to use fear and violence to stop a specific proceeding of the first branch of the federal government, which they did not like."
According to New York Times journalists Jonathan Martin and Alexander Burns—who interviewed the Kentucky Republican for their book This Will Not Pass: Trump, Biden and the Battle for American Democracy—McConnell was "exhilarated" by the potential damage the insurrection would inflict on Trump.
Though McConnell appears to have taken a public stance that is against—or at least less deferential—to Trump, he previously backed the former president's "Big Lie" that the 2020 election was stolen. He openly undermined Biden's decisive win from the start, sowing discord when it was politically convenient.
And perhaps most crucially, in his capacity as the then-Senate Majority Leader, he rammed through Trump's Supreme Court appointments—a trio of GOP hardliners who are likely to vote in his favor and scuttle all lawsuits pertaining to the attack.
Given these facts, it was no surprise critics gave McConnell zero credit for his interview responses.
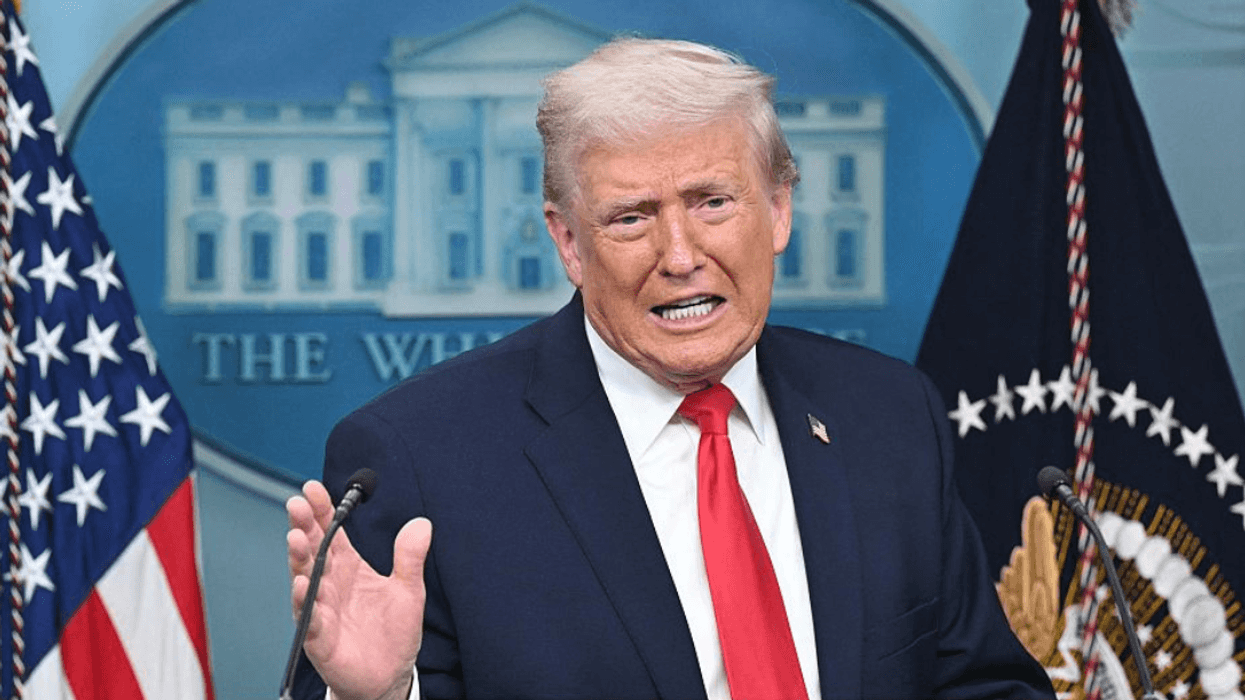
Trump has for years insisted he has "absolute immunity" over actions he took while in office, part of a concerted effort to have courts toss out lawsuits pertaining to the Capitol riot.
Moreover, he has long suggested that he is protected by executive privilege, which gives presidents the ability to assert confidentiality and withhold information in the public interest.
To sustain this narrative, Trump refused to comply with the House Select Committee tasked with investigating the insurrection on multiple fronts and notably declined to submit documentation regarding his mental stability—despite the fact that legal analysts have noted executive privilege does not extend to efforts to stop the certification of an election Biden won.
Legal experts contend that executive privilege specifically belongs to the office-holder: Biden himself.








 @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram @allthereis/Instagram
@allthereis/Instagram












 r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit r/psychologyofsex/Reddit
r/psychologyofsex/Reddit