Conservative columnist Matt K. Lewis used a misleading map of the United States to defend the electoral college.
"Getting rid of the electoral college also means creating a system where this map isn’t enough to elect a Republican," Lewis, who currently contributes to The Daily Beast, wrote.
The map is inaccurate, as others pointed out. The following map shows the results of the 2016 presidential election via dasymetric dot density.
Much of the country is sparsely populated outside of coastal urban centers. This map shows just how Democratic the country is when you look at population alone.
Here's a similar point:
And another:
The following map shows the electoral college makeup after former President Barack Obama's election win in 2012. Notice anything?
And there's been even more debate about the merits of the electoral college as well. Historian and university professor Angus Johnston laid out the case against it.
There is a very serious effort underway to effectively undo the electoral college that would not require so-called faithless electors or an actual constitutional amendment. For some time, critics (now joined by million of petitioners) have argued that the electoral college is an archaic institution that leaves America out of touch with modern democracies, where the national popular vote winner is always simply the winner.
But getting a constitutional amendment approved has always seemed highly unlikely. After all, the three-fourth majority of states needing to ratify it include many that would lose power without the college.
Enter the National Popular Vote project, which has come up with a practical way around this and has garnered significant support. Its strategy is simple: convince states with at least 270 of the electoral college votes to agree that their electors will vote for the candidate who won the popular vote, no matter who won the state’s electoral college votes.
According to the initiative’s website, the electoral college’s shortcomings “stem from state winner-take-all statutes (i.e., state laws that award all of a state’s electoral votes to the candidate receiving the most popular votes in each separate state). Because of these state winner-take-all statutes, presidential candidates have no reason to pay attention to the issues of concern to voters in states where the statewide outcome is a foregone conclusion.”
For example, two-thirds of the 2012 general-election campaign events (176 of 253), were in just four states––Ohio, Florida, Virginia and Iowa. “State winner-take-all statutes adversely affect governance,” the site continues. “‘Battleground’ states receive 7% more federal grants than “spectator” states, twice as many presidential disaster declarations, more Superfund enforcement exemptions, and more No Child Left Behind law exemptions.”
Finally:
The National Popular Vote interstate compact would not take effect until enacted by states possessing a majority of the electoral votes—that is, enough to elect a President (270 of 538). Under the compact, the winner would be the candidate who received the most popular votes from all 50 states (and DC) on Election Day. When the Electoral College meets in mid-December, the national popular vote winner would receive all of the electoral votes of the enacting states.The bill ensures that every vote, in every state, will matter in every presidential election.
The NPV project also criticizes how the electoral college currently overweight votes in a few key swing states. Candidates basically ignore the states that are safely in one camp or the other. The NPV project would change that and force candidates to campaign and earn the votes of everyone everywhere.
But defenders of the Electoral College say that’s just the point. If the popular vote were all that mattered, politicians would only go after vote-rich centers in the cities and ignore rural voters’ concerns because they’d gain few votes. Proponents counter that currently, that’s already the case, with reliably red states getting little to no visits or efforts by candidates. As things stand, a handful of battleground states gain all of the attention and nearly always hold the key to the election.
During the Constitutional Convention of 1787, those in attendance used the Virginia Plan, which called for Congress to elect the president, as a basis for discussion. Delegates from most states agreed with this mode of election. But a committee formed the details of this proposal suggested instead the election be by a group of people apportioned among the states in numbers mirroring the number of that state’s representatives in Congress. These electors, delegates proposed, would be chosen by each state however their individual legislatures “may direct.”
Those in favor of this proposal cited fears of political “intrigue” should the president be elected by a small group of insiders, and suggested that such action would leave the president beholden to their interests.
Other delegates did prefer popular election of the president. But James Madison––who would become our nation’s fourth president––acknowledged it would be harder to attain a consensus on the proposal because of the prevalence of slavery in southern states.
“There was one difficulty however of a serious nature attending an immediate choice by the people,” he said at the time. “The right of suffrage was much more diffusive in the Northern than the Southern States; and the latter could have no influence in the election on the score of Negroes. The substitution of electors obviated this difficulty and seemed on the whole to be liable to the fewest objections.”
The Convention later approved the Electoral College proposal, in a victory for delegates from smaller states who expressed concern larger states would monopolize the election.













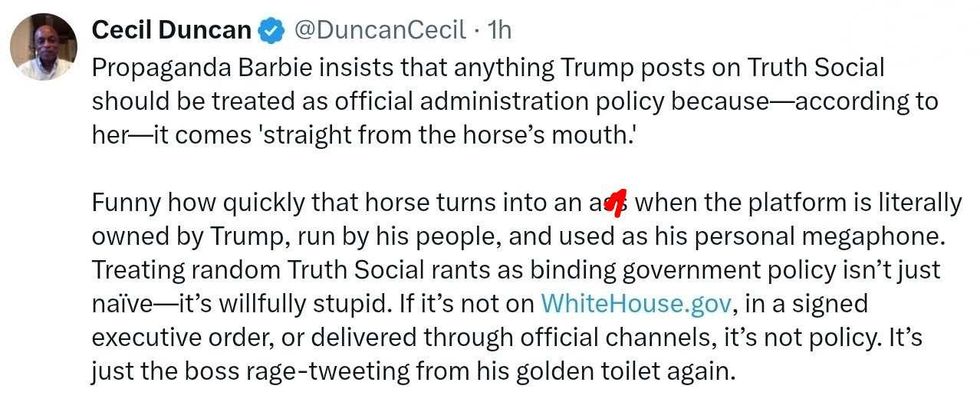 @DuncanCecil/X
@DuncanCecil/X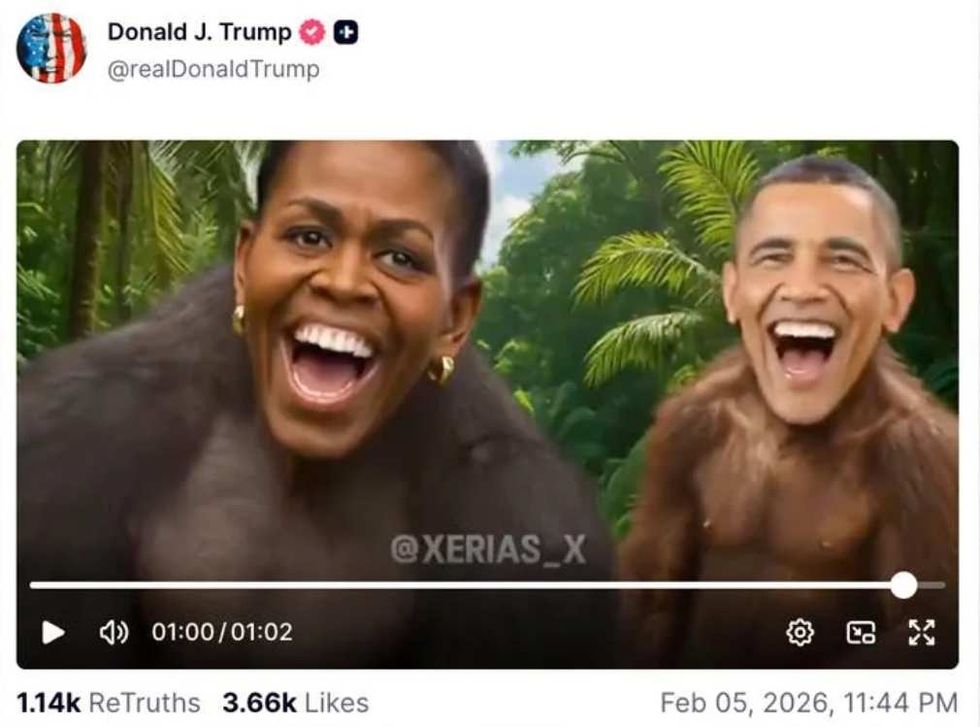 @@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social @89toothdoc/X
@89toothdoc/X @xray_media/X
@xray_media/X @CHRISTI12512382/X
@CHRISTI12512382/X
 @sza/Instagram
@sza/Instagram @laylanelli/Instagram
@laylanelli/Instagram @itssharisma/Instagram
@itssharisma/Instagram @k8ydid99/Instagram
@k8ydid99/Instagram @8thhousepath/Instagram
@8thhousepath/Instagram @solflwers/Instagram
@solflwers/Instagram @msrosemarienyc/Instagram
@msrosemarienyc/Instagram @afropuff1/Instagram
@afropuff1/Instagram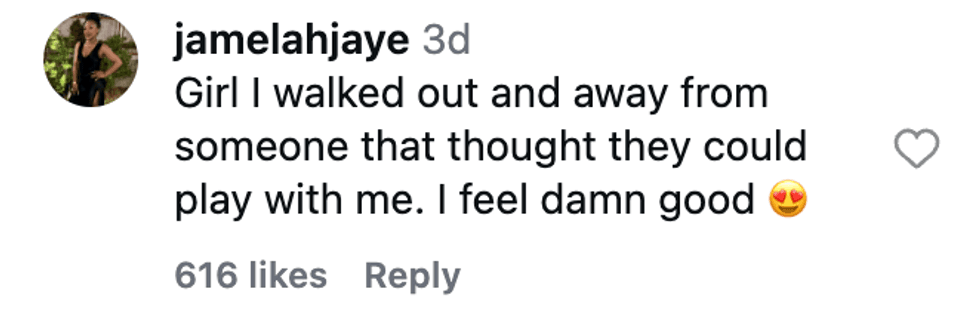 @jamelahjaye/Instagram
@jamelahjaye/Instagram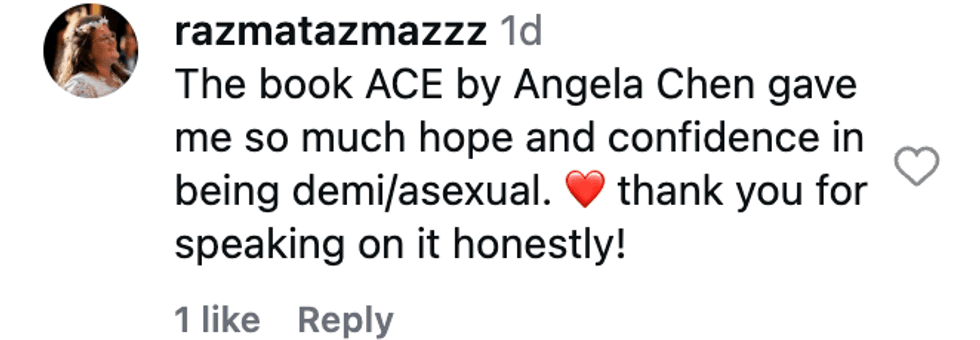 @razmatazmazzz/Instagram
@razmatazmazzz/Instagram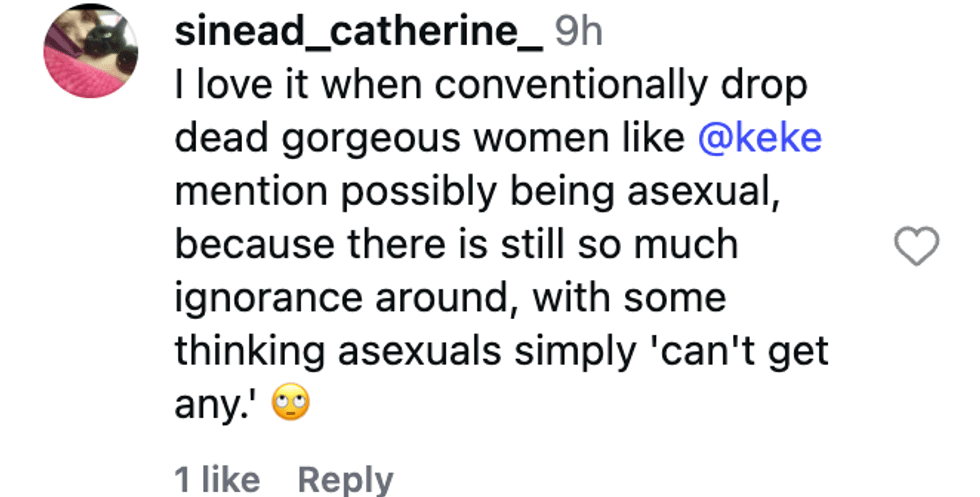 @sinead_catherine_/Instagram
@sinead_catherine_/Instagram @popscxii/Instagram
@popscxii/Instagram