Smartphone apps do a lot of things these days. They can turn on your home thermostat, test your blood-alcohol content, and even diagnose car trouble. One thing they apparently can’t do, however, is eliminate human error from processes that require consistent decision making. Such as birth control.
You may have heard of Natural Cycles, the fertility app designed by Swedish physicists. It was the first app in the world to be certified by the European Union as a form of contraception, and as of late 2017 had more than 600,000 users in 160 countries. Based on an algorithm using a woman’s basal body temperature to predict fertility, Natural Cycles was reported to have an effectiveness rate around 93 percent — comparable to that of the oral contraceptive pill.
Turns out that wasn’t enough for a hospital in Stockholm, which has reported Natural Cycles to Swedish authorities. As national public broadcaster SVT reported in January, out of 668 women who sought an abortion in a Stockholm hospital September through December 2017, 37 had been relying on Natural Cycles for birth control.
According to the app’s website, “Natural Cycles is backed by a unique algorithm that takes your temperature and many other factors like sperm survival, temperature fluctuations and cycle irregularities into account. It not only detects ovulation, fertility and the different stages of your cycle, it also calculates accurate predictions for upcoming cycles.” It costs £39.99 ($52) a year and comes with a thermometer for daily temperature monitoring.
In an online statement, the company admits it is responding to and investigating each reported case of contraceptive failure.
“An unwanted pregnancy is, of course, very unfortunate and we deeply care every time one of our users becomes pregnant unplanned,” the statement reads. “Unfortunately, no contraception is 100 percent effective and unplanned pregnancies are an unfortunate risk with any contraception.”
There are no reports on whether the women with unintended pregnancies were using the app as directed, but in a clinical study published by Natural Cycles’ founders, more than half of the women who had unintended pregnancies while using the app had sexual intercourse on days the app had indicated were fertile.
“We give red and green days and clear recommendations on which days to abstain and which days we consider the risk of pregnancy to be negligible,” Natural Cycles cofounder Raoul Scherwitzl told Business Insider.
While the app’s 93 percent effectiveness rate is indeed comparable to oral birth-control pills, according to the CDC, it’s not as effective as an injectable shot, implant or intrauterine device, whose effectiveness doesn’t rely on abstaining from sex on certain days or remembering to take a pill at the same time every day.
"Think about the gap they have to close,” said Dr. Nathaniel DeNicola, an OBGYN at University of Pennsylvania, in an interview with Gizmodo on Natural Cycles. “You're going from a less than 1 percent pregnancy rate [with IUDs] to a 25 percent pregnancy rate [with the fertility method]. That's a pretty big gap to close just by recording temperatures on a mobile device, even with an algorithm."
Experts recommend that women who have difficulty remembering to take pills or use fertility awareness methods (such as Natural Cycles) consider birth control that doesn’t rely on schedules. See your healthcare provider for more information.





 The Benny Show
The Benny Show




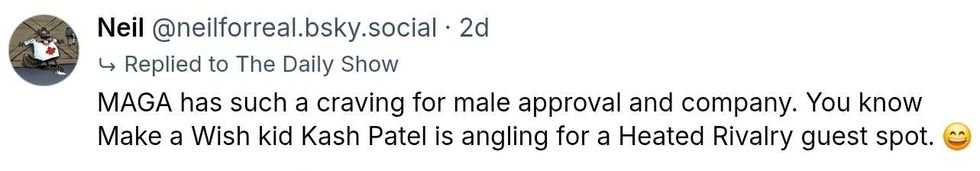 @neilforreal/Bluesky
@neilforreal/Bluesky @savannahcat/Bluesky
@savannahcat/Bluesky @qadishtujessica.inanna.app
@qadishtujessica.inanna.app @v-ron/Bluesky
@v-ron/Bluesky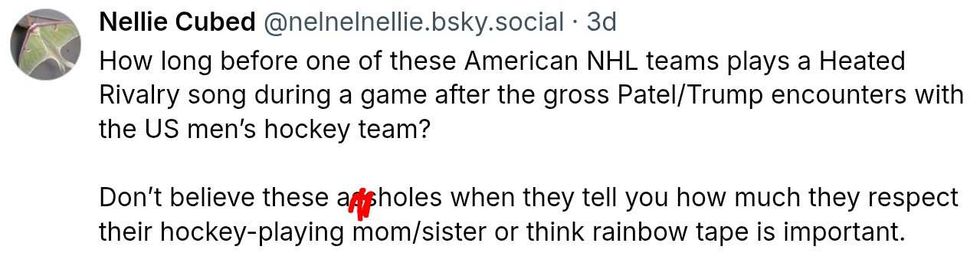 @nelnelnellie/Bluesky
@nelnelnellie/Bluesky @beatlenumber9/Bluesky
@beatlenumber9/Bluesky @pinkzombierose/Bluesky
@pinkzombierose/Bluesky
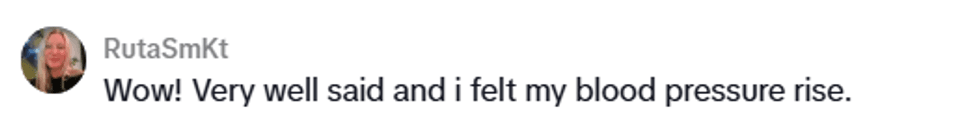 @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok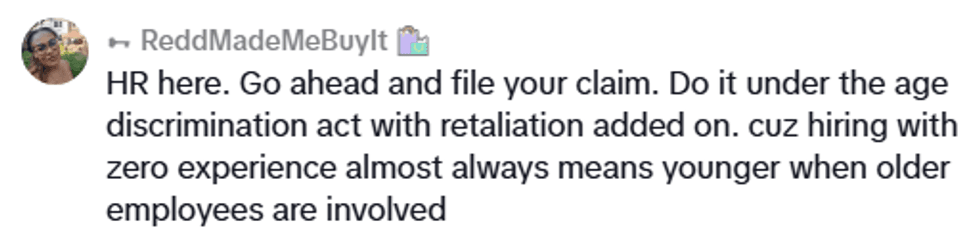 @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok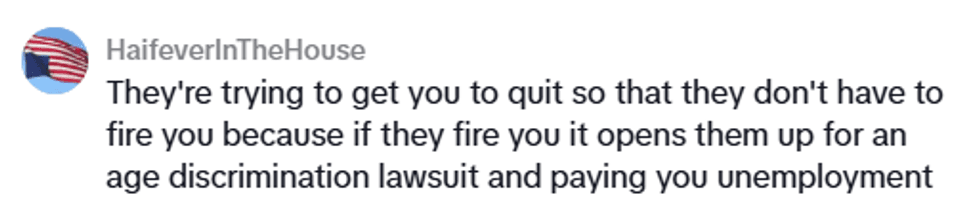 @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok @theunobsolete/TikTok
@theunobsolete/TikTok
 @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok @laysuperstar/TikTok
@laysuperstar/TikTok