The United States Supreme Court is allowing two class action lawsuits against the city of Flint, Michigan to proceed, upholding a 2017 decision by the 6th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals. In July, the 6th Circuit, based in Cincinnati, Ohio, overturned a lower court ruling that dismissed the cases. The Supreme Court also rejected appeals filed by the city of Flint, the drainage commissioner of Genesee county, and the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality.
Plaintiffs in the case are suing the city of Flint over the ongoing and still-unsolved issue of lead-contaminated drinking water in the majority black-populated Detroit suburb.
The Supreme Court gave the civil rights case the green light after deciding that limitations imposed on lawsuits under the Safe Drinking Water Act don't apply. Because the high court determined this is a civil rights case, the plaintiffs may be able to seek monetary damages.
More than 100,000 people in Flint and the surrounding areas were forced to consume toxic, lead-tainted water since the crisis began.
The scandal involving contaminated water began in 2014 when Flint's water supply was changed from Lake Huron to the locally-available Flint River. Since then, Flint River water polluted from industrial runoff caused lead to leach from the pipes that deliver water to the residents of Flint. In one lawsuit, Melissa Mays along with other Flint residents and parents sued the city in November 2015 at the behest of themselves and their families. The second suit, in which Beatrice Boler, Edwin Anderson, and other residents cited civil rights violations on behalf of both residents and businesses of Flint, was filed in January 2016.
Despite having switched back to Lake Huron in 2015 in an attempt to mitigate the problem, lead-tainted water continued to flow into the city until the spring of 2017, when authorities began removing and replacing the lead pipes.
But Flint, Michigan is not the only U.S. city with a lead problem. Water contaminated with lead has been identified in more than 2,000 cities nationwide, a likely and deadly consequence of our country's outdated and degrading infrastructure, reported USA Today.
The water systems, which reported lead levels exceeding Environmental Protection Agency standards, collectively supply water to 6 million people. About 350 of those systems provide drinking water to schools or day cares. The USA TODAY NETWORK investigation also found at least 180 of the water systems failed to notify consumers about the high lead levels as federal rules require.
No amount of water in lead is safe to drink. Children are at the greatest risk for lead poisoning—lead poisoning can inhibit cognitive development in children, and if severe enough, can lead to death. Symptoms of lead poisoning typically include:
- Developmental delay
- Learning difficulties
- Irritability
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Sluggishness and fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Hearing loss
- Seizures
- Eating things, such as paint chips, that aren't food (pica)











 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok
 @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok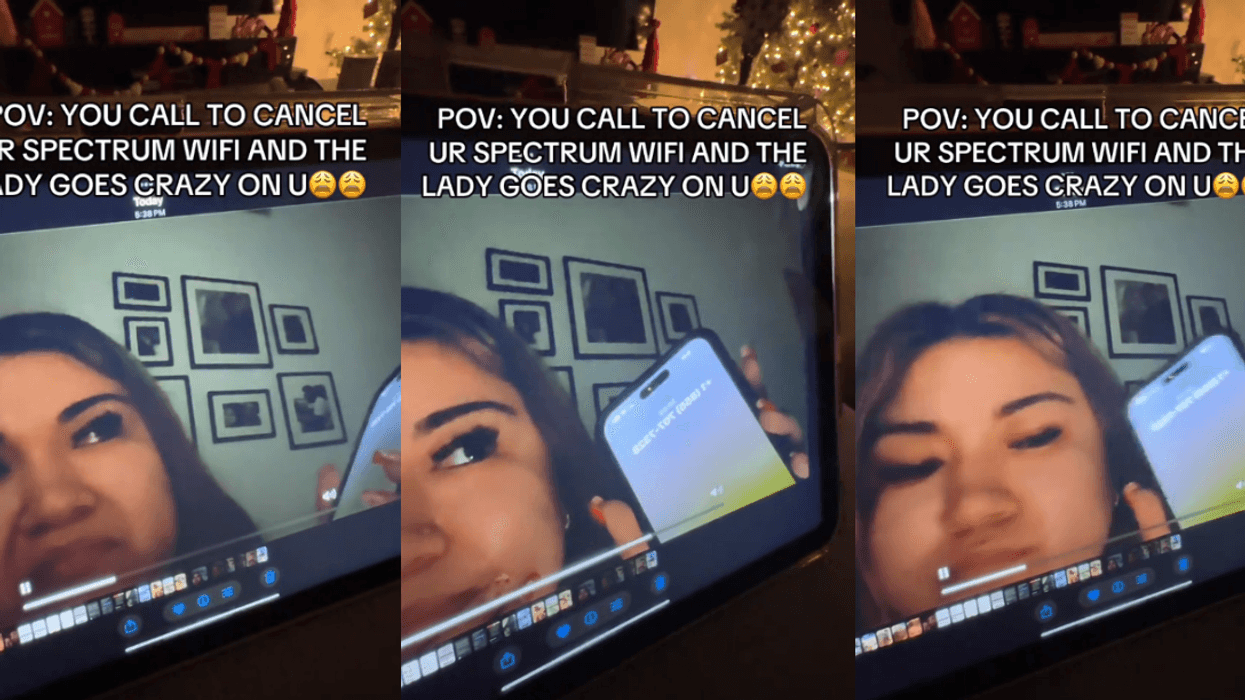
 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok
 @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok