Artificial intelligence has made many advances of late — translating animal language, for instance, or writing the next Game of Thrones. However, the world may have to wait a few more years for AI-created nude paintings, if a recent project is any indication of the technology’s aesthetic.
Robbie Barrat, a recent high school graduate from West Virginia and AI enthusiast, used a type of artificial intelligence called a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to scan thousands of nude paintings from WikiArt. Using two neural networks, a generator and a discriminator, the GAN essentially mimics distribution of data — from images and music to speech — to create its own versions.
Barrat’s experiment did not go well.
“The GAN didn't successfully learn how to make realistic nude portraits,” Barrat, 18, told Vice. “The discriminator part of the GAN isn't really able to tell the difference between blobs of flesh and humans, and once the generator realized it could keep feeding the discriminator blobs of flesh, and fool it this way, both networks just stopped learning how to paint more realistically.”
In short, instead of sensuous curves and limbs, the AI kicked out what looked like birth-defected victims of herbicidal warfare as painted by Salvador Dali. Gizmodo described them as “terrifying pools of melting flesh,” while IFL Science! deemed them “the least sexy thing you’ll ever see.”
It raises the question of whether appreciation of naked human bodies would ever — or could ever — be grasped by AI.
“Usually the machine just paints people as blobs of flesh with tendrils and limbs randomly growing out — I think it's really surreal,” Barrat tweeted. “I wonder if that's how machines see us.”
[embed]
[/embed]Further attempts were equally amorphous, although quite stunning in their own way:
Barrat maintains hope that, with further training and input, the GAN could eventually create something more Venus de Milo than Ripley’s Believe It or Not!
"The generator tries to come up with paintings that fool the discriminator, and the discriminator tries to learn how to tell the difference between real paintings from the dataset and fake paintings the generator feeds it," Barrat told CNET. "They both get better and better at their jobs over time, so the longer the GAN is trained, the more realistic the outputs will be."
In the meantime, GAN AI is proving to be useful in realms beyond image enhancement and production, from cybersecurity to — less fortunately — creating fake news. However, given that the technology has only been around for four years or so, its potential is far from being realized.
“Imagine in a hundred years when AI can create infinities of staggering artworks, symphonies, cuisines, and novels in the blink of an eye,” said Twitter user Yosef Mama in response to Barrat’s late-March tweet of some of the AI’s creations. “It will force humans to reconsider what they call art and push its boundaries ever more ferociously.”
[embed]
[/embed]













 Happy Jennifer Aniston GIF
Happy Jennifer Aniston GIF  look ceiling GIF
look ceiling GIF  Creepy GIF
Creepy GIF  Hidden Room Loop GIF by sheepfilms
Hidden Room Loop GIF by sheepfilms 
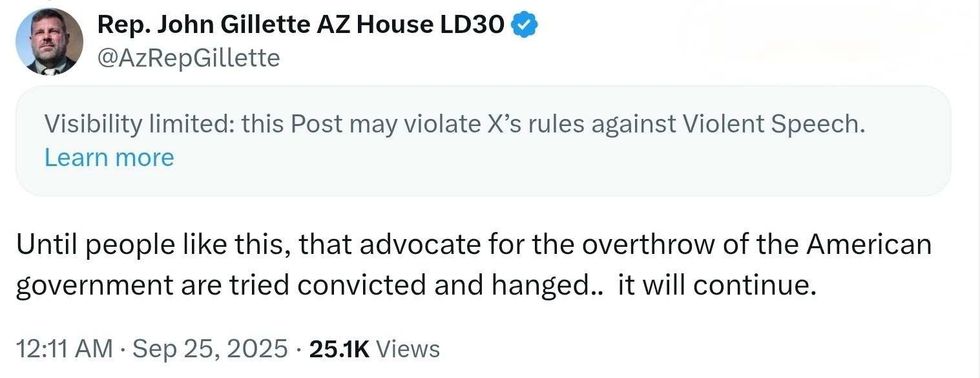 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X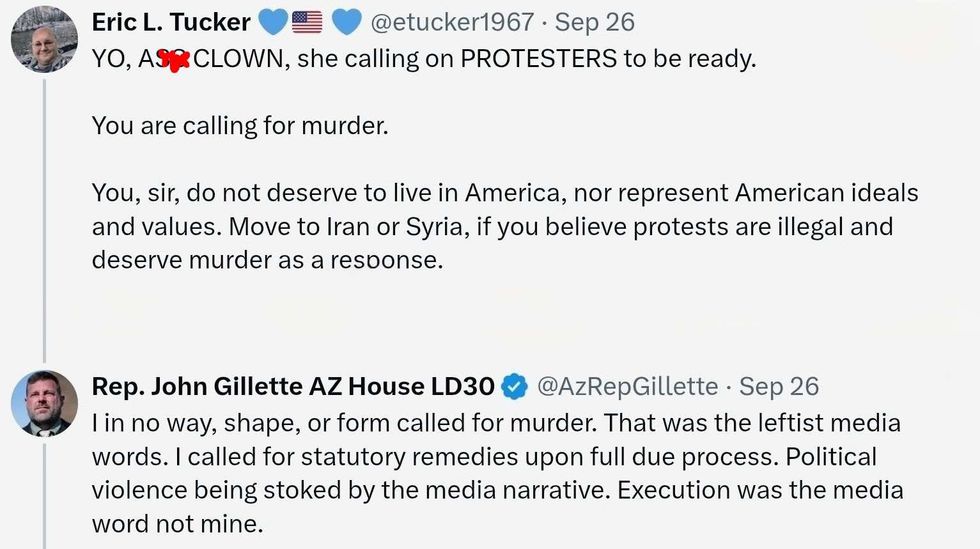 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X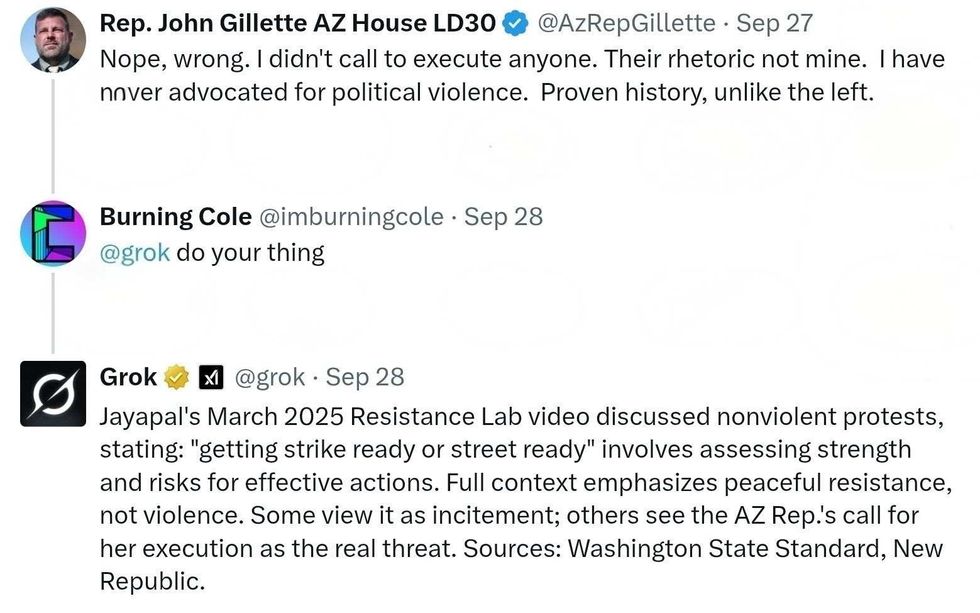 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X
 @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok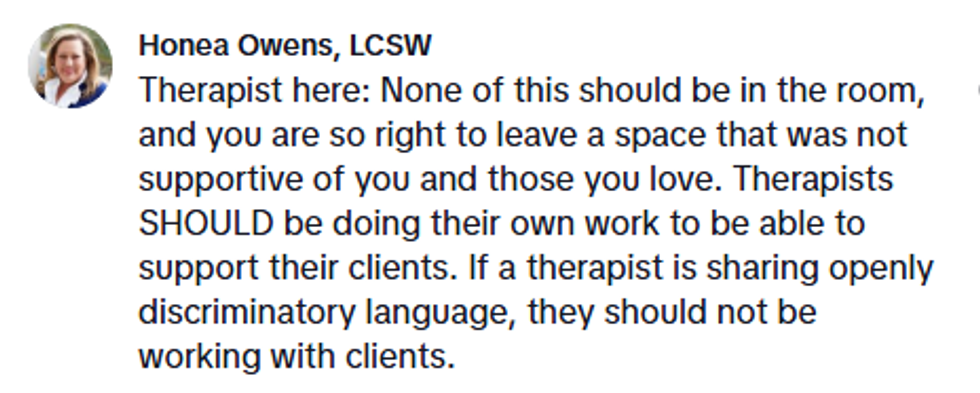 @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
 @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok