Republican lawmakers across the country are railing against comprehensive historical teaching in the nation's public schools, especially in regards to race. They argue that critical race theory—an academic approach examining the racism long embedded in systems of United States government and culture—is nothing more than indoctrination.
Former President Donald Trump banned any mention of systemic racism in federal diversity training programs and, most recently, Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-KY) called critical race texts like The 1619 Project "divisive nonsense" in a letter to Education Secretary Miguel Cardona, signed by three dozen of McConnell's Republican colleagues.
Republican state legislatures across the country have mobilized to introduce proposals banning The 1619 Project and other comprehensive texts on race from being taught to young adults.
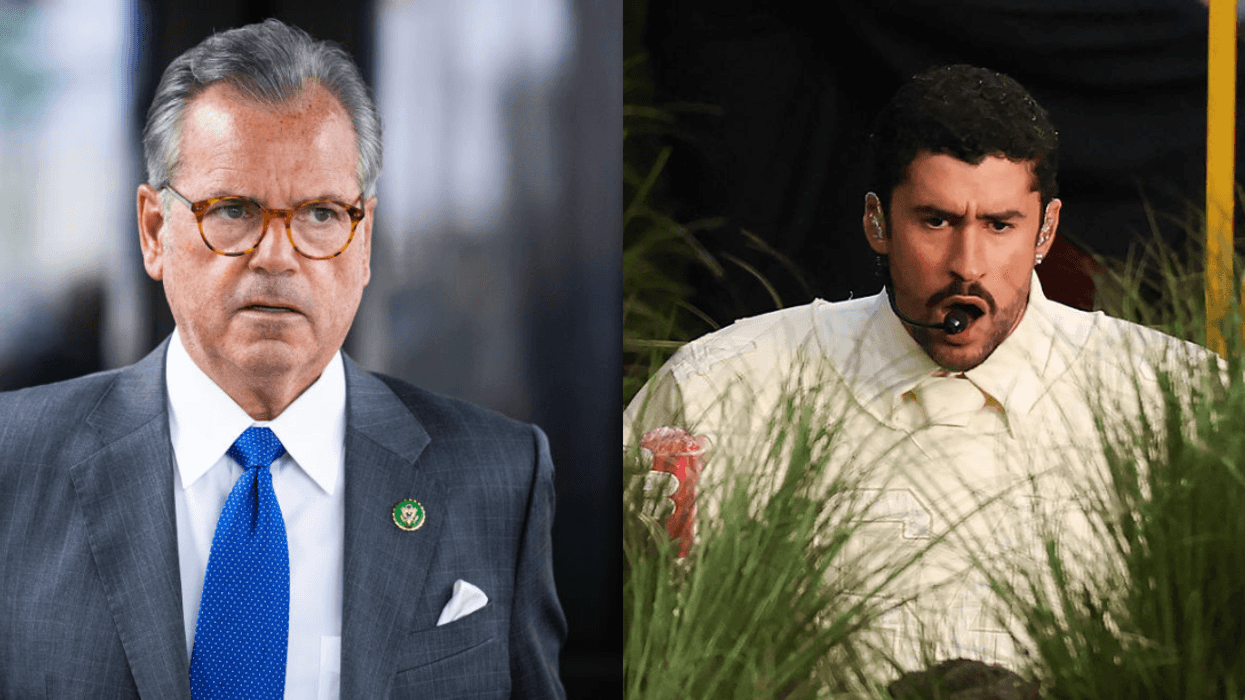
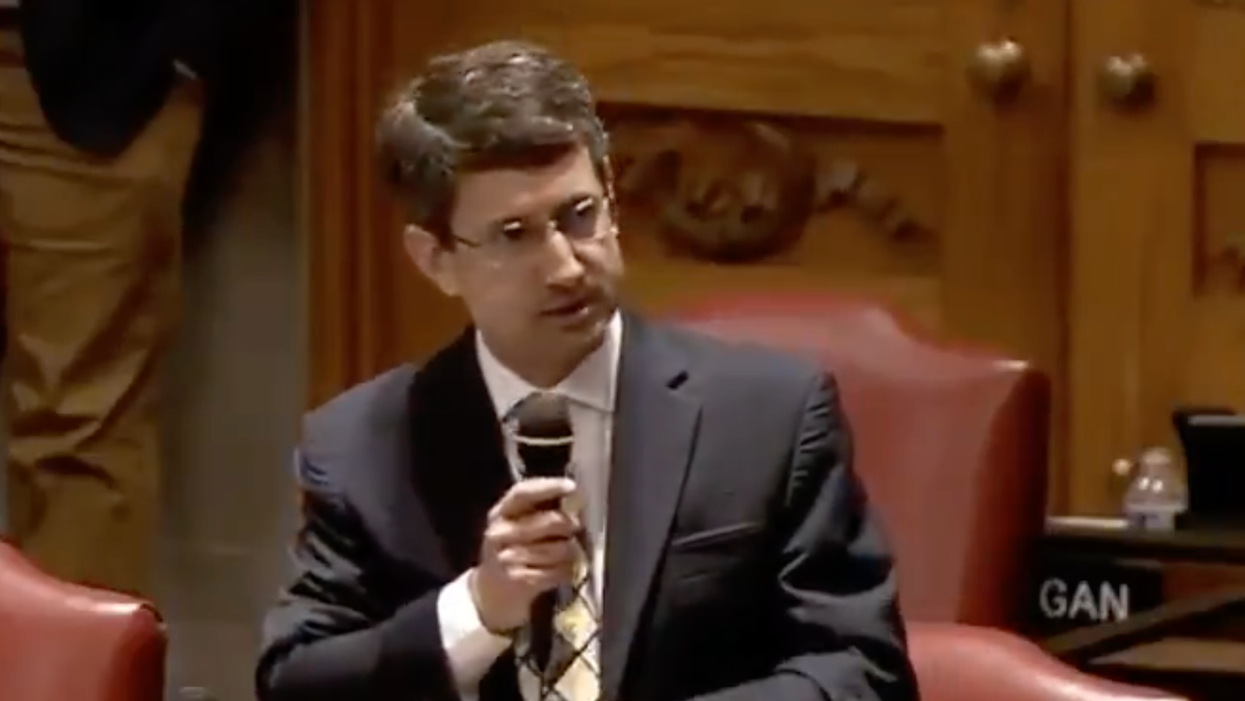
A debate on such legislation was taking place this past week in Tennessee, where state Representative Justin Lafferty accidentally demonstrated the need for unflinching lessons regarding United States history..
Watch below.
Lafferty argued that the founding fathers actively combatted racism and chattel slavery by introducing on the Three-Fifths Compromise, which counted Black Americans as three-fifths of a whole person for the purposes of taxation and apportionment in Congress. Black Americans were still not granted voting rights.
At the 1787 Constitutional Convention, the South wanted Black Americans to be counted as whole people (again, without voting rights) to give the southern region a near-insurmountable advantage in regards to congressional representation.
Lafferty argued that, by the establishing the Three-Fifths Compromise, the founders were deliberately stifling slavery's ability to continue in the United States:
"By limiting the number of population in the count, they specifically limited the number of representatives that would be available in the slaveholding states, and they did it for the purpose of ending slavery. Well before Abraham Lincoln. Well before Civil War. Do we talk about that? I don't hear that anywhere in this conversation across the country ... Talking about incorporating another view of history while ignoring the writings we have access to is no way to go about it."
Lafferty's argument has been put forth before by conservatives looking to paint a rosier picture of the United States' founding and promote the idea that America is inherently exceptional, but that doesn't make the argument any more accurate.
In fact, at the very same Constitutional Convention Lafferty says the founders fought to end slavery, they actually adopted clauses that guaranteed its continuance. At the convention, it was decided the slave trade would be prohibited from ending before 1808, and even then it wouldn't be required to end. What's more, the founders also adopted policies ensuring the federal government would take the sides of slave owners, rather than enslaved peoples who rebelled or escaped.
But even without those, the Three-Fifths Compromise was far from beneficial for enslaved people.
Historian Paul Finkelman, who specializes in the history and legal impact of American slavery, wrote in a 2013 New York Times op-ed:
"[B]y giving the South power disproportionate to its free population, the three-fifths clause set the stage for Southern control of the federal government and, in conjunction with a difficult amendment process, guaranteed a continuation of slavery. James Madison believed in the direct election of the president but created the Electoral College, which, with the three-fifths clause in place, gave the South great power in presidential elections."
Historians like Dr. Joanne Freeman and Kevin Kruse soon weighed in.
But it didn't take a historian's expertise to know Lafferty was wrong.
Lafferty's Republican colleagues applauded his comments after the speech.







 @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram





 @ameliaknisely/X
@ameliaknisely/X WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook