Almost 30 years ago, the World Health Organization (WHO) removed homosexuality from the Mental Disorders section of their International Classification of Diseases (ICD) when the 10th revision, ICD-10, was published in 1992. However, a condition they labeled as “gender identity disorder” remained under the heading of a mental illness as well as several conditions related to anxiety or depression due to sexuality and gender identity.
But on June 18, 2018, that changed with the publication of the 11th edition of the ICD.
ICD-11 has removed homosexuality completely as a medical disorder and created a new category — sexual health — for the relabeled “gender incongruence.” Gone is the negative connotation of identity disorder and the stigma of transgender being a mental disorder.
Disorder, a state of confusion, focuses on only the individual’s perception of their gender being flawed and uncertain. Incongruence focuses on a true disconnect as opposed to a perceived one.
Medicine defines gender incongruence as “a condition where a person feels a conflict between their physical or assigned gender and the one that they identify with.” However, it’s important to note that not all transgender people also have gender incongruence.
“All available evidence was reviewed and discussed by an external advisory group, together with the scientific basis of this condition and the feedback from the professional community and concerned communities formed the basis of this decision,” said Dr. Lale Say, the WHO Coordinator of Adolescents and at-Risk Populations Team. Dr. Say works at the Department of Reproductive Health and Research of the WHO.
But why do semantics and categories matter?
Prior to 1992, homosexuality’s classification as a mental disorder led to people being treated to “cure” their sexuality. After its removal from both the ICD-10 and the United States Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the practice of conversion therapy to try to change people’s sexual orientation fell out of favor.
In 2018, the practice of sexual orientation conversion is seen as a fringe element of pseudoscience and strongly discouraged among qualified mental health providers.WHO says there is sufficient evidence that transgender is not a mental disorder. Classifying it as a mental disorder can cause “enormous stigma” for those who identify as transgender. Experts hope the new categorization helps change how transgender people are treated.
“[The change] is expected to reduce stigma and will help better social acceptance of individuals living with gender incongruence," said Say. "In terms of healthcare provision, we don’t expect much change because this category will still have a place in ICD. In fact, it may even increase access because it will reduce stigma and it will help individuals to seek care more.”
So why not remove gender identity from the ICD completely, like homosexuality?
Countries use the codes issued by the ICD to determine investment of resources as well as how to set certain insurance billing standards. The move from mental disorder to sexual health can reduce stigma, but also ensure access remains for necessary health interventions.
Transgender people with gender incongruence require medical intervention if they decide to seek gender reassignment. Hormone therapies and surgery are part of that process.
For that reason, WHO wants to maintain gender incongruence in the ICD. But without the stigma.
Advocates and members of the transgender community have reacted to the news of the WHO changes in ICD-11.












 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok
 @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok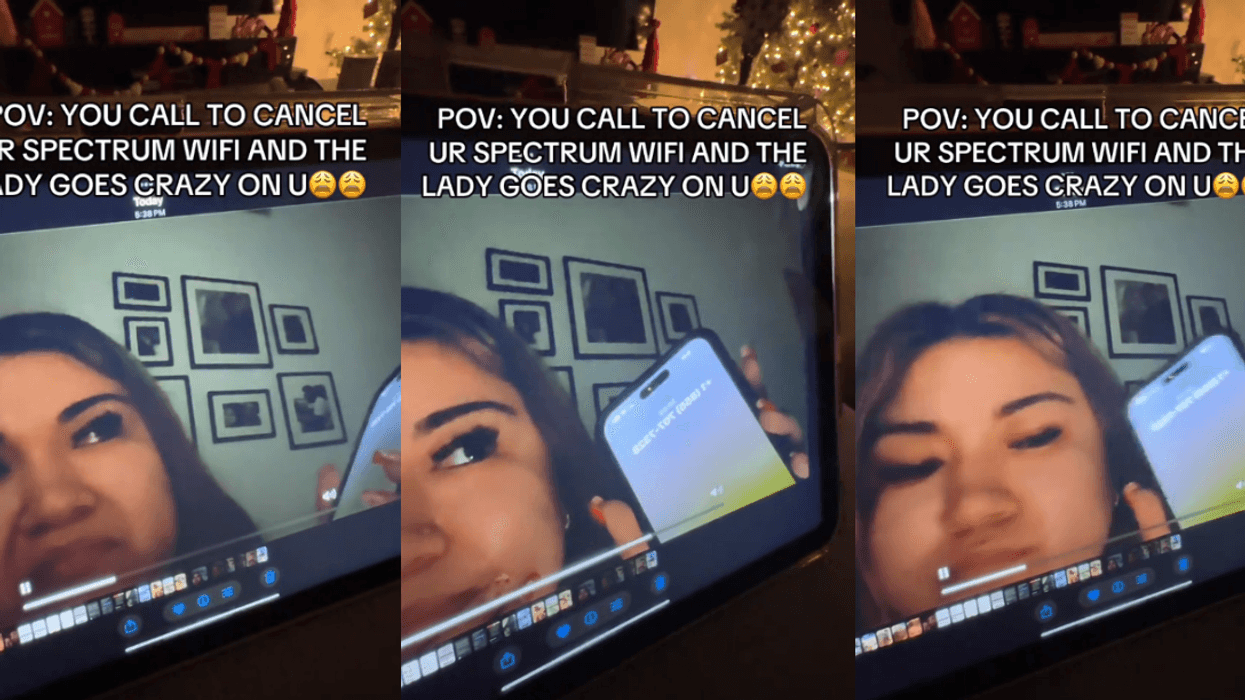
 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok
 @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok