Microchip implant technology is getting under people's skin.
But in Sweden, it's a welcome practice adopted by thousands of people who want to put their fears of having their personal data compromised aside.
The rice grain-sized microchips store all of one's identity and personal information and is implanted into one's hand.
The microchipping procedure involves a syringe to inject the chip and people compare the sensation to that of a "slight sting."
It was first introduced confidentially in Sweden and several other countries in 2015, according to Agence France-Presse,
Today, there are over 3,000 Swedes who walk around with the embedded chip in their hands.
Ulrika Celsing is a 28-year-old employee of media agency Mindshare and is chip-enabled.
She uses the identification technology to enter the work space simply by waving her hand over a small scanning box. After entering a code, the doors open to allow access.
"It was fun to try something new and to see what one could use it for to make life easier in the future," she told AFP.
Celsing can use the chip in place of her gym card and also use it to book railway tickets now that Sweden's SJ national railway company began incorporating the microchip reservation service.
As of last year, SJ conductors can now scan the hands of passengers with the biometric chips to collect fares.
Although the technology assures privacy protection against possible hacking, Celsing remains cautious.
"I don't think our current technology is enough to get chip hacked. But I may think about this again in the future. I could always take it out then."
But Ben Libberton, a microbiologist working for MAX IV Laboratory in the southern city of Lund, is not so acquiescent to the technology.
While the chips could pose a threat to the immune system from infection, Libberton is more concerned about the data in the chip causing more harm.
"At the moment, the data collected and shared by implants is small, but it's likely that this will increase."
"If a chip can one day detect a medical problem, who finds out and when?"
The researcher told AFP that "the more data is stored in a single place as could happen with a chip, the more risk it could be used against us."
Biohacking — the modification of bodies with technology – is gaining momentum.
Hannes Sjöblad, the founder of the Swedish biohacking group Bionyfiken, said "The human body is the next big platform." He sees the future of wearables like the Apple Watch becoming a thing of the past.
"We are updating our bodies with technology on a large scale already with wearables. But all of the wearables we wear today will be implantable in five to 10 years."
"Who wants to carry a clumsy smartphone or smartwatch when you can have it in your fingernail? I think that is the direction where it is heading."
Great strides come with greater responsibilities.
The fear of the unknown is unsettling for many people.
Libberton told AFP that the Swedes are more open to the invasive technology. "In Sweden, people are very comfortable with technology and I would say there is less resistance to new technology here than in most other places."
Could the U.S. be far behind?
H/T - GettyImages, Twitter, BusinessInsider, Yahoo








 @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram @jennifer.garner/Instagram
@jennifer.garner/Instagram

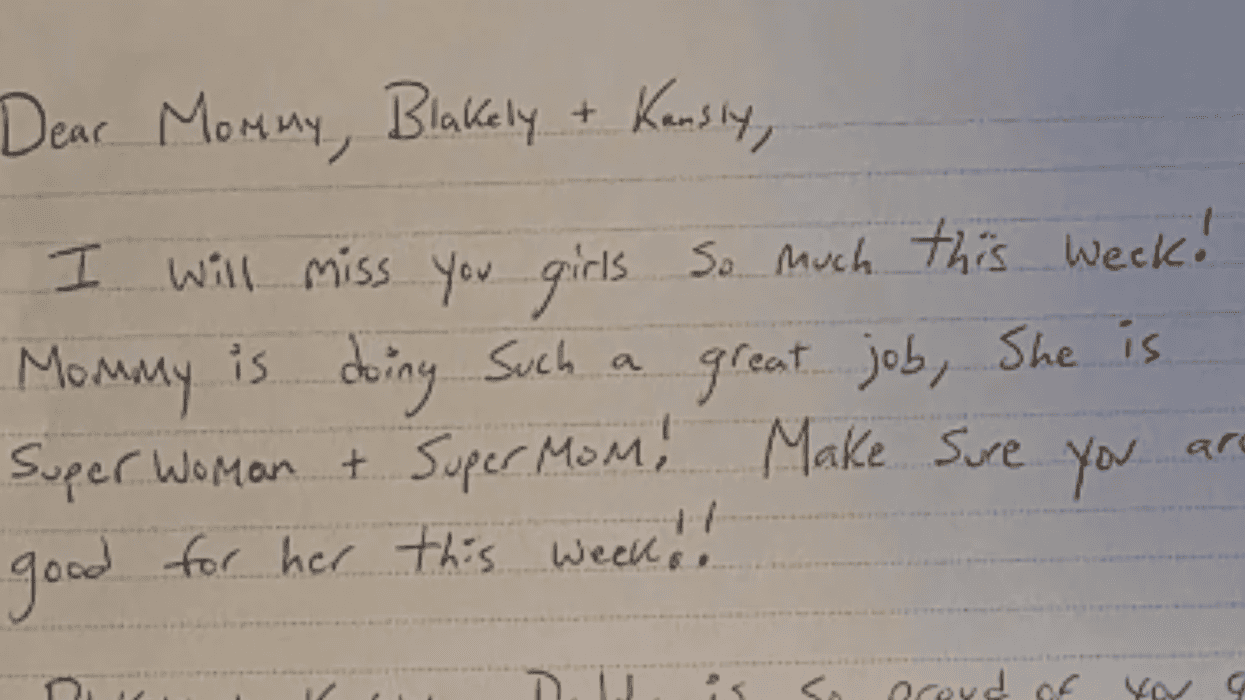


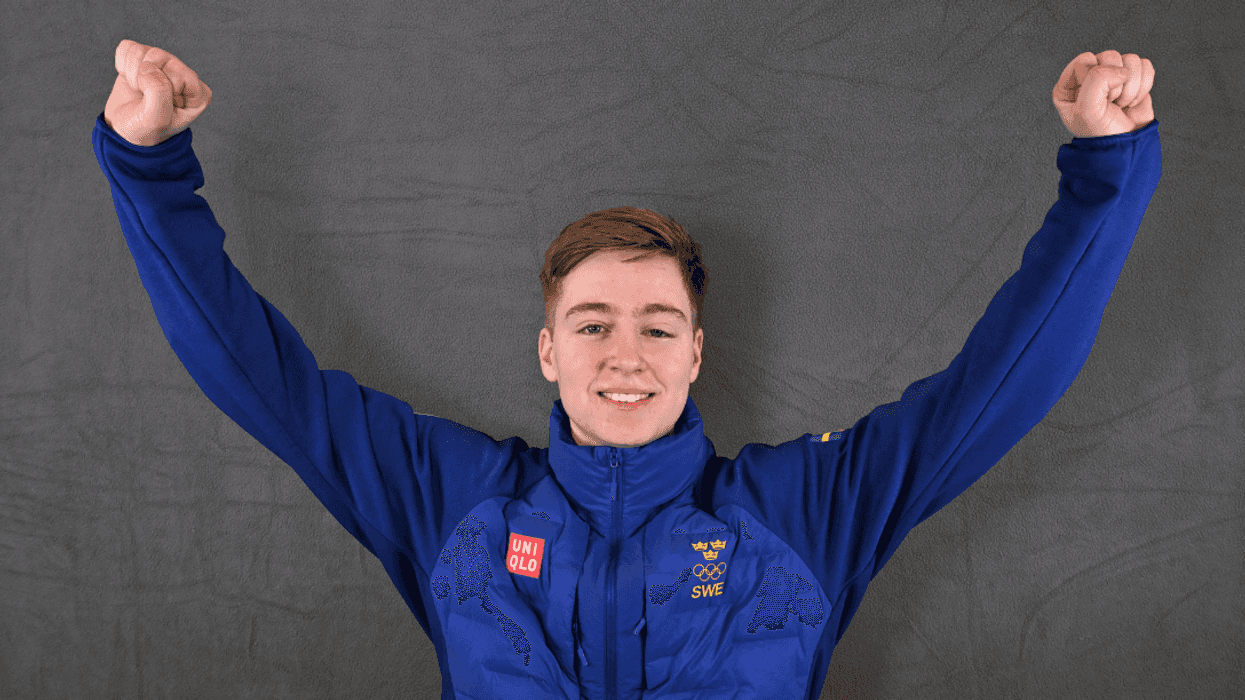


 @ameliaknisely/X
@ameliaknisely/X WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit r/WestVirginia/Reddit
r/WestVirginia/Reddit WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook WDTV 5 News/Facebook
WDTV 5 News/Facebook