The United States Supreme Court issued a ruling on Monday that greatly undermines the ability of workers to sue their employers for withholding pay or exercising discriminatory practices.
In a 5-4 ruling along party lines, the Court sided with employers who force employees to sign arbitration waivers, which eliminate the right for workers to mount class action lawsuits against companies for back pay and discriminatory damages. The ruling upholds existing workplace contracts which state that any disputes must be settled by private arbitrators.
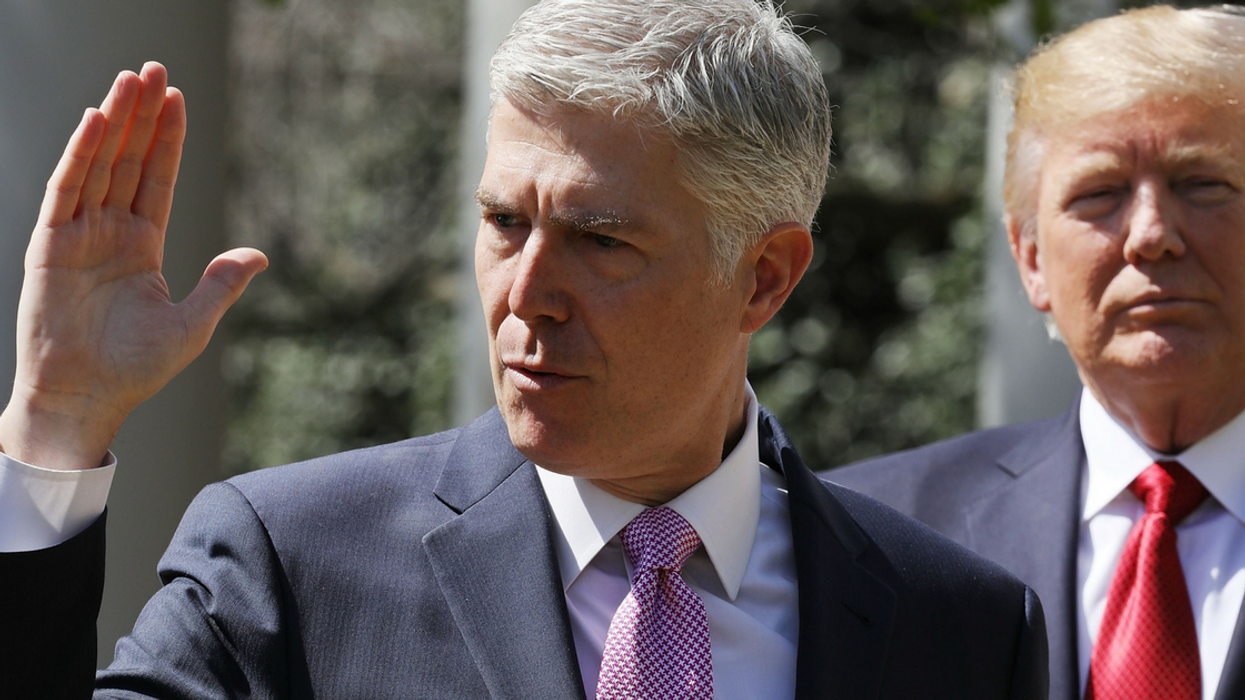
Justice Neil Gorsuch, whom President Donald Trump appointed last year, wrote the deciding opinion, in which he said that National Labor Relations Act was not put in place to "displace" federal arbitration law.
"The policy may be debatable but the law is clear: Congress has instructed that arbitration agreements like those before us must be enforced as written."
Gorsuch's controversial appointment to the Supreme Court came after Senate Republicans blocked President Obama's effort in 2016 to nominate Merrick Garland after the unexpected death of conservative Justice Antonin Scalia. Republicans claimed that because it was an election year, any SCOTUS pick should be put on hold until after the American people had made their choice for president.
Workers challenged employers' enforcement of strict arbitration clauses in employment contracts, arguing before the Supreme Court that the NLRA guarantees workers "mutual aid and protection" in confronting employers over workplace abuses.
Liberal Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg dissented, blasting the majority ruling as "egregiously wrong." Ginsburg argued that the NLRA exists to protect the rights of workers to collectively pursue litigation, which is enormously more difficult and financially burdensome for those who are forced to go it alone.
"Employees' rights to band together to meet their employers' superior strength would be worth precious little if employers could condition employment on workers signing away those rights."
When the case, National Labor Relations Board v. Murphy Oil USA, Inc., was brought before SCOTUS last year, Ginsburg said, "there is strength in numbers," and that it's the Court's duty to "protect the individual worker from being in a situation where he can't protect his rights."
Sheila Hobson, a former Murphy Oil employee, sued the company over overtime work that she claimed herself and coworkers were forced to perform without compensation. After they banded together to launch a class action suit against Murphy Oil, their lawyer informed them that they had rescinded their right to sue when they signed their employment contracts, which included arbitration waivers.
Both The National Labor Relations Board and the Obama administration supported the plaintiffs' claims. The Obama White House even submitted a brief to the Supreme Court, urging the justices to side with workers. Officials within the Trump administration, however, sided with employers, in (as what would be considered then) a rare demonstration of policy reversal from a previous administration.
Last year, the Economic Policy Institute issued a report in which it stated that upwards of 25 million workers in the United States sign away their right to take their employer to court for withholding pay and other discriminatory practices. The EPI's report expressed concern that arbitration waivers would be "even more widespread practice" if the Supreme Court were to side against the collective bargaining power of laborers.
"Class-action lawsuits are often the most powerful way for employees to secure back pay when their minimum wage or overtime rights have been violated or to secure damages when their bosses run afoul of discrimination laws."
Employees now have little recourse in combating wage theft and instances of sexual harassment in the workplace. With the Court's ruling in place, American workers can likely expect abusive practices by employers to not only become more common, but that such misdoings will continue to go unchecked.














 Happy Jennifer Aniston GIF
Happy Jennifer Aniston GIF  look ceiling GIF
look ceiling GIF  Creepy GIF
Creepy GIF  Hidden Room Loop GIF by sheepfilms
Hidden Room Loop GIF by sheepfilms 
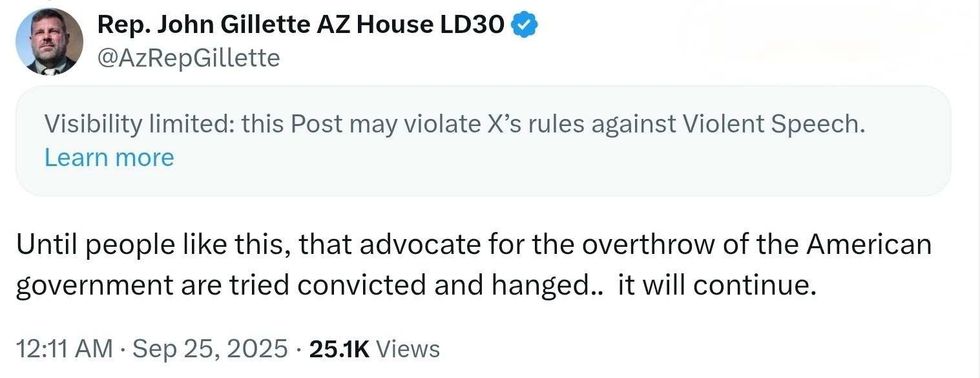 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X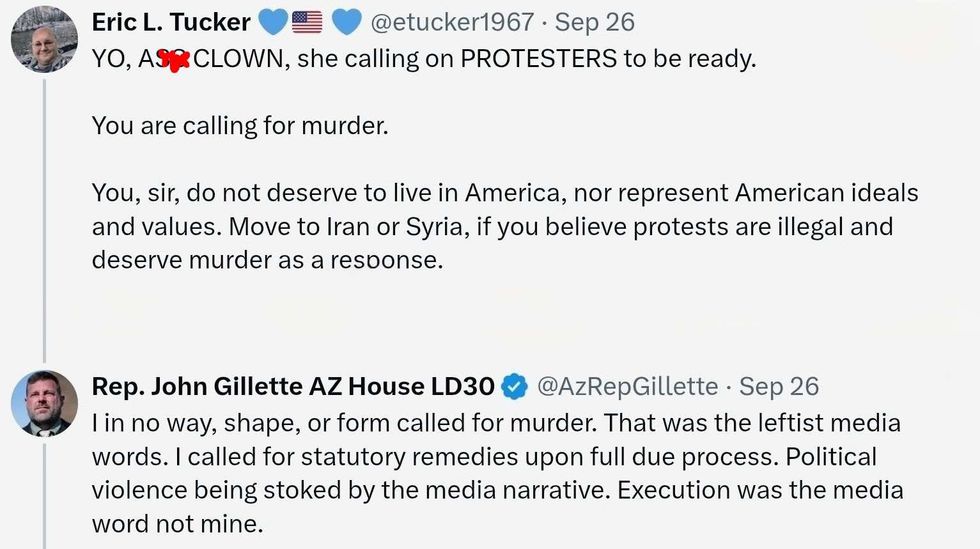 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X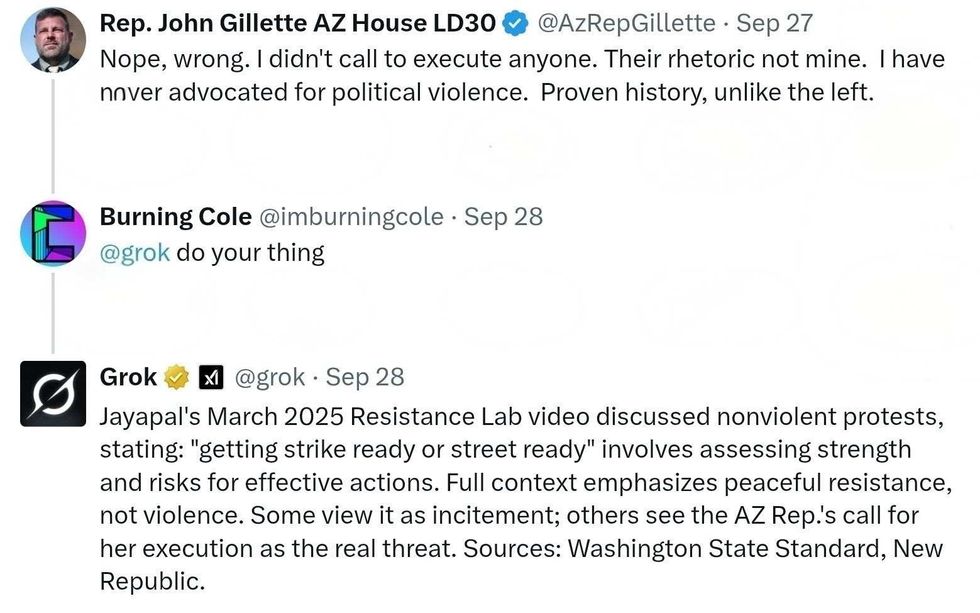 @AzRepGillette/X
@AzRepGillette/X
 @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok @nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
@nicolekatelynn1/TikTok
 @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok @valerieelizabet/TikTok
@valerieelizabet/TikTok