Birds in or near urban areas have long been known to augment their nests with found materials — from plastic bags and foil to electrical cables and cigarette butts. Though it’s hard not to see this as a depressing visual reminder of litter and sprawl, recent research has proven that cigarette butts in nests serve a remedial purpose not only for birds but for people, too.
Last year, a group of scientists led by Monserrat Suárez-Rodríguez and Constantino Macías Garcia of the National Autonomous University of Mexico found that birds were not only weaving smoked, torn-up cigarette butts into their nests to repel parasitic ticks, but they were doing it intentionally.
In an on-campus experiment involving 32 wild pairs of nesting house finches, Suárez-Rodríguez and Macías Garcia identified nests with eggs, waited until the eggs hatched, then swapped the nests — which typically measure three to seven inches wide, and two inches deep — with imitation felt nests lined with native material.
To the new nests, the researchers added either live ticks, dead ticks or no ticks. Once the chicks had fledged, the researchers collected the nests and found that the finches had added cigarette butts only to the nests with live ticks. None of the nests with dead or no ticks had added butts, indicating that the birds were adding the cigarette butts specifically as fumigation agents. Because of nicotine’s known anti-parasite properties, especially against arthropods (invertebrates with an exoskeleton, such as insects, spiders, and crustaceans), the researchers found the butts did indeed repel ticks.
“It’s fascinating, and an exciting example of animals being innovative and making use of the materials available to them,” comparative ecophysiologist Steve Portugal of Royal Holloway, University of London, told New Scientist.
Reduced numbers of ticks in bird nests not only lessens the risk of disease for the birds, as ticks carry more bacteria, viruses, and parasites than any other arthropod — including mosquitoes — but plays an important epidemiological role for people as well. It turns out birds in populated areas are “reservoirs” for Lyme disease, a long-ranging bacterial infection transmitted by ticks.
So, does this mean smokers should start stockpiling butts under trees to save urban populations from Lyme disease?
Not exactly, say the researchers. Turns out the cigarettes are still kind of bad for the birds.
“The butts cause [genetic] damage to finches by interfering with cell division, which we assessed by looking at their red blood cells,” said Macias Garcia.
However, some scientists still think the dangers of nicotine are still less than the benefits of keeping ticks away.
“I think the anti-parasite effects the cigarette butts provide must outweigh any negative problems they cause,” said Portugal. “Alternatively, the genotoxic effects take longer to manifest, and the adult birds aren’t aware of any problem.”
One thing everyone can likely agree on, however, is that the subject bears more research. Can the birds discern between smoked and unsmoked butts? Could they learn to incorporate a comparable, less harmful antiparasitic material? Hopefully, time will tell.
“It really makes me wonder: might these birds show a preference for cigarette brands high in nicotine? If they did, that might suggest this behaviour has truly evolved as an adaptive response to challenges from parasites,” Timothy Mousseau, an ecologist at the University of South Carolina in Columbia, told Nature.














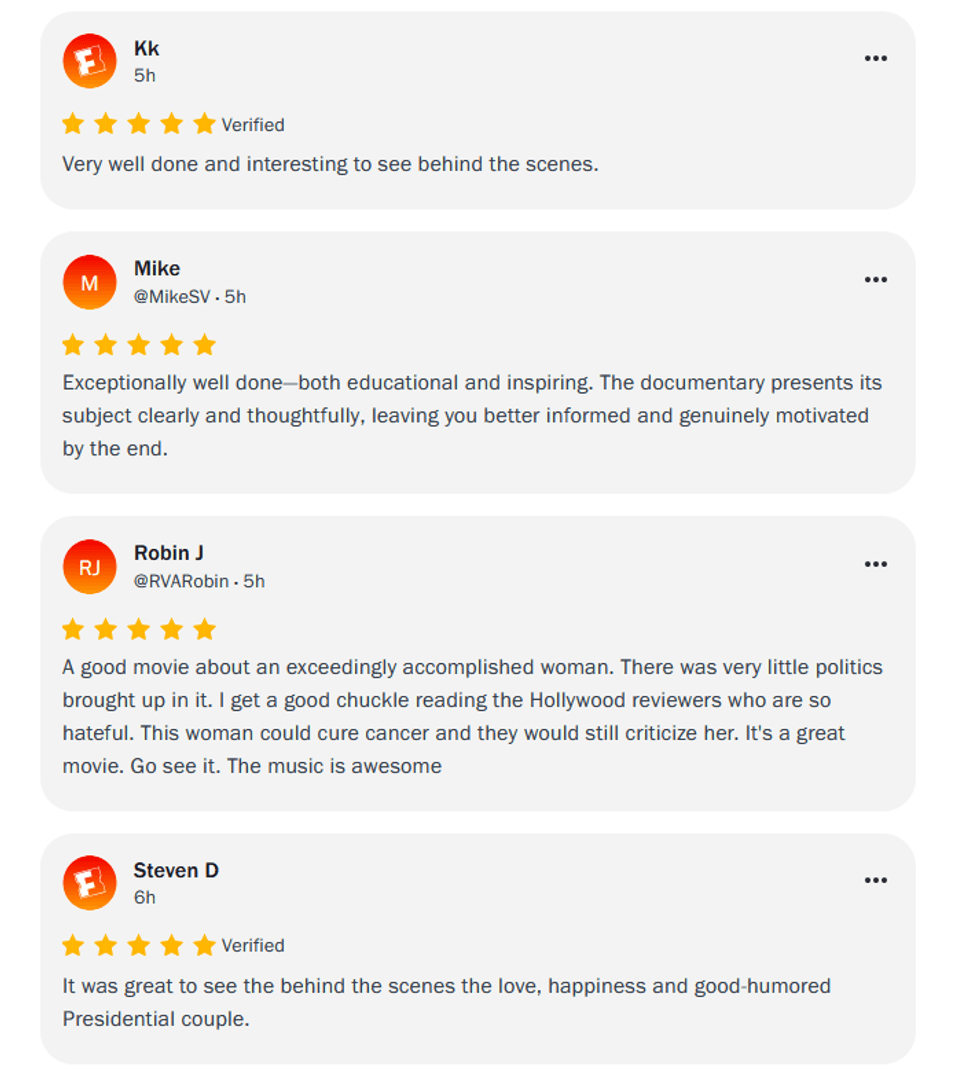 @obamaatredrobin/X
@obamaatredrobin/X
 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social

 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok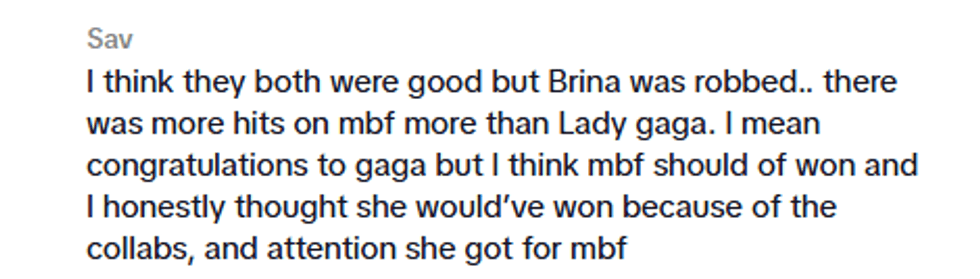 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok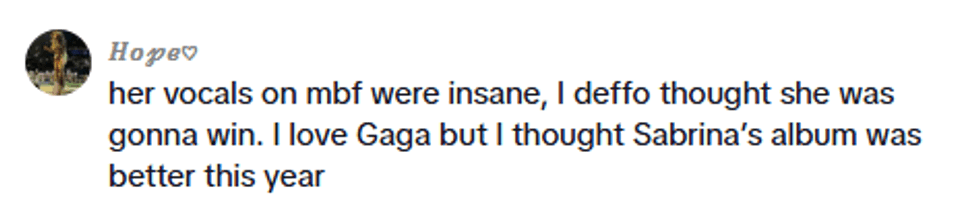 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok