[DIGEST: The Guardian, The New York Times]
Traders worldwide punished markets in reaction to Britain’s vote to leave the European Union last night, amid fears the change would trigger an economic recession in Britain and have global spillover effects. The Dow Jones opened more than 400 points down, and the pound sterling plunged to a 31-year low after investors initially had bought up the pound and British banking shares after opinion polls had predicted a win for the Remain camp. Within the first few minutes of trading Friday morning, the FTSE 100 fell more than 8%. It was the FTSE’s biggest fall since the 2008 collapse of US investment bank Lehman Brothers. The market has since recovered some of that loss as UK government officials stepped in to quell fears.
Piers Hillier, chief investment officer at Royal London Asset Management, is pessimistic, citing the spectre of prolonged economic uncertainty. “On the back of this morning’s result we expect the UK will fall into a recession,” he warned. “Unfortunately I see unstable market conditions lasting for between three and five years whilst new trade agreements are drawn up. It is our view that the UK government will be left with no choice but to stimulate the economy through fiscal and monetary means, flooding the system with liquidity if necessary.”
Mark Carney, governor of the Bank of England, attempted to allay fears of market turmoil in a televised statement, saying that “inevitably, there will be a period of uncertainty and adjustment following this result… [But] we are well prepared for this. The Bank will not hesitate to take additional measures as required as markets adjust and the UK economy moves forward.”
The political fallout has also begun. Prime Minister David Cameron, who was widely criticized for having proposed the referendum to protect his own political fortunes, then unsuccessfully led the campaign to remain, announced he would step down in October. “I will do everything I can as prime minister to steady the ship over the coming weeks and months,” Cameron said. “But I do not think it would be right for me to try to be the captain that steers our country to its next destination.”
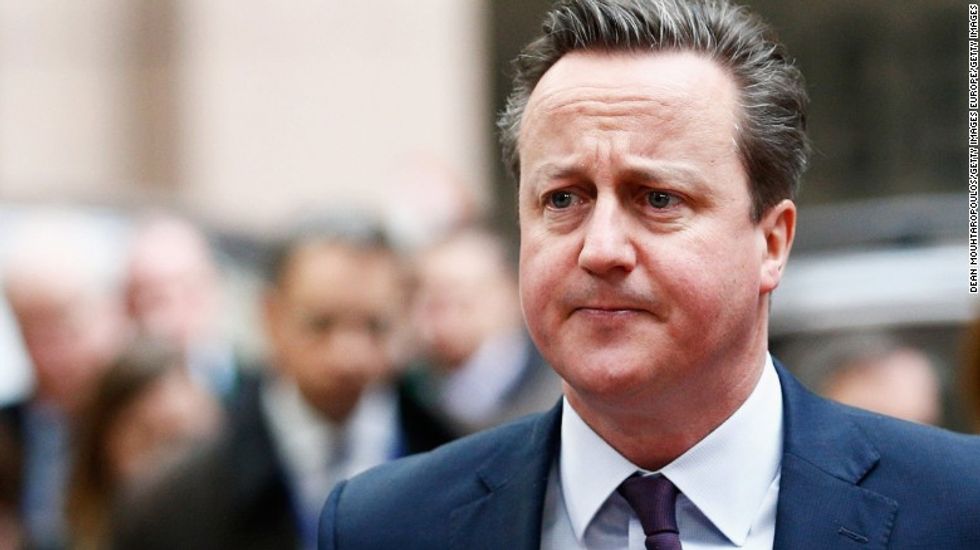

Leave proponent leaders were quick to hail the vote. “Dare to dream that the dawn is breaking on an independent United Kingdom,” said Nigel Farage, the leader of the UK Independence Party. Following Cameron’s departure, there is speculation that former London mayor and outspoken advocate for the Leave vote, Boris Johnson, could assume power as the next Prime Minister.
The decision whether to leave or remain largely split along age and geographic lines, with voters over 65 in suburban areas outside of London
comprising the bulk of the anti-EU polling, while younger voters and voters in Scotland, Northern Ireland and London were strongly in favor of remaining. Critics of the Leave campaign accused the movement of inciting anti-immigrant, nativist sentiments, while others noted the Remain campaign cited economic ruination as a fear tactic.
Whether economic catastrophe follows after the vote depends largely on the settlements negotiated. Britain could lose access to the single market for duty-free trade and other financial services. Even after leaving the EU, Britain might be required as a condition of trade to continue to accept freedom of movement and labor for citizens of the EU, one of the Leave camp’s primary objections to membership. But one thing now is clear: Economic uncertainty over the future of the bloc will affect investment and planning. Even those few economists who favored leaving admit Brexit would affect economic growth until at least 2030.
Some experts remain optimistic. Mark Littlewood, director general of the Institute of Economic Affairs, does not believe the vote is a sign of economic self harm. “Today’s vote to leave the European Union presents the UK with a great and exciting opportunity to look outwards to the rest of the world, to take a more internationalist approach and move towards a position of free trade on a global basis, with the EU but also beyond it,” he said.
But this sentiment is not widely shared among business leaders, the majority of whom had supported staying in the EU. They reassured their workers they would adapt to the Brexit vote, but warned they may need to restructure their businesses. During campaigning, the International Monetary Fund predicted a fall in shares and housing prices, though this pitfall might be a boon to first-time buyers grappling with an increasingly expensive market. Property experts predicted the vote would spark a “Brexit bubble” as the UK becomes cheaper for overseas investors.
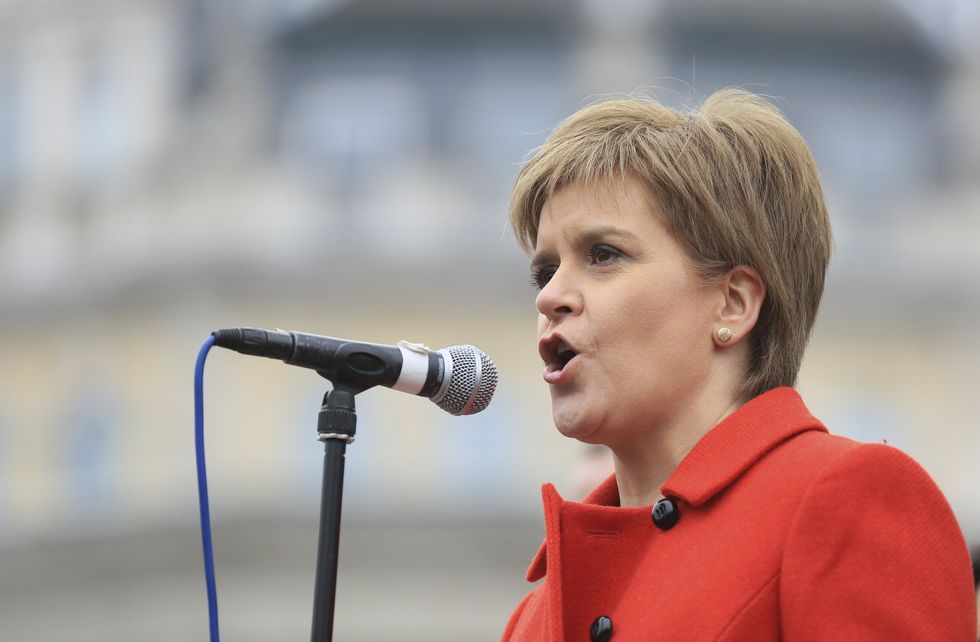

There is also a real possibility the United Kingdom might not survive the vote intact amid calls for an independence referendum in Scotland. The vast majority of Scotland voted to remain in the bloc. “I think an independence referendum is now highly likely,” said Scotland’s first minister, Nicola Sturgeon, who called the result “democratically unacceptable.” A prior referendum on Scottish independence was only recently narrowly defeated. The shockwave is also being felt in Northern Ireland, where Deputy First Minister Martin McGuinness called for a border poll on a united Ireland. The prospect that authorities would again require passports along the border with Northern Ireland is a sobering one to many. Britain's own breakup could well become the inevitable consequence of its divorce from the union.








 draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com





 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok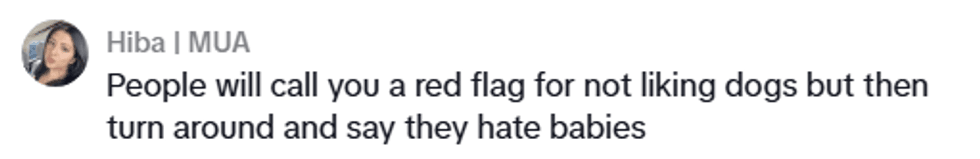 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok
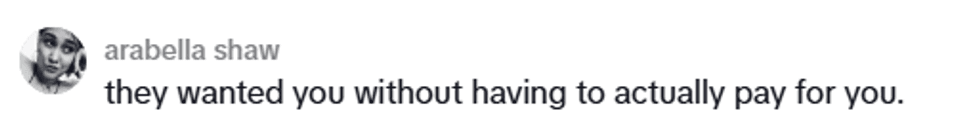 @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok