The future that TED Talks have long promised is one step closer to reality, thanks to a new deal between pharmaceutical giant GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and home DNA-testing kit service 23andMe.
The four-year agreement will grant GSK exclusive access to 23andMe’s database of genetic information, with the goal of developing new, targeted drugs and therapies. This isn’t the first time that 23andMe has offered its customers’ data to another organization for research, but those partnerships have previously been transparent. What does this new deal mean for genetic privacy and who will benefit from the partnership?
To privacy advocates, there’s little more alarming than the sale of genetic information. The data could be used by insurance companies to identify certain genetic markers as high-risk, leading to increased premiums even decades after the test is performed. Law enforcement could subpoena the data from 23andMe (or any other genetic testing company) without informing the customers and without their consent. The law surrounding questions of genetic privacy and ownership are in their infancy. And no genetic testing company can ensure that your genetic information remains private.
But in this case, the most serious issue seems to be profit. 23andMe’s estimated 5 million customers can choose to opt out of having their DNA used in research. Those who don’t opt out have essentially donated their genome to science. But that munificence is one-sided: whatever drugs or treatments are developed using the customers’ genetic information will be sold by GSK or 23andMe for profit.
And there’s certainly profit to be made. Separate from this deal, GSK has invested $300 million in 23andMe. It’s a relative bargain for GSK, because 23andMe’s database is up to 10 times larger than other available databases, and its customers have already paid for partial sequencing — typically a major expense.
For its part, GSK is confident that the partnership will produce effective treatments, which will benefit patients across the world. To begin, they’re focusing on treatments for Parkinson’s disease based on a gene called LRRK2 that is mutated in some Parkinson’s patients.
“When you get a genetically validated target and you pursue it, it’s twice as likely to end up being a medicine,” said GSK chief science officer Hal Barron.
Previously, 23andMe had been carrying out some genetic research itself, in partnership with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and University of California, Los Angeles and University of Southern California. In those cases, customers could see a clear benefit in allowing research to be carried out on their genome. Just by allowing the company to use the material that the customer had already given, they felt like part of a larger solution.
“It’s one thing for NIH to ask people to donate their genome sequences for the higher good,” Peter Pitts, president of the Center for Medicine in the Public Interest, told NBC News. “But when two for-profit companies enter into an agreement where the jewel in the crown is your gene sequence and you are actually paying for the privilege of participating, I think that’s upside-down.”












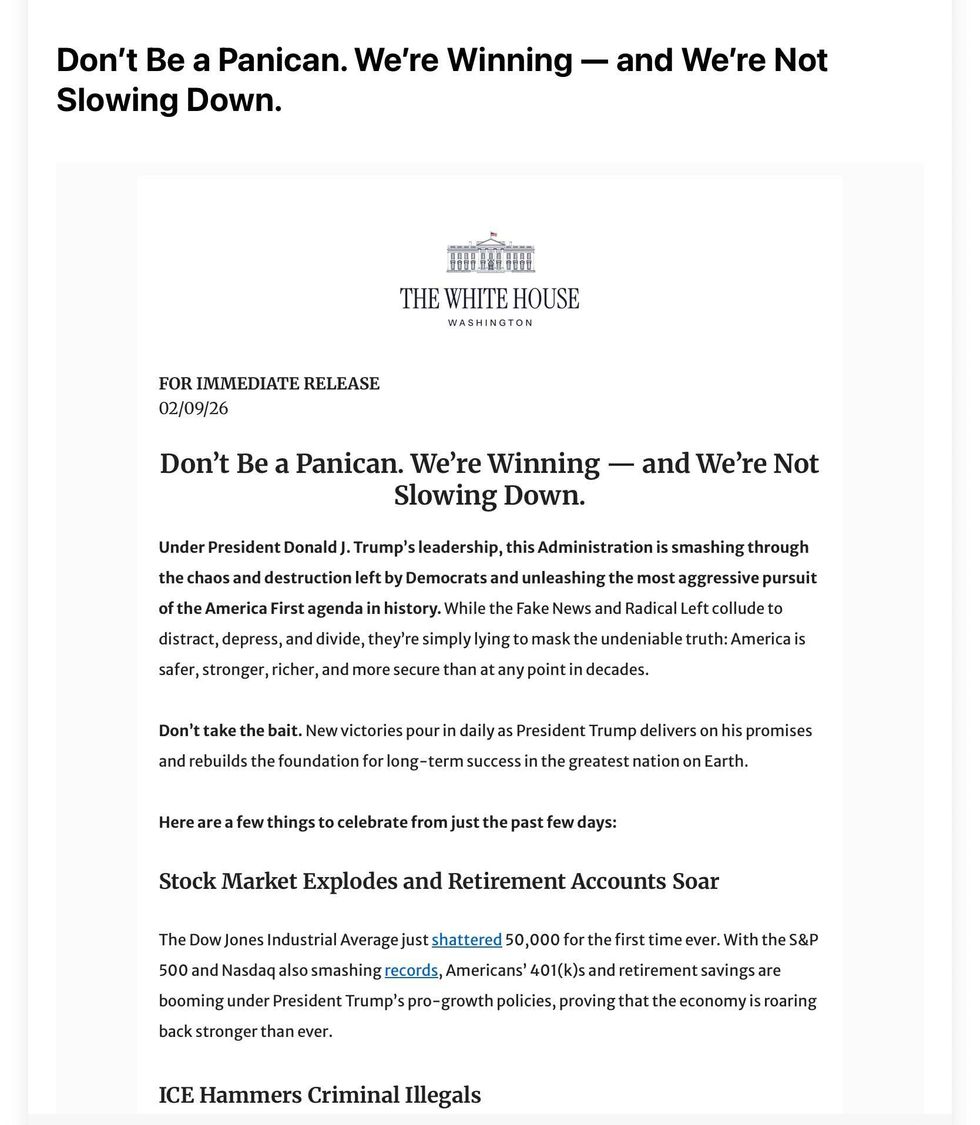 The White House
The White House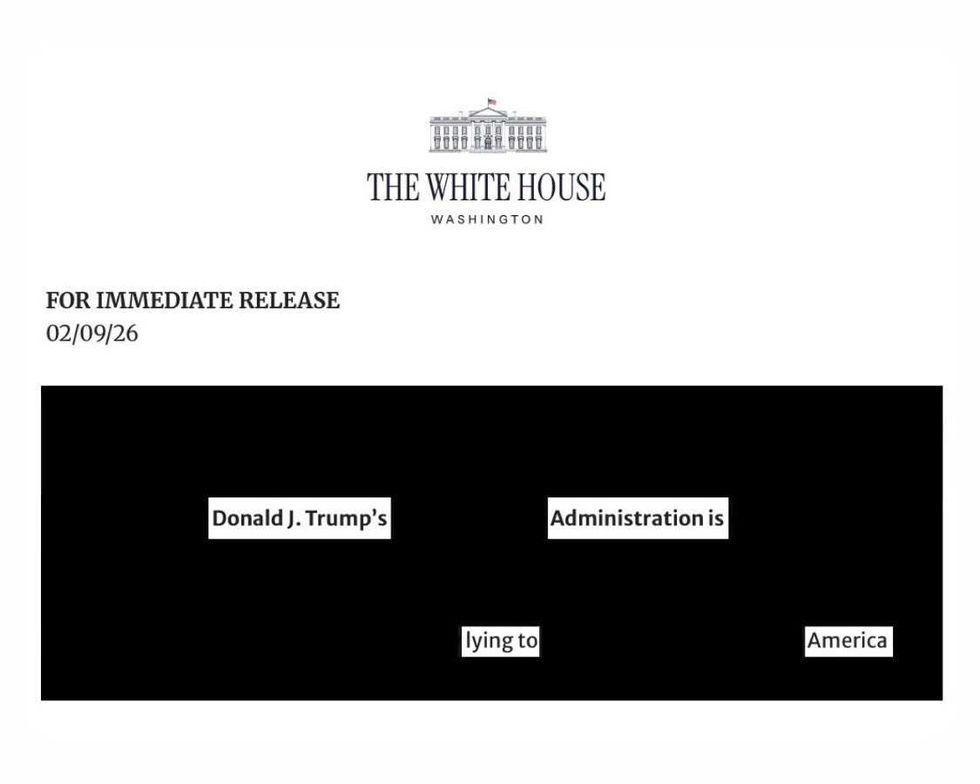 @JBPritzker/X
@JBPritzker/X

 @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok @glammy1217/TikTok
@glammy1217/TikTok
 @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok @peachie.peach21/TikTok
@peachie.peach21/TikTok