It has been quite a while since user and consumer data has had the promise of being completely secure. Sony, Target, Equifax, and Yahoo! are just a handful of the names that come to mind when discussing the topic of security and information hacks. In mid-March 2018, Facebook was added to that seemingly infinite list of data breaches, but there was something different about this one - it was done legally.
Where the 2014 Sony breach or the massive 2017 Equifax breach were orchestrated by criminal third parties, the Facebook “leak” of user information was due to the social networking site’s application programming interface (API) and a very crafty data analytics firm.
It had been known since 2015 that Cambridge Analytica (CA), which was directly connected to Donald Trump’s presidential campaign, was using Facebook to harvest user data from millions of profiles to build a more efficient marketing database. While that may sound like it crosses the line of legality, it was Facebook’s own API that allowed the informational breach to occur.
Prior to a 2015 update to the API, a loophole granted third-party developers access to data of both users of their apps and the friends of those users. CA merely utilized this careless gap in the interface to collect data from over 50 million users. The analytics firm did allegedly turn around and use this information for marketing purposes for the Trump campaign, which did go against Facebook’s terms of service.
Why a story that’s almost three-years-old is gaining traction once again is more about news outlets connecting the dots between CA’s actions and Facebook’s acknowledgment that such an abuse of user data was going on. The one upside to all of this, as pointed out by vice president and deputy general counsel at Facebook Paul Grewal, is that “[n]o systems were infiltrated, and no passwords or sensitive pieces of information were stolen or hacked.”
Those concerned that their private personal information has once again been stolen can rest easy. Kind of. What this sort of data breach does is make the public aware of what information is technically not private, even when an account is set to strict privacy settings. Status updates, interests, and check-ins are an example of the type of information lifted by CA and used in the tactical targeting of millions of users. It all calls back to a good rule of thumb: Don’t post anything on social media you don’t want to become publicly known.
Though Facebook’s actions and API fell within all legal confines, the outcry, which comes from sources like WhatsApp’s co-founder Brian Acton, is based more on the company’s ethics than the law. The social networking company did reverse the known loophole in its API, but only after CA was caught red-handed using a system that Facebook had implemented. It doesn’t help that advocacy groups have been trying to push for user data privacy, which would have avoided such a fiasco.
&ref_url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.theverge.com%2F2018%2F3%2F20%2F17145200%2Fbrian-acton-delete-facebook-whatsapp&tfw_site=vergeHow you react to the breach of data is a matter of personal preference. While some users may view it as a company being ingenious and cleverly using what legal resources are available, others may see it as an advantageous and unethical act facilitated by the very social media network they trusted with their data.












 @DuncanCecil/X
@DuncanCecil/X @@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social @89toothdoc/X
@89toothdoc/X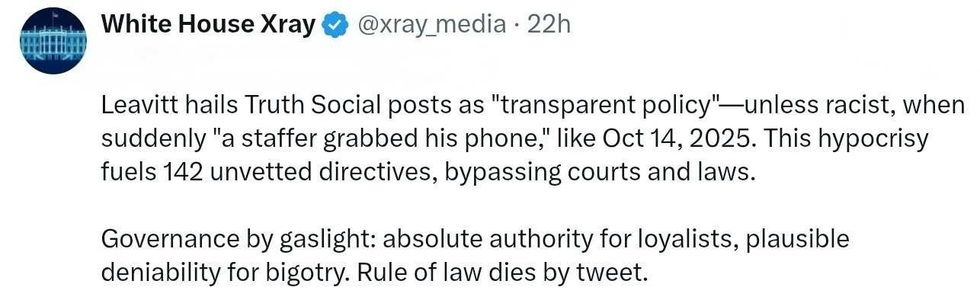 @xray_media/X
@xray_media/X @CHRISTI12512382/X
@CHRISTI12512382/X
 @sza/Instagram
@sza/Instagram @laylanelli/Instagram
@laylanelli/Instagram @itssharisma/Instagram
@itssharisma/Instagram @k8ydid99/Instagram
@k8ydid99/Instagram @8thhousepath/Instagram
@8thhousepath/Instagram @solflwers/Instagram
@solflwers/Instagram @msrosemarienyc/Instagram
@msrosemarienyc/Instagram @afropuff1/Instagram
@afropuff1/Instagram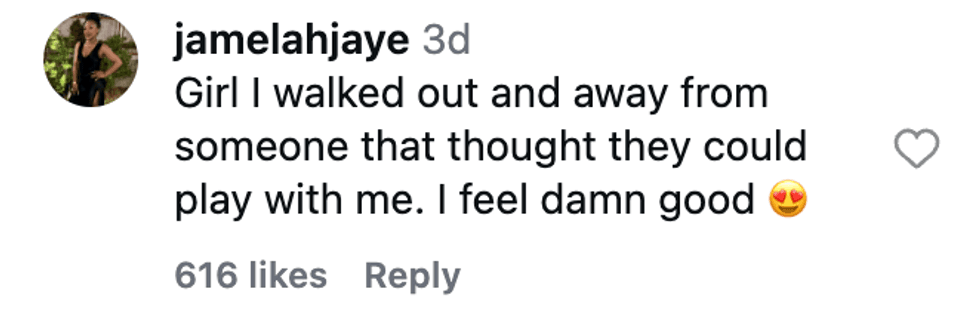 @jamelahjaye/Instagram
@jamelahjaye/Instagram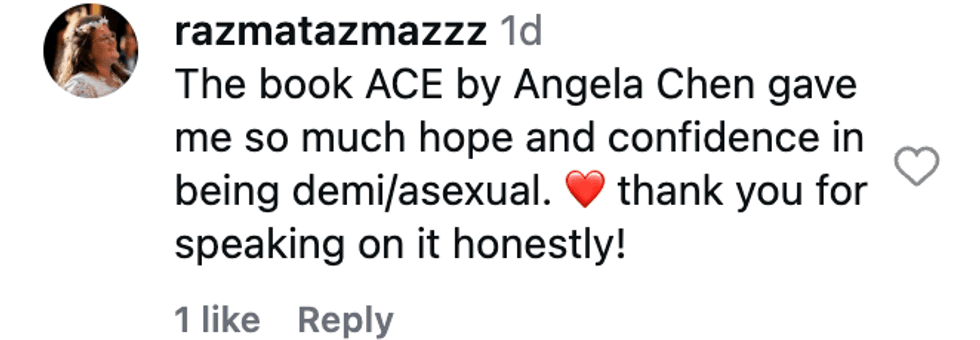 @razmatazmazzz/Instagram
@razmatazmazzz/Instagram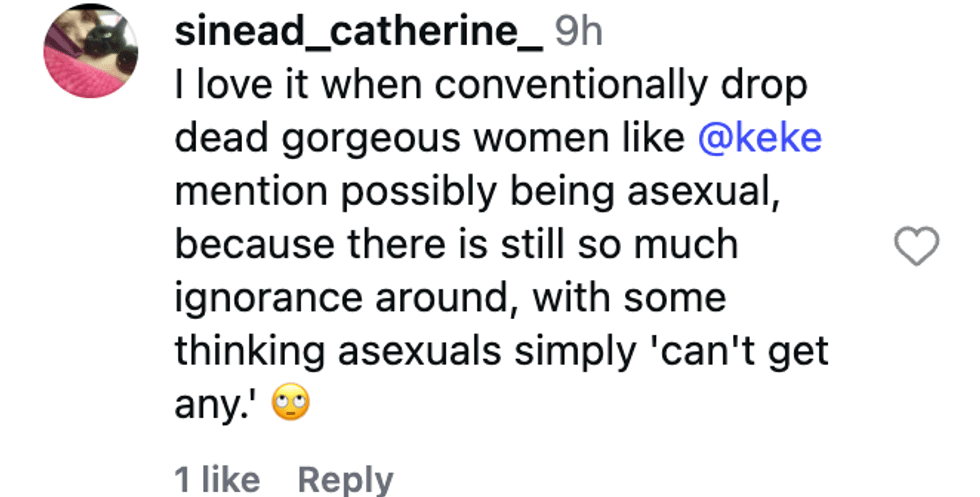 @sinead_catherine_/Instagram
@sinead_catherine_/Instagram @popscxii/Instagram
@popscxii/Instagram