In early July, a New York Times story about how Chinese officials are using facial recognition technology to track down lawbreakers went viral.
The story opened with a short anecdote about a police officer in Zhengzhou who used his special glasses to catch a heroin smuggler. His glasses were powered by artificial intelligence that allowed him to match the faces around him — each of which had been recorded by numerous security cameras around the city — with the face of the perpetrator. People around the world tweeted about the dystopian nature of this use of technology, making the usual jokes about the movie Minority Report. In the U.S., many worried about whether we might be next. As with most viral news stories, this was knocked off the top of the trending list by the next story.
Just a few days later, however, Microsoft president Brad Smith gave some credence to those worries in a blog post calling for Congress to regulate the use of facial recognition technology in the U.S. before it’s too late.
“All tools can be used for good or ill,” he wrote. “Facial recognition technology raises issues that go to the heart of fundamental human rights protections like privacy and freedom of expression.”
Microsoft’s choice to address these issues by calling for regulation was reminiscent of Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s comment to Congress in March that, “Actually, I’m not sure we shouldn’t be regulated.” Zuckerberg was concerned about political organizations using his platform to spread false news or damaging information (and about being perceived as partial to one political party over the other); Smith of Microsoft is worried about the government using its technology to probe citizens’ lives and infringe upon their rights.
Smith’s blog post was in line with his company’s recent efforts to position itself as the “moral compass” of Silicon Valley. But it also came after an outcry that threatened that image.
In June, while the country was up in arms over actions by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement, several people on Twitter shared links to a January blog post in which Microsoft general manager Tom Keane discussed a contract with ICE and noted that a Microsoft product, Azure Government, had passed a high-security threshold. The post also mentioned that this new Authority to Operate for Azure might help facilitate ICE’s work, including, potentially, using facial recognition.
Amid the uproar, Smith wrote, Microsoft looked into it, and found that ICE was not using Azure for facial recognition or anything having to do with family separation. Acknowledging calls for the company to cut ties with ICE altogether, Smith made a different suggestion: more regulation.
“The only effective way to manage the use of technology by a government is for the government to proactively manage this use itself,” he wrote. “While we appreciate that some people today are calling for tech companies to make these decisions … we believe this is an inadequate substitute for decision making by the public and its representatives in a democratic republic.”
Specifically, Smith called on the government to consider: whether law enforcement use of facial recognition, as in China, should be subject to human oversight and restrictions; whether civilians should be part of that oversight; what might prevent facial recognition from being used in racial profiling; whether retailer should have to post notices about facial recognition technology, as they do about security cameras; and several other related questions.
As Smith was quick to point out, Microsoft isn’t the only company dealing with this issue. Salesforce and Amazon have also been the focus of shareholder pressure and boycotts regarding relationships with ICE, and Facebook came under fire in an April lawsuit alleging that it turned on face-matching services without asking users first. But Microsoft is the first to call for a “bipartisan and expert commission” to take regulatory action.
With a divided Congress in the midst of hearings about what Facebook does or does not owe to its users and the republic, however, Microsoft may have to wait its turn.







 @tulipanet/Bluesky
@tulipanet/Bluesky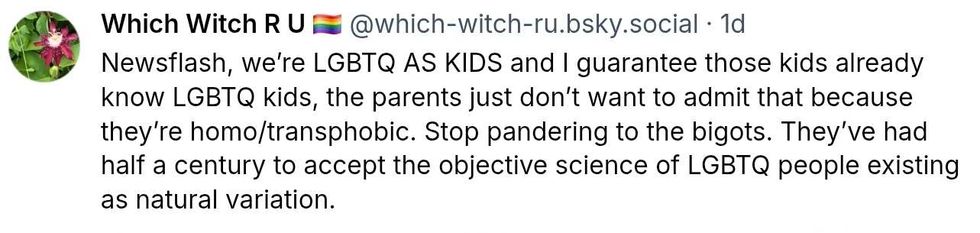 @which–witch–ru/Bluesky
@which–witch–ru/Bluesky @phillip–rees/Bluesky
@phillip–rees/Bluesky








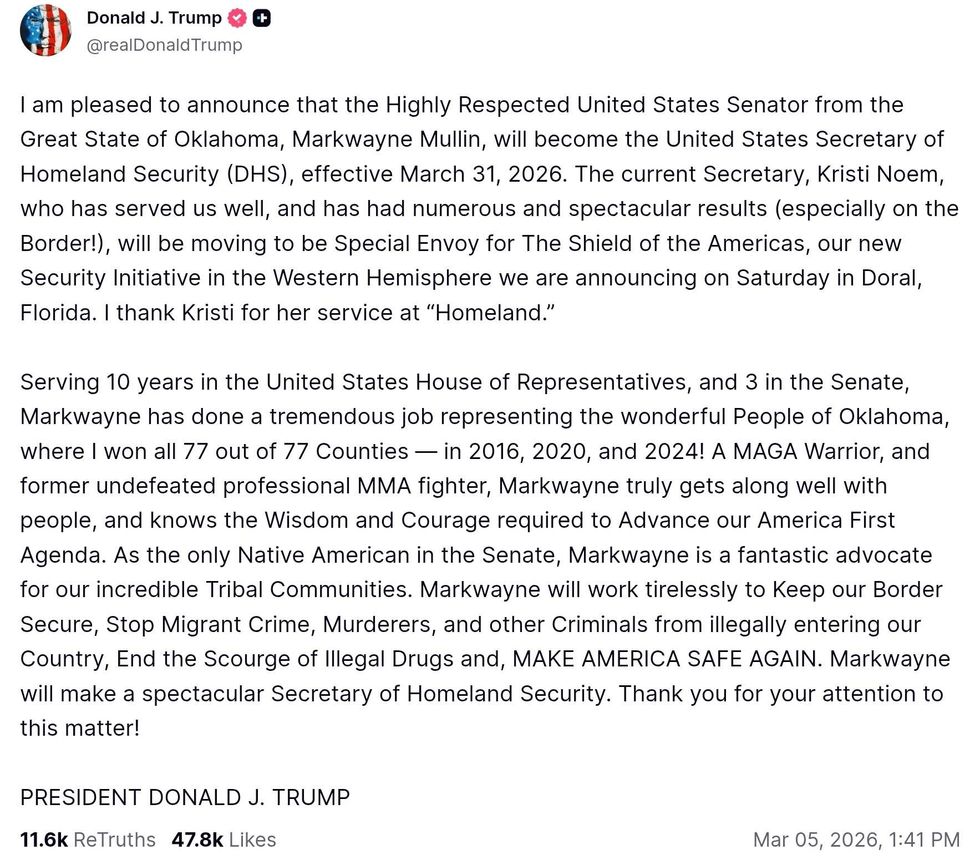 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social