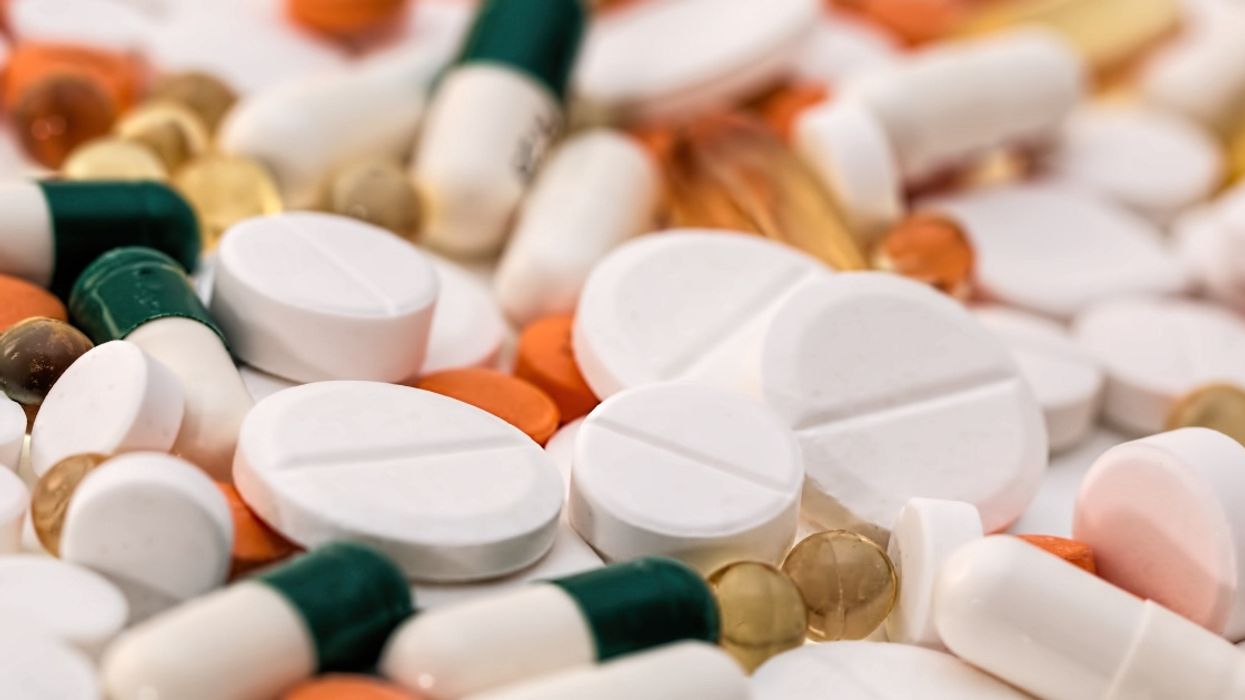
Could a drinkable medicine be in the future for Alzheimer's patients? A new study published by researchers from Yale University has shown promise on a new kind of treatment.
The treatment has been tested on mice bred to have similar symptoms to Alzheimer's. The drug, based on an old antibiotic called cefixime, was found to improve the subjects' memory on two doses a day for a month.
Alzheimer's studies have shown a link between the disease and a buildup of protein plaques on the brain. As the plaques increase, an immune response is triggered to attack it. It is believed the combination of plaques and immune response contribute to the disease.
This gave the research team a target. By finding a drug that can prevent the binding of prion proteins and amyloid beta, they can prevent the plaque. Cefixime was found to have this unexpected effect, but only after being adjusted and put into a liquid form.
It's looking pretty good!
"Saw my grandpa lose himself to Alzheimer's, I really hope this helps turn the tide against the disease. Everytime I see new news on this a bit of excitement and relief hits me :)"
- short-circuit-soul
"Can we refer to it as a "potion" instead of a cocktail? Somehow that would make it zound more appealing."
- Herr_Red
Alzheimer's is the 6th leading cause of death in the United States. From 2000 to 2015, there was a 123% increase in deaths attributed to the disease. While billions of dollars have been and will continue to be spent on research, the complexity of the disease and human memory make breakthroughs difficult.
In addition, many early trials are performed on mice, which while an inexpensive test subject, are also very distinct from primates, particularly humans. Over 80% of all clinical mouse models end up not applying to humans.
Because of this, let's maybe temper our expectations.
"So much research that gives optimism and then crushes ones hopes when no actual treatment comes out of it."
- bluecat200
"This could easily take up to 15 years to make it to the market IF it passes all levels of clinical and non-clinical testing, for anybody thinking this is gonna be on the market within 2019"
- scubadude2
"Their molecules blocked amyloid-beta aggregation in vitro and by oral administration in a mouse Alzheimers model. So it's yet to be tested in humans; unfortunately, many drugs appear promising in animal stages, then fail in further models (monkey or human).
Hopefully this one fares better! We'll have to wait and see."
- Mijamahmad
"I know this is an amazing advancement and all but I can't take it seriously with the way it's phrased. b/c all I can think of when reading the phrase "designer molecules" is some snooty french guy making fashionable outfits for each individual molecule."
- Kronos5115
It's not all doom and gloom. This result showed a repairs to synaptic connections, which is a positive step. The scientific process will move forward with more testing to ensure safety and verify its efficacy. The researchers are beginning the process of determining the toxicity of the solution on humans before moving on to further trials.
What's most fascinating is that an antibiotic was found to have positive effects on Alzheimer's. Other drugs that treat diabetes and arthritis have been shown to possibly benefit people with dementia. The drug was also used in another trial for a different form of dementia and worked there too.
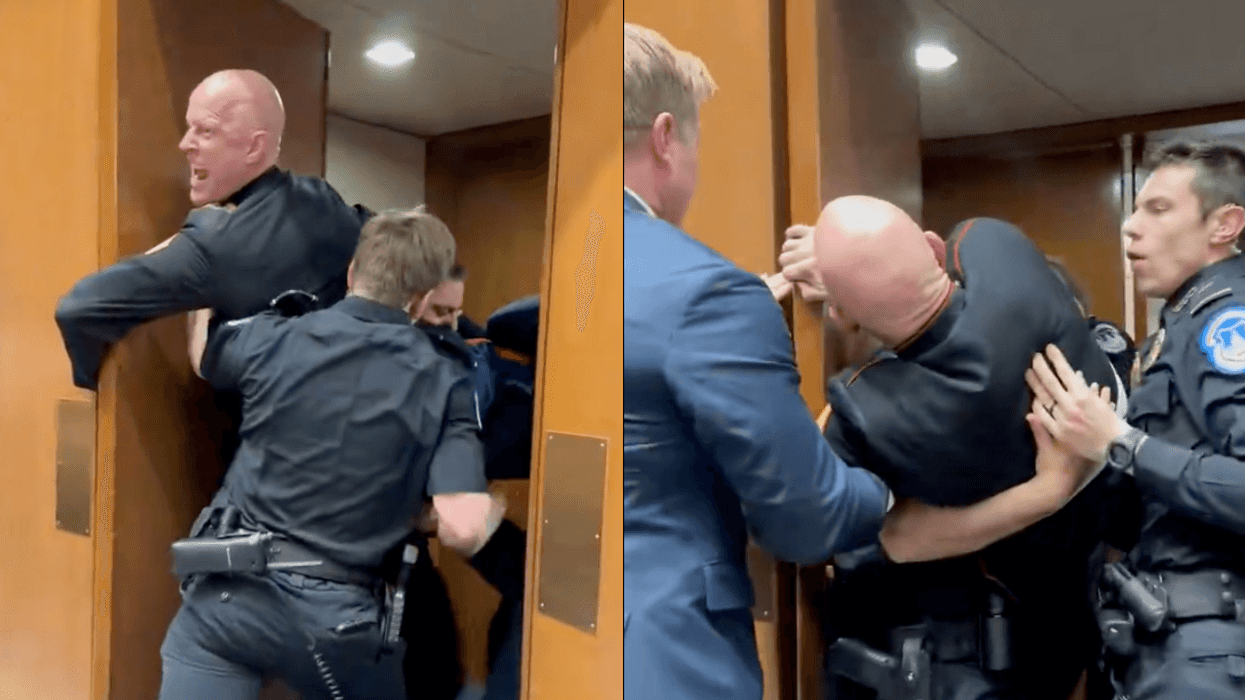
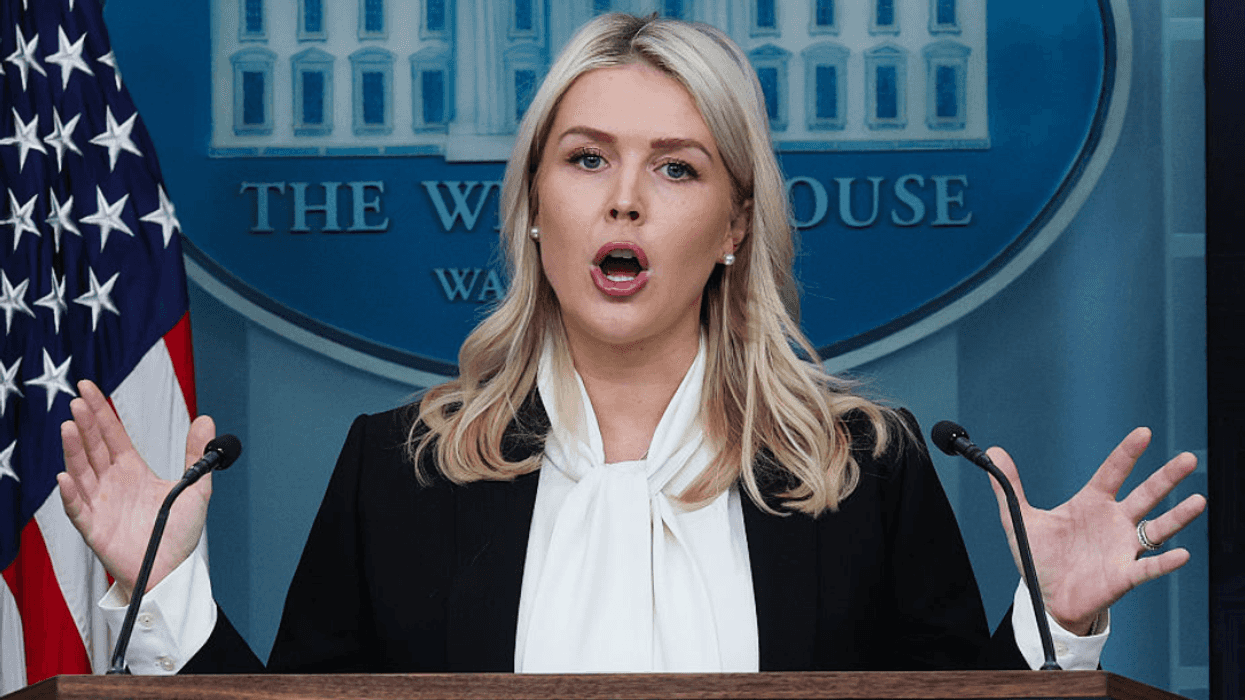
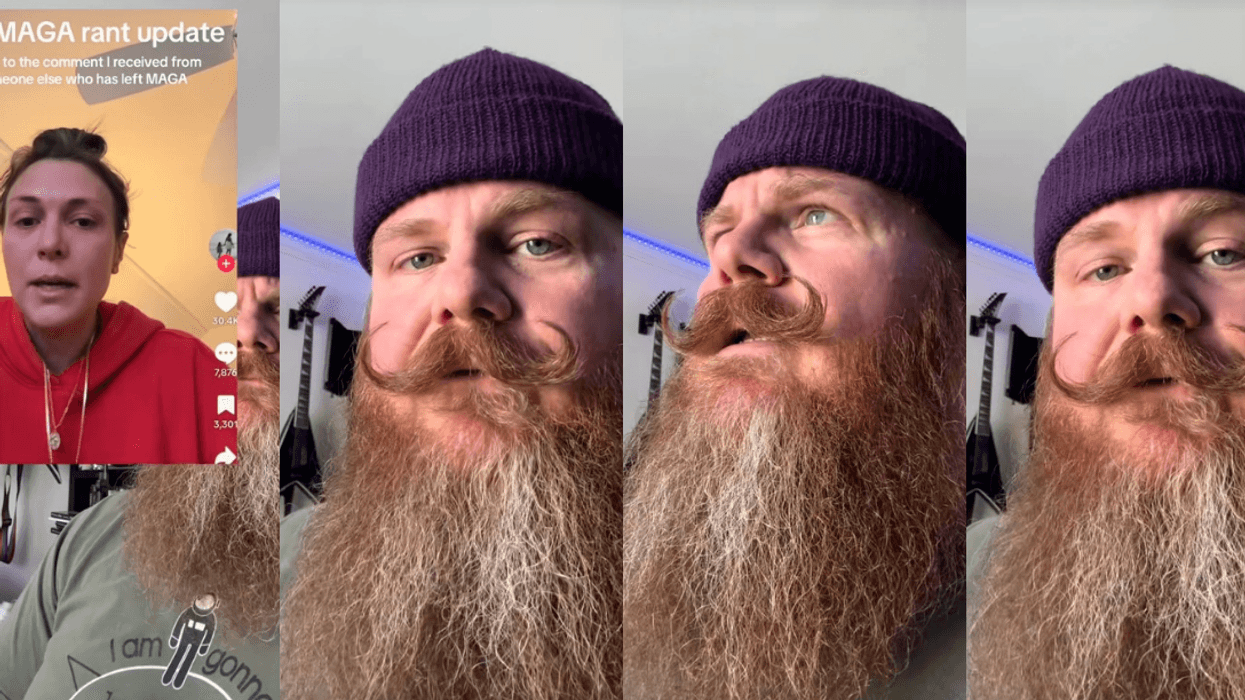
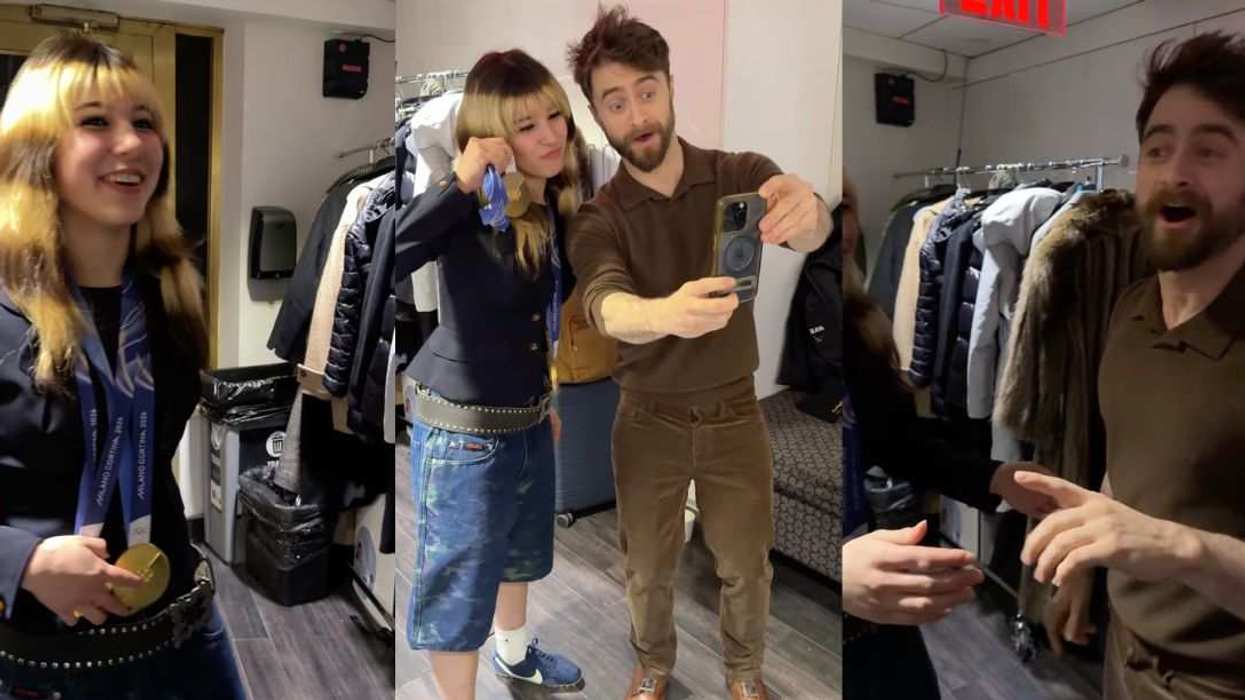











 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok
 @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok
 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok
 @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok