There's long been a running joke about how some people look like their pets. Sometimes the gag hinges on the person in question being narcissistic enough to choose a dog that best mirrors their own reflection, while other times the joke centers around how, over time, we begin to morph into the visage of those we spend the most time with.
Regardless of the premise, the point has always been how humorous it is to look like one's pet. That may have all changed after one clever Twitter user posted his own totally twinsome pics that have everybody interested in owning their cross-species twin status.
Disney's "101 Dalmatians" showcased one of the best bits ever done on the remarkable resemblance between dogs and their owners.
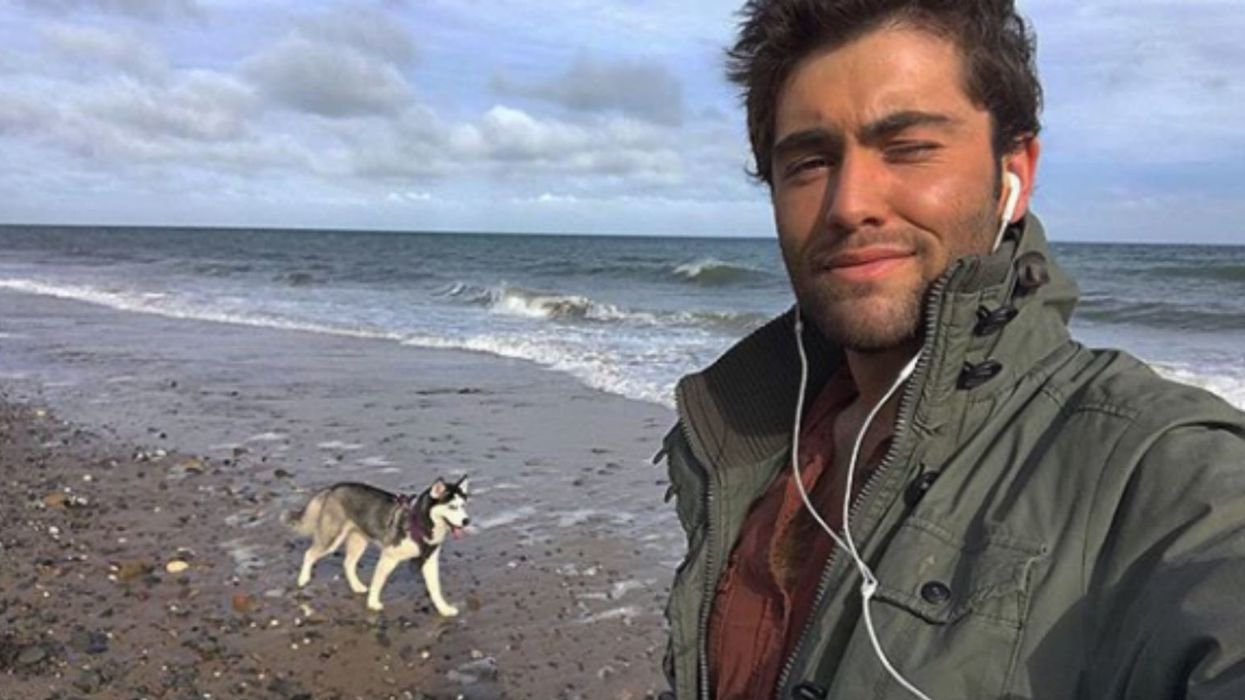
It all started with Liam Rice, a dashing 24-year-old model-type who also happens to be an animal care officer at the Manx Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (MSPCA) on the Isle of Man. Rice posted a series of photos to his Twitter that featured him and his equally handsome Siberian Husky in similar poses or with near-identical expressions.
Check them out:
So beguiling is this duo that they inspired a host of "twinning" photos. Twitter users shared pics with their own furry family members, all of them equally twinneriffic!
Love the scrunched up face in this one:
Went the extra mile:
Love the use of light and shadow:
OMG:
Yes! It's that perennial staring-out-the-window-pensively shot:
Excellent:
And now to end on something completely different:
Face the facts:
Back in 2014, a psychologist and researcher at Japan's Kwansei Gakuin University named Sadahiko Nakajima found evidence to support the notion that humans and their canine friends actually do look alike. According to the Huffington Post, Nakajima "...conducted a 2009 study where people were, at a rate significantly higher than chance, able to match dogs and their owners simply by looking at photographs of their faces."
Pairing his research with other similar studies, Nakajima came to the conclusion that, "popular belief in dog-owner physical resemblance is empirically valid."
But why? Well, Nakajima also claimed to have nailed that down, too.
He says it all comes down to the eyes. In fact, he conducted another experiment—the results of which were published in 2013 in the journal Anthrozoös. In it, he wanted to see if "...the pet-human resemblance could be traced to a specific facial feature."
And guess what? They could.
Pet and owner pairs were pretty easily identified when all features were visible (participants had an 80 percent success rate), but when certain features (mouths, eyes, noses) were obscured, that all changed. The bottom line? When the eyes were concealed, accuracy rates plummeted to 50 percent, but as long as the eyes were showing, it didn't matter much what else was hidden. Participants' accuracy rates were at 73 and 74 percent as long as the eyes were visible.
So that solves the pesky "Do they actually look alike?" question and tells us what features are allowing these pet/owner combos to be identified. But why did Nakajima think owners had dogs that resembled them? According to HuffPost:
"'...a major reason of the dog-owner facial resemblance is the so-called 'mere exposure effect,'' or the idea that a person might choose to get a dog who looks similar to themselves because of a preference for the familiar."That's his theory—but you can choose whether or not to take it at face value.






 Columbia Heights Public Schools
Columbia Heights Public Schools



 Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
 Gym Weights GIF by Guava Juice
Gym Weights GIF by Guava Juice 
 Man With A Plan
Man With A Plan  Happy Feeling Good GIF by BEARISH
Happy Feeling Good GIF by BEARISH  Roadside Assistance Flat Tire GIF
Roadside Assistance Flat Tire GIF 
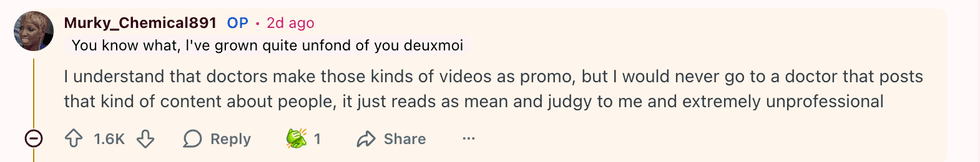 u/Murky_Chemical891/Reddit
u/Murky_Chemical891/Reddit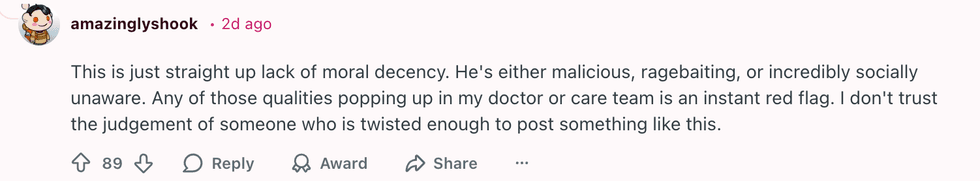 u/amazinglyshook/Reddit
u/amazinglyshook/Reddit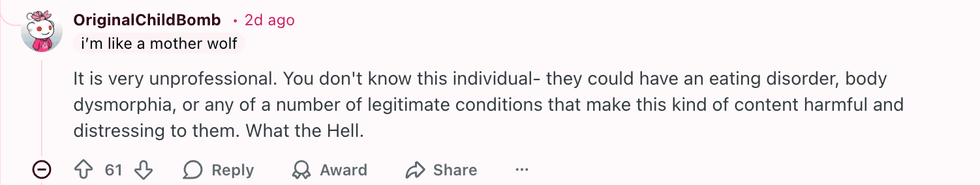 u/OriginalChildBomb/Reddit
u/OriginalChildBomb/Reddit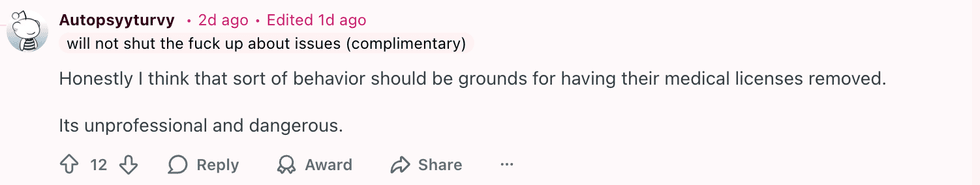 u/Autopsyyturvy/Reddit
u/Autopsyyturvy/Reddit u/_iridessence_/Reddit
u/_iridessence_/Reddit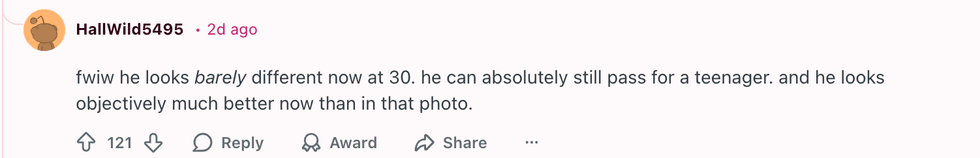 u/HallWild5495/Reddit
u/HallWild5495/Reddit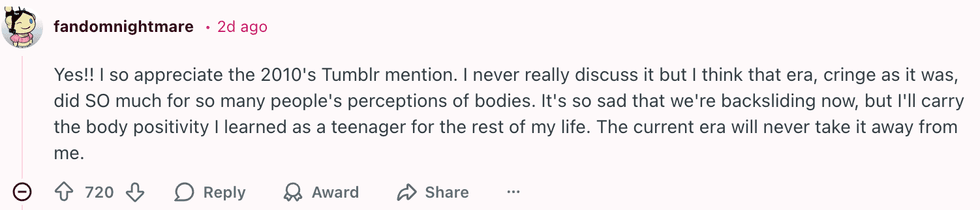 u/fandomnightmare/Reddit
u/fandomnightmare/Reddit 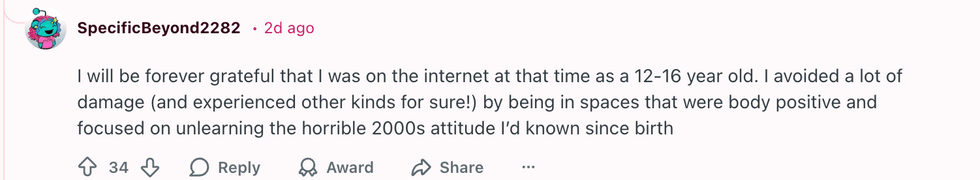 u/SpecificBeyond2282/Reddit
u/SpecificBeyond2282/Reddit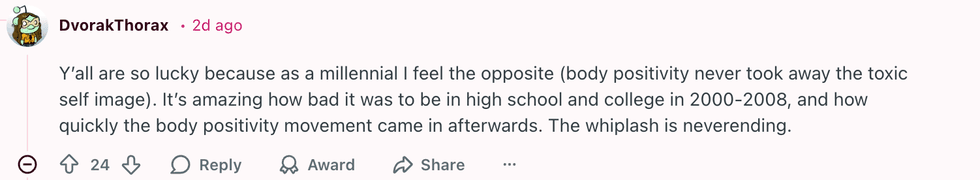 u/DvorakThorax/Reddit
u/DvorakThorax/Reddit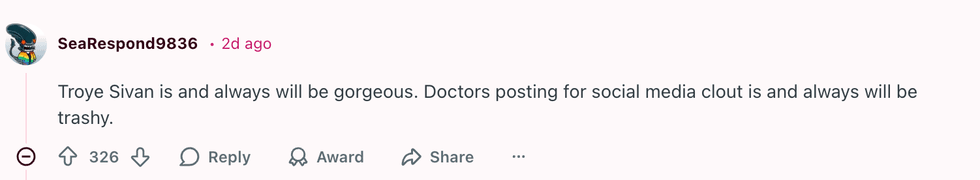 u/SeaRespond9836/Reddit
u/SeaRespond9836/Reddit u/According-Garden-129/Reddit
u/According-Garden-129/Reddit
 @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok