The United States Patent and Trademark Office awarded Amazon two patents for a wristband that would precisely track its warehouse workers’ movements. While the wristbands may help increase productivity, critics warn that the technology raises serious privacy concerns, and would add an extra layer of surveillance to an already intense work environment.
We may not think much about what happens to our Amazon purchases between when we click “order” and when it arrives at our door, but that single click sets a streamlined process in motion. The details of the order are transmitted to a worker via a handheld computer. The worker then retrieves the product from an inventory bin or shelf, and packs it into a delivery box. Repeat, repeat, repeat.
In fact, Amazon demands such efficiency from their workers that it expects an order to be fulfilled every 33 seconds. It’s not uncommon for a worker to walk upwards of 11 miles in a single shift.
The patent application explains that the wristband technology could work to save even more time by streamlining the fulfillment system. The wristbands would use ultrasonic tracking to determine the exact location of a worker’s hands as they retrieve items from the shelves or bins. The worker would receive feedback from the wristband, in the form of vibration (or “haptic feedback,” as it’s described in the patent application), when their hand was moving in the right direction.

While we all want our Amazon shipments to arrive quickly, some fear that these wristbands will provide yet another layer of stress to an already stressful work environment. For instance, former warehouse worker Max Crawford told the New York Times “After a year of working on the floor, I felt like I had become a version of the robots I was working with.”
He described falling over from dizziness due to the breakneck speed of the packing requirements, and not being able to use the restroom because of difficult quotas.
Adding wristbands to the picture adds an additional level of stress, said stress expert Dr. Teresa D’Oliveira of King’s College London. She warned that this technology could increase “physical or psychological pressures” on workers.
It could also add an additional layer of surveillance, pinging workers who take a bathroom break, fidget unnecessarily, or even scratch an itch.
Amazon disputes these claims. In a statement, the company said “The speculation about this patent is misguided. Every day at companies around the world, employees use handheld scanners to check inventory and fulfill orders. This idea, if implemented in the future, would improve the process for our fulfillment associates.
By moving equipment to associates’ wrists, we could free up their hands from scanners and their eyes from computer screens.” Amazon continued: “Like most companies, we have performance expectations for every Amazon employee and we measure actual performance against those expectations, and they are not designed to track employees or limit their abilities to take breaks."
It is still unclear whether these wristbands will ever actually get made—most products that receive patents do not end up being produced. But current and former Amazon employees said they would not be surprised by the technology, and that the company already uses similar tracking technology in its warehouses.
“They want to turn people into machines,” said Caldwell. “The robotic technology isn’t up to scratch yet, so until it is, they will use human robots.”













 @obamaatredrobin/X
@obamaatredrobin/X
 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social

 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok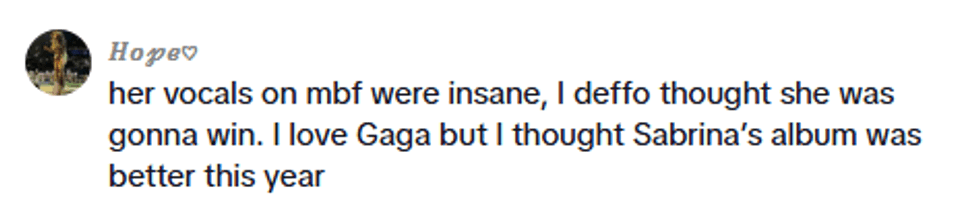 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok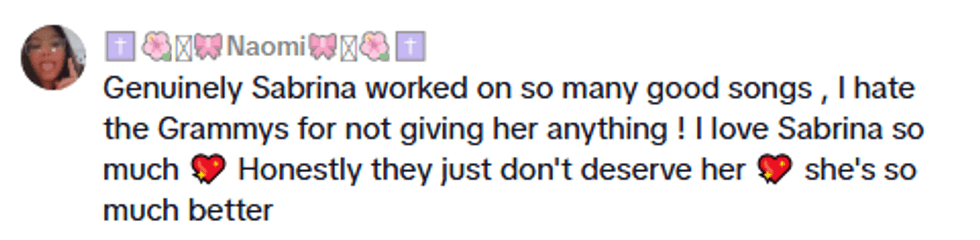 @.a.zan/TikTok
@.a.zan/TikTok