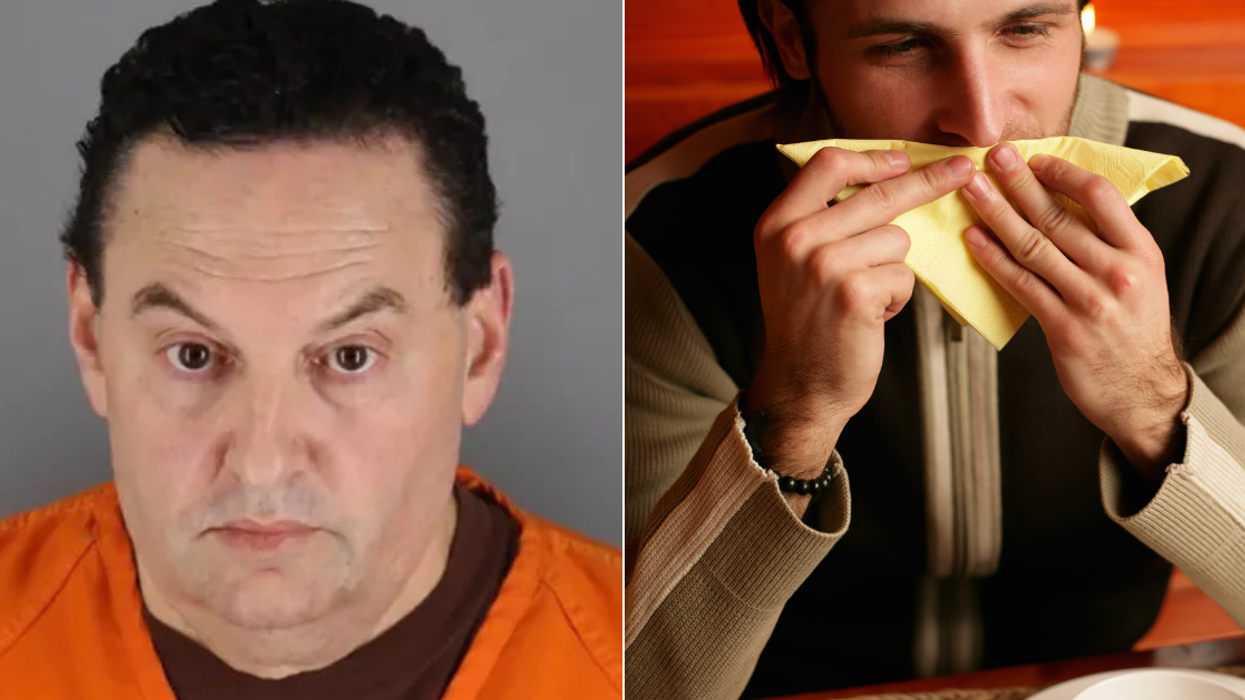
The U.S. Supreme Court has previously ruled that items are fair game once they have been thrown in the garbage, and a discarded napkin was enough to lead to the arrest of 52 year-old Jerry Westrom for a murder committed 26 years ago. DNA evidence from the napkin was matched to DNA evidence from the scene of Jeanne Ann "Jeanie" Childs' death back in 1993.
This case is yet another example of police using genealogy databases, which use client's DNA to help them find family members, to solve cold cases. The databases can be used to find family members of those who submitted their DNA by finding similarities to the perpetrator's DNA.
Police then work backward from that innocent person to determine which of their family members fits the profile of the perpetrator. They can then obtain a sample of that person's DNA to compare to the crime scene evidence.
This method was used to catch the Golden State Killer last year.
There are significant ethical and privacy concerns related to these private DNA databases. A report from October indicates that identifying people through their family's DNA and some basic biographic information is on the horizon. One private DNA testing company already has an agreement to work with the FBI.
Minneapolis police haven't disclosed their whole process, or which database company they used, but they have said in a statement that the break in the cold case came after "cold case investigators consulted with the FBI's experts, and a private DNA company."
Hennepin County District Attorney Mike Freeman said in a press conference "DNA samples were sent to genealogists who helped us match them together."
Twitter users' reactions varied. Some were concerned about the use of DNA databases, while others were glad they were being used to solve cold cases.
According to the StarTribune, Westrom was charged with second-degree murder. He has denied the allegations, and bail was set at $500,000 with conditions. He has been released on bail and is due to return to court on March 13th.








 @RepOgles/X
@RepOgles/X @RepOgles/X
@RepOgles/X




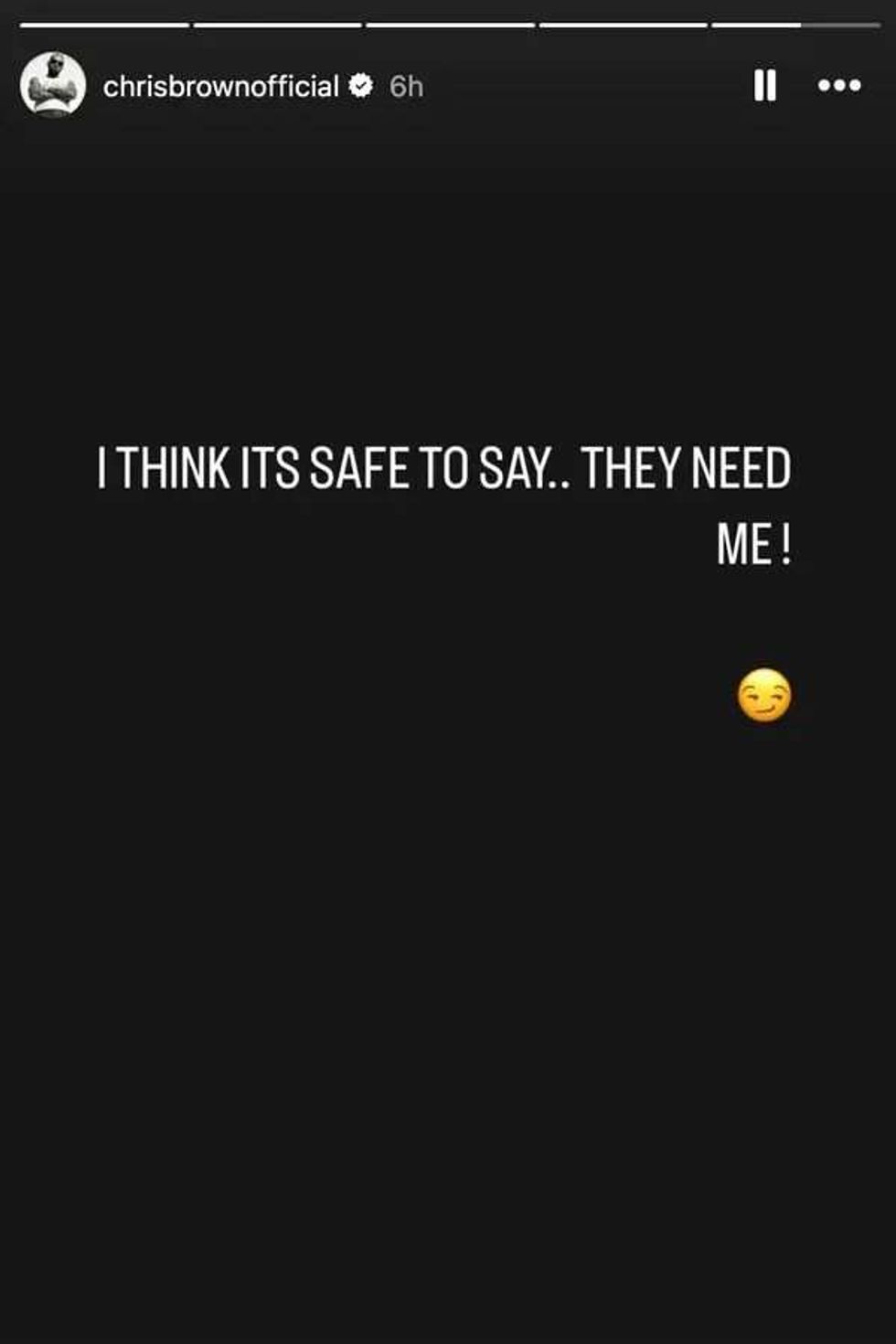 @chrisbrownofficial/Instagram
@chrisbrownofficial/Instagram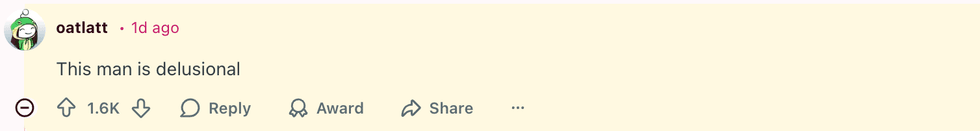 u/oatlatt/Reddit
u/oatlatt/Reddit u/LoveTheAhole/Reddit
u/LoveTheAhole/Reddit u/SoFetch89/Reddit
u/SoFetch89/Reddit u/00trysomethingnu/Reddit
u/00trysomethingnu/Reddit u/kittybuscemi/Reddit
u/kittybuscemi/Reddit u/___nic/Reddit
u/___nic/Reddit u/WaterMagician/Reddit
u/WaterMagician/Reddit u/west-brompton/Reddit
u/west-brompton/Reddit u/GhostlySpinster/Reddit
u/GhostlySpinster/Reddit u/Asleep_Tap6199/Reddit
u/Asleep_Tap6199/Reddit u/afreudtolove/Reddit
u/afreudtolove/Reddit u/myfriendtoldmetojoin/Reddit
u/myfriendtoldmetojoin/Reddit
 @charlesbeckinsale/Instagram
@charlesbeckinsale/Instagram @liamgriffin/Instagram
@liamgriffin/Instagram @valentinoguseli/Instagram
@valentinoguseli/Instagram @17is/Instagram
@17is/Instagram @torahbright/Instagram
@torahbright/Instagram @mcfetridge/Instagram
@mcfetridge/Instagram @colleenquigley/Instagram
@colleenquigley/Instagram @jonathanwaynefreeman/Instagram
@jonathanwaynefreeman/Instagram
 @amberglenniceskater/Instagram
@amberglenniceskater/Instagram