President Donald Trump is presiding over a White House which, at 34 percent, has reportedly seen the highest turnover rate among its staff in decades. A New York Times report notes that the president "has struggled to fill openings, unwilling to hire Republicans he considers disloyal and unable to entice Republicans who consider him unstable."
“We have vacancies on top of vacancies,” said Kathryn Dunn Tenpas, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution who has studied White House turnover over the last six administrations. “You have initial vacancies, you have people who left in the first year and now you have people who are leaving in the second year.”
Tenpas observes in a Brookings Institution report that Trump's turnover "is record-setting, more than triple that of Obama and double that of Reagan." She argues that Trump "has valued loyalty over qualifications and suffered from a White House that has functioned in a chaotic manner." These choices have "made it difficult to retain staff and have contributed to the governance difficulties he has encountered."
The graph below, she notes, is the level of turnover across the first term for President Trump’s five immediate predecessors, as well as his first year in office.

Tenpas expects the trend to continue in his second year, for myriad reasons. While she acknowledges that staff changes "no doubt rid the White House staff of bad apples," vacancies require "hiring a replacement, helping the replacement learn the ropes, and other staff shouldering more work until the new hire is up-to-speed (or permanently if the position stays vacant). Those remaining face disruptions and inefficiencies during the process."
Perhaps the most damning effect of high turnover: It "deprives the White House of the previous incumbents relationships":
In presidential politics, much like any business environment, the coin of the realm is personal relationships—ties to the Hill, party leaders, interest group leaders, advocacy organizations, and journalists are critical to presidential success. While a replacement may be able to reclaim those relationships, or at least some of them, to the degree the relationships cannot be replaced, too much turnover can be a hindrance for a new administration and its pursuit of policy goals.
Republican operatives have said they worry that working at the White House would cast dark shadows over their careers. The highly charged atmosphere, exacerbated by the president's often inflammatory tweets and the looming specter of special counsel Robert Mueller''s investigation into Russian meddling isn't helping matters either.
There isn’t a huge appetite from many Republicans on the outside to explore job opportunities in this administration,” said Ryan Williams, a former spokesman for Mitt Romney, the party's nominee in 2012. “While there are a lot of vacancies and usually a position in the White House is one of the most prestigious jobs in Washington, that’s just not the feeling with this administration, given the turmoil and the chaos.”
The White House has indicated that it will attempt to resolve its turnover problem; on Friday, it announced 32 new appointments. But most of those appointments, like James Carroll, now the acting national drug policy director, were promotions from within. Carroll, for example, is on his fourth appointment since the president took office, having started in the White House counsel’s office, then becoming general counsel for the budget office and serving most recently as deputy chief of staff.







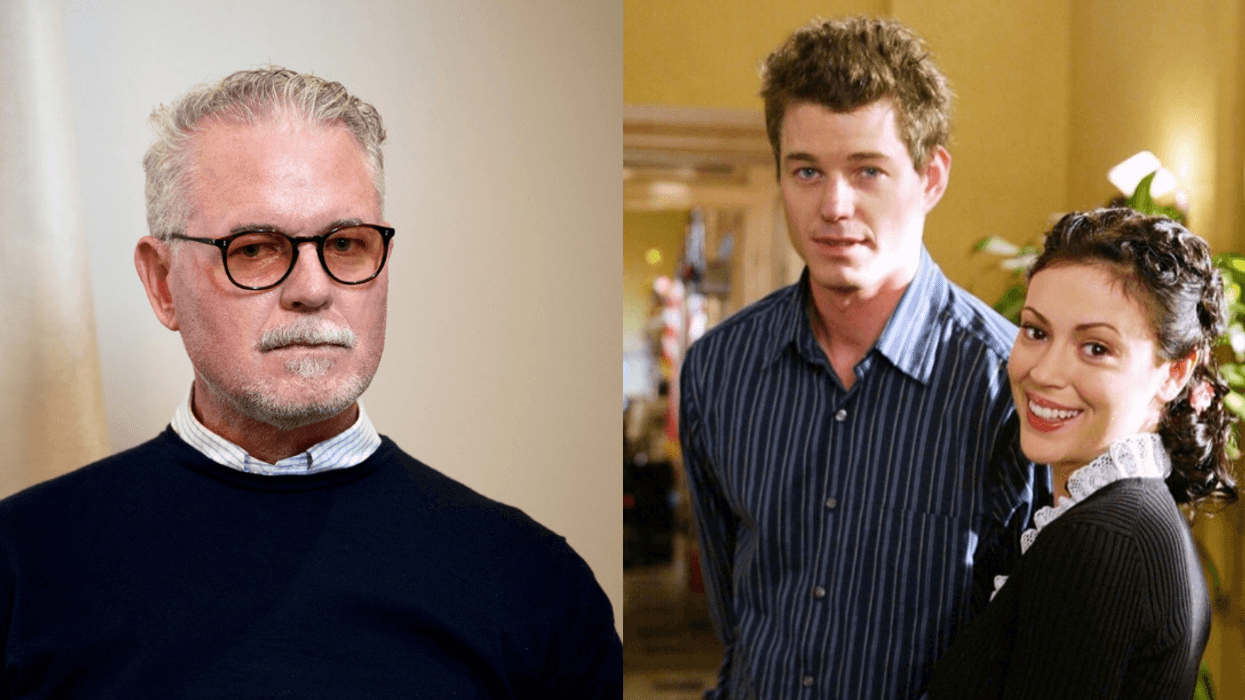
 reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @rebeccagayheartdame/Instagram
reply to @rebeccagayheartdame/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram
reply to @milano_alyssa/Instagram





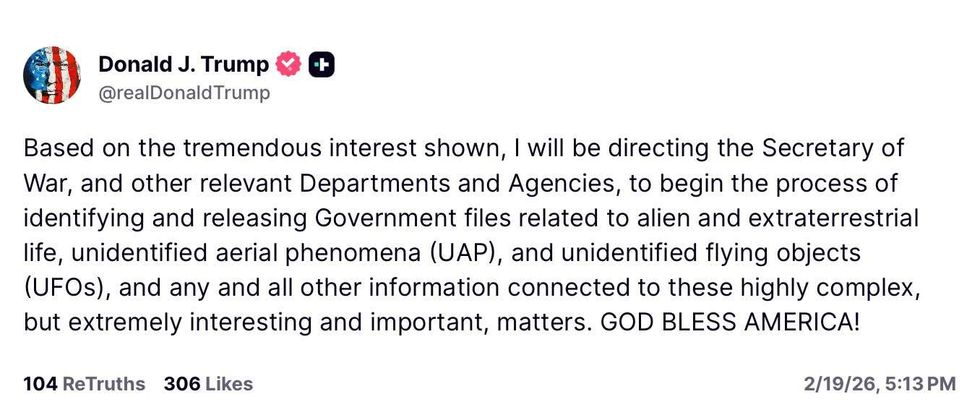 @realDonaldTrump/Truth Social
@realDonaldTrump/Truth Social


 @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram @gutterutterart/Instagram
@gutterutterart/Instagram