Antibodies derived from llamas have been shown to combat the virus in laboratory tests.
Researchers hope the antibodies – known as nanobodies due to their small size – could eventually be developed as a treatment for patients with severe symptoms.
The immune system produces antibodies when it is being attacked, or in response to infections.
Llamas, camels and alpacas naturally produce quantities of small antibodies with a simpler structure that can be turned into nanobodies.
The team from the Rosalind Franklin Institute, Oxford University, Diamond Light Source and Public Health England engineered their new nanobodies using a collection of antibodies taken from llama blood cells.
They found that the nanobodies bind tightly to the spike protein of the virus, blocking it from entering human cells and stopping infection.
In the study published in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, the team also identified that the nanobodies bind to the spike protein in a new and different way to other antibodies already discovered.
James Naismith, director of The Rosalind Franklin Institute and professor of structural biology at Oxford University, said:
“These nanobodies have the potential to be used in a similar way to convalescent serum, effectively stopping progression of the virus in patients who are ill."
“We were able to combine one of the nanobodies with a human antibody and show the combination was even more powerful than either alone."
“Combinations are particularly useful since the virus has to change multiple things at the same time to escape – this is very hard for the virus to do."
“The nanobodies also have potential as a powerful diagnostic."
Professor Ray Owens, from Oxford University – who leads the nanobody program at the Franklin, said the researchers are hopeful they can push the breakthrough on into pre-clinical trials.
Professor David Stuart, from Diamond Light Source and Oxford University, said:
“The electron microscopy structures showed us that the three nanobodies can bind to the virus spike, essentially covering up the portions that the virus uses to enter human cells."
Researchers started from a lab-based library of llama antibodies, and are now screening antibodies from Fifi, one of the 'Franklin llamas' based at the University of Reading, taken after she was immunized with harmless purified virus proteins.
The team is looking at preliminary results which show that Fifi's immune system has produced different antibodies from those already identified, which will enable cocktails of nanobodies to be tested against the virus.
In a separate study published in Nature Medicine, scientists say they have uncovered how a crucial component of the immune system responds to the spike protein of the virus behind the worldwide pandemic.
Virus particles have a "crown" of proteins that resemble spikes, which enable the virus to attach and enter cells in humans.
The spike protein is crucial in inducing neutralizing antibodies to protect from reinfection.
Neutralizing antibodies not only bind to the viral spike protein, but prevent it from being able to attach to and enter human cells.
Researchers from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) investigated how the immune system, particularly B and T cells, responds to the spike.
B cells are responsible for producing the antibodies that recognize the virus, while T cells play an important role in supporting the development of the B cell response.
Dr. Jennifer Juno, from the University of Melbourne – and a postdoctoral researcher at the Doherty Institute – said they looked at people who had recovered from the virus who had mostly experienced mild or no symptoms.
She said:
“We found that those who showed strong neutralizing antibody activity had a robust B cell response, but most surprisingly, we also found that a particular subset of T cells, called T-follicular helper cells, was a great predictor of an effective immune response."
She added:
“Now we know how the immune system responds to the spike protein, and we have these biomarkers, or predictors of what elicits a good or poor immune response to [the virus], we can look at the vaccine candidates and see what will offer the best protection."










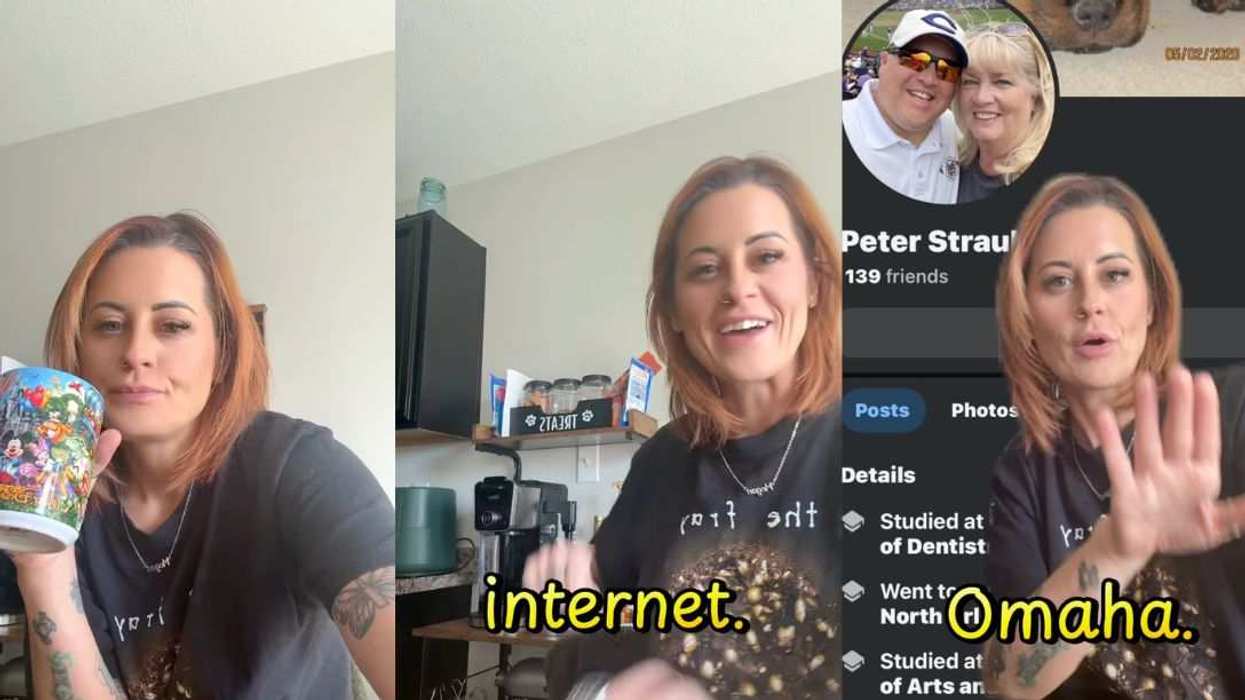



 @maddiemcrojas/Instagram
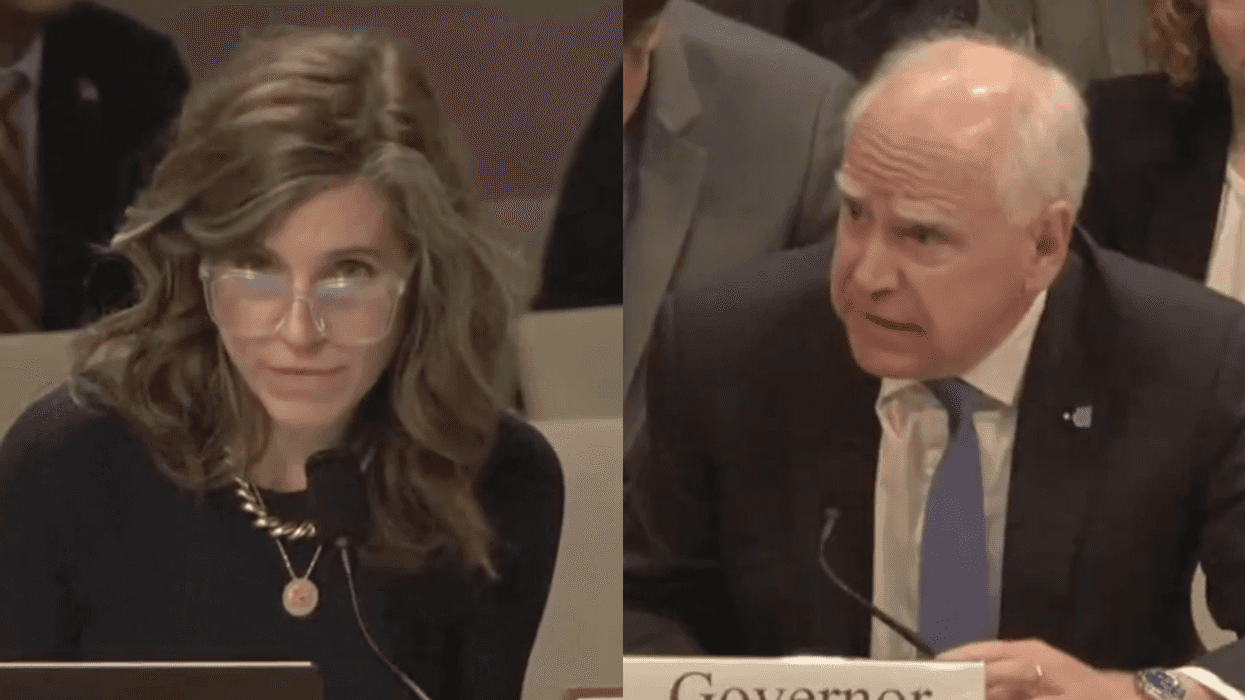
@maddiemcrojas/Instagram @eeemgeeebeee/Instagram
@eeemgeeebeee/Instagram @chefmelissaking/Instagram
@chefmelissaking/Instagram @catsonacouch/Instagram
@catsonacouch/Instagram @alwayskimhill/Instagram
@alwayskimhill/Instagram @_completelybooked/Instagram
@_completelybooked/Instagram @whereisrobinusa/Instagram
@whereisrobinusa/Instagram @veeeekaaay/Instagram
@veeeekaaay/Instagram @getlei_d/Instagram
@getlei_d/Instagram @andrebsteele/Instagram
@andrebsteele/Instagram @xxthisiskkxx/Instagram
@xxthisiskkxx/Instagram @ddrobjr/Instagram
@ddrobjr/Instagram
