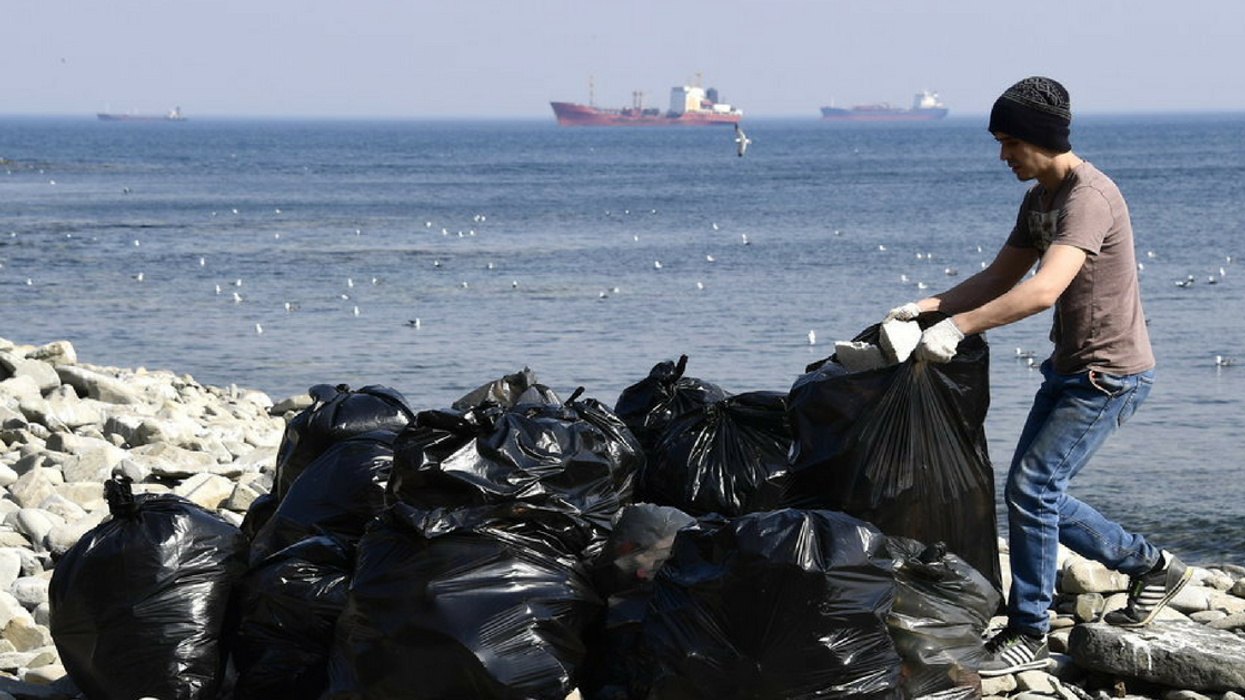
Plastic waste has been found at the bottom of the Mariana Trench in the Pacific, at a depth of nearly 36,000 feet. A recent study has scientists issuing warnings that our oceans are even more polluted than was previously thought.
In a study published in Science Direct, researchers released the Deep-sea Debris Database, which tracks plastic waste that has settled on the ocean floor, including in the very deepest spots under Earth's waters. The database, a project led by The Global Oceanographic Data Center (GODAC) of the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC), "archives photographs and videos of debris that have been collected since 1983 by deep-sea submersibles and remotely operated vehicles."
A staggering 89 percent of plastic debris cataloged by deep sea dives consisted mainly of single-use plastic, such as shopping bags, bottles, and packaging. In some areas, plastic bags and other trash were entangled in marine communities. Plastic waste is suffocating underwater ecosystems, and the presence of plastic in the deepest parts of Earth's oceans denotes a bigger problem than was previously imagined.
"From the 5010 dives in the database, 3425 man-made debris items were counted. More than 33% of the debris was macro-plastic, of which 89% was single-use products, and these ratios increased to 52% and 92%, respectively, in areas deeper than 6000 m. The deepest record was a plastic bag at 10898 m in the Mariana Trench. Deep-sea organisms were observed in the 17% of plastic debris images, which include entanglement of plastic bags on chemosynthetic cold seep communities."
Last month, the United Nations Environmental Committee issued a statement acknowledging the connection between human activity and deep-ocean pollution. The UN also explained that plastic pollution can stifle the growth of deep-sea ecosystems, which have naturally slow rates of growth.
Essentially, human waste is choking Earth's oceans.
"The ubiquitous distribution of single-use plastic, even to the greatest depths of the ocean, reveal a clear link between daily human activities and the remotest of environments."
"Once in the deep-sea, plastic can persist for thousands of years. Deep-sea ecosystems are highly endemic and have a very slow growth rate, so the potential threats from plastic pollution are concerning."
The study also found that 17 percent of the documented plastic waste was "found with at least one organism." Considering how sparsely populated the deep ocean is, this means that plastic is interacting with a substantial portion of marine life.
Last year, the study's lead author, Alan Jamieson told The Guardian:
"We still think of the deep ocean as being this remote and pristine realm, safe from human impact, but our research shows that, sadly, this could not be further from the truth. The fact that we found such extraordinary levels of these pollutants really brings home the long-term, devastating impact that mankind is having on the planet."
"The very bottom of the deep trenches like the Mariana are inhabited by incredibly efficient scavenging animals, like the 2cm-long amphipods we sampled, so any little bit of organic material that falls down, these guys turn up in huge numbers and devour it."
The presence of plastic waste in the deep ocean presents a depressing outlook for the future health of Earth's seas. In 2017, scientists discovered that some parts of the Mariana Trench contained more chemical pollutants than the most contaminated waterways in China, a country which will soon be the world's largest polluter. Scientists think that plastic waste breaking down deep under water may be the culprit as byproducts and toxins are released into the environment.
Another danger to both marine and human life is the abundance of micro-plastics, which sea life ingests and then passes up through the food chain.
"Micro-plastic ingested by zooplanktoncan be transferred to higher trophic level animals, including commercially important fish species, through the food web [9,10], with potential effects on human health."
In 2015, Hawaii became the first U.S. state to ban single-use plastic bags. California followed suit shortly thereafter, and New York is considering a similar ban. In April, Queen Elizabeth II announced after watching Blue Planet 2 that the United Kingdom will be banning single-use plastic straws, cotton buds and drink stirrers. The European Union is also currently weighing a ban on single-use plastics.






 Columbia Heights Public Schools
Columbia Heights Public Schools




 Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images
 Gym Weights GIF by Guava Juice
Gym Weights GIF by Guava Juice 
 Man With A Plan
Man With A Plan  Happy Feeling Good GIF by BEARISH
Happy Feeling Good GIF by BEARISH  Roadside Assistance Flat Tire GIF
Roadside Assistance Flat Tire GIF 
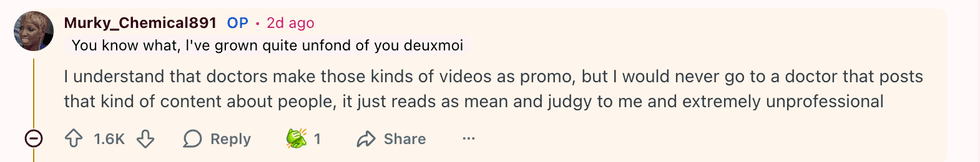 u/Murky_Chemical891/Reddit
u/Murky_Chemical891/Reddit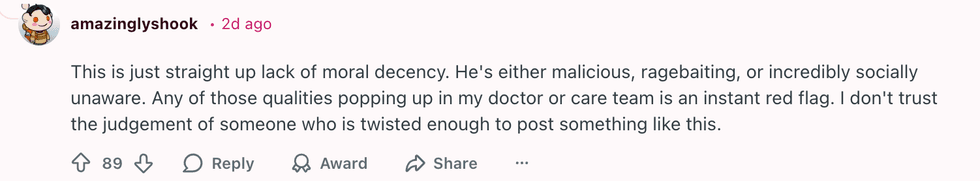 u/amazinglyshook/Reddit
u/amazinglyshook/Reddit u/OriginalChildBomb/Reddit
u/OriginalChildBomb/Reddit u/Autopsyyturvy/Reddit
u/Autopsyyturvy/Reddit u/_iridessence_/Reddit
u/_iridessence_/Reddit u/HallWild5495/Reddit
u/HallWild5495/Reddit u/fandomnightmare/Reddit
u/fandomnightmare/Reddit  u/SpecificBeyond2282/Reddit
u/SpecificBeyond2282/Reddit u/DvorakThorax/Reddit
u/DvorakThorax/Reddit u/SeaRespond9836/Reddit
u/SeaRespond9836/Reddit u/According-Garden-129/Reddit
u/According-Garden-129/Reddit
 @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok @its.avelyn/TikTok
@its.avelyn/TikTok