It’s no secret that America’s bees are in trouble. From colony-collapse disorder to threats from fungicides and neonicotinoid pesticides, the iconic pollinators’ ranks are so diminished that scientists report more than 700 North American bee species are headed toward extinction.
Near the top of the list of challenges facing bees — especially honeybees — is a tiny, tick-like parasite called the Varroa mite (Varroa destructor). And German scientists think they may have accidentally found a way to eradicate it without pesticides or harm to the bees.
According to a recent study, researchers at University of Hohenheim in Stuttgart fed one group of bees a sugar solution meant to be toxic, and another an untreated sugar solution. However, the mites on both groups of bees died. After extensive testing, they discovered it was trace amounts of a water-soluble salt in the sugar solution itself — lithium chloride — that was killing the mites. And it only took 25 millimoles (a unit of measurement for chemical reactions that counts the number of atoms or molecules) to do so; 90 to 100 percent of the mites were dead within 24 and 72 hours.
“Lithium chloride can be used to feed bees in sugar water. In our experiments, even small amounts of saline solution were enough to kill the mites sitting on the bees within a few days — without side effects for the bees," Dr. Peter Rosenkranz, head of the University of Hohenheim’s State Institute of Apiculture, said in a statement.
Varroa mite infestations are exclusive to honeybees. They attach to the insect’s body; consume its fat for food, thereby weakening the bee; and transfer pathogens such as deformed wing virus, which results in pupae that develop shriveled and/or malformed wings. The mites were introduced to Florida in the mid-1980s and have spread rapidly since — 42 percent of commercial beehives were infected with Varroa mites in 2017.
Varroa mites are also believed to be a major contributing factor to colony collapse disorder (CCD) in both the U.S. and Canada, a mysterious and not-yet-fully-understood phenomenon where all adult bees in a hive suddenly disappear, leaving food and the queen behind. CCD is spreading at an alarming rate; in April 2016, researchers reported that beekeepers lost 44 percent of their colonies over the previous year — up from 39 percent in 2014. If things continue at the current rate, scientists say, managed honeybees will be extinct by 2035.
Commercial beekeepers are currently limited to controlling Varroa destructor with acids or miticides. Not only can some of these products leave residue that can be harmful to other animals (one popular miticide, oxalic acid, is found in hardware stores as wood bleach), the mites can develop resistance over time.
Lithium chloride could be an unprecedented game-changer for ecologists and apiculturists — not only is it inexpensive and easy to procure, it won’t accumulate in beeswax and could someday be applied to both wild and managed swarms.
“The results presented here already indicate that [lithium chloride] has potential as an effective and easy-to-apply treatment for artificial and natural swarms and particularly for the huge number of package bees used for pollination in the United States,” the researchers wrote in the study.








 @carol_haynes_/Instagram
@carol_haynes_/Instagram @lwhiteza/Instagram
@lwhiteza/Instagram @iamdrkandace/Instagram
@iamdrkandace/Instagram @solveigerway/Instagram
@solveigerway/Instagram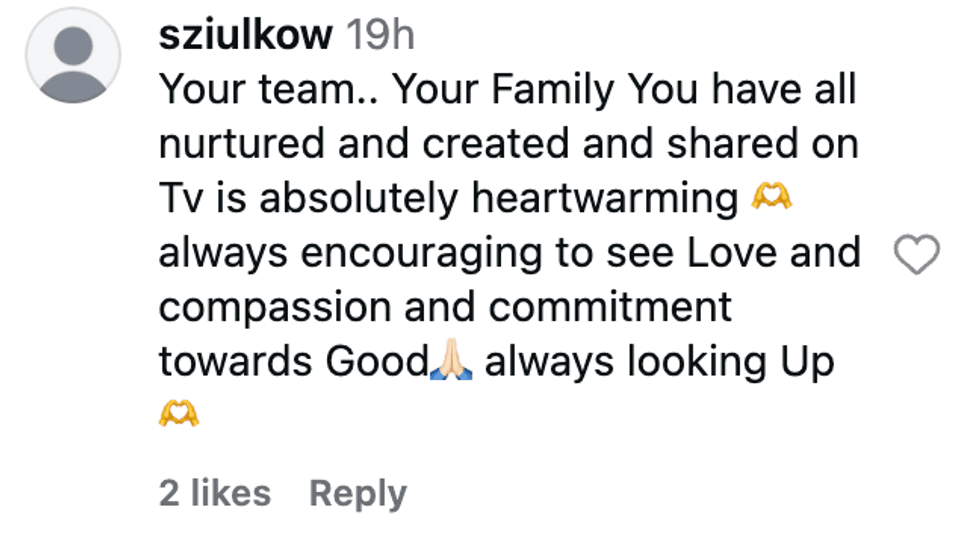 @sziulkow/Instagram
@sziulkow/Instagram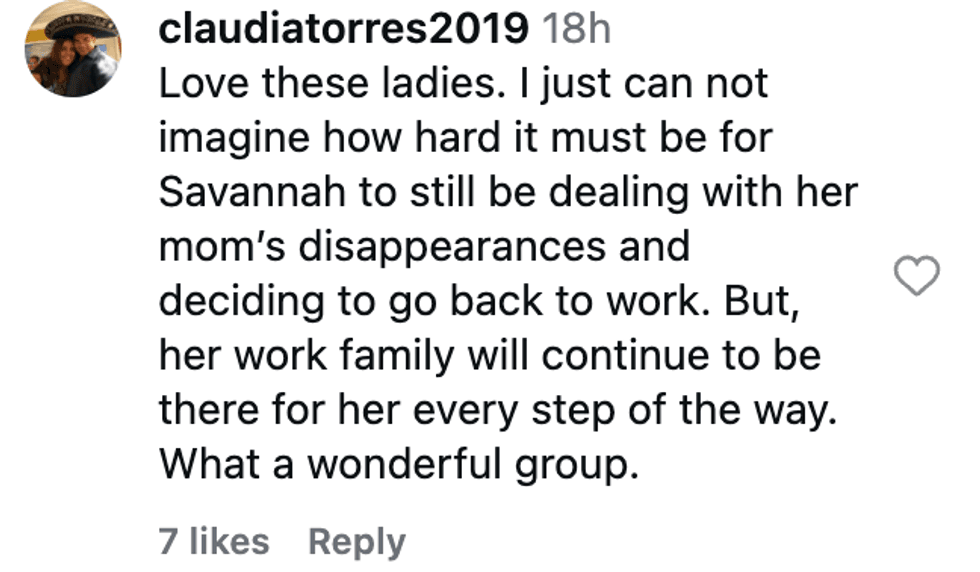 @claudiatorres2019/Instagram
@claudiatorres2019/Instagram @carolken/Instagram
@carolken/Instagram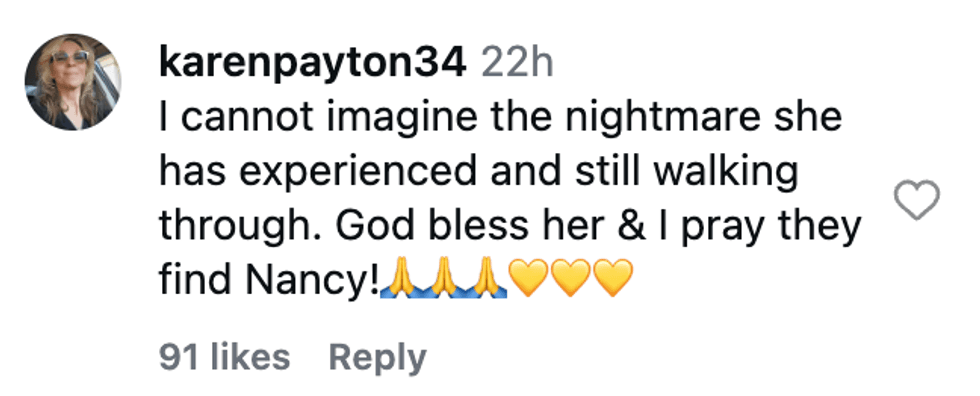 @karenpayton34/Instagram
@karenpayton34/Instagram @mamaburnside/Instagram
@mamaburnside/Instagram @alr_thrives/Instagram
@alr_thrives/Instagram @dr.rxq/Instagram
@dr.rxq/Instagram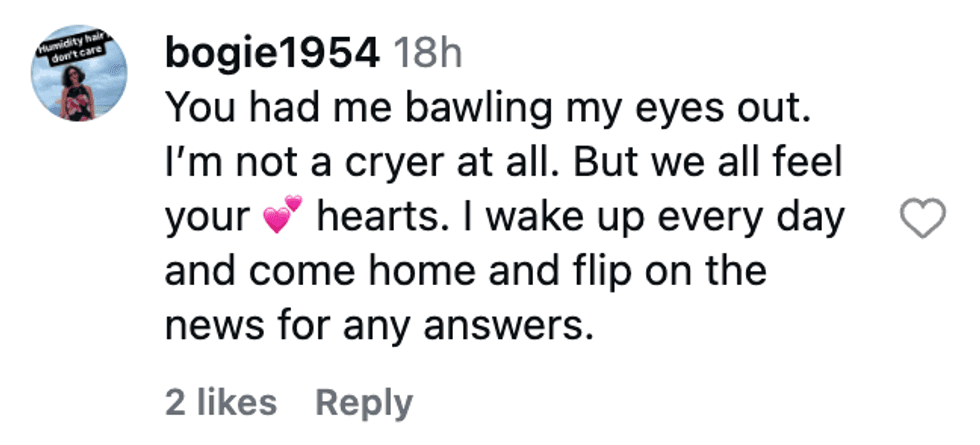 @bogie1954/Instagram
@bogie1954/Instagram



 @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram @todayshow/Instagram
@todayshow/Instagram
 @JBPritzker/X
@JBPritzker/X
 @margoshry/Instagram
@margoshry/Instagram @rachaelkirkconnell/Instagram
@rachaelkirkconnell/Instagram @guysetpodcast/Instagram
@guysetpodcast/Instagram @jordanfisher/Instagram
@jordanfisher/Instagram @cassidy.condie/Instagram
@cassidy.condie/Instagram @alexashoen/Instagram
@alexashoen/Instagram @tormansonn/Instagram
@tormansonn/Instagram @erinlimrhodes/Instagram
@erinlimrhodes/Instagram @willganss/Instagram
@willganss/Instagram
 draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com draftbarrontrump.com
draftbarrontrump.com