According to a federal court in New York, if you’ve ever linked to a Tweet on your blog, you could be guilty of copyright infringement. This, of course, is an entirely different song once sung by courts, which declared that copyright liability lands with the host and not the linking party.
The ruling came about when Justin Goldman accused media outlets like Time, Vox, Breitbart and Boston Globe of infringing copyright when they embedded a Tweet that included a picture he took of NFL superstar, Tom Brady. Goldman had been the photographer, but the Tweet came from a separate outlet. Regardless, the cameraman claimed that any story that had used his photo — which depicted Brady in the Hamptons while Kevin Durant was being eyed by the Celtics — had infringed on his copyright.
Judge Katherine Forrest’s ruling could alter how news outlets report on current events. Since much of today’s news comes from social media outlets, one may be required to find an alternative source if the story breaks on Twitter or Facebook. According to Forrest’s decision, embedding and in-line linking to a Tweet can be seen as copyright infringement. This, however, goes against the 2007 Ninth Circuit case Perfect 10 v. Amazon, which protected publishers in instances of embedding social media content.
Forrest spoke out against the Ninth Circuit ruling, stating:
[W]hen defendants caused the embedded Tweets to appear on their websites, their actions violated plaintiff’s exclusive display right; the fact that the image was hosted on a server owned and operated by an unrelated third party (Twitter) does not shield them from this result.
So far, the New York court is the only one to have adopted this view. If it does spread across the country and the ruling in the Ninth Court is deemed incorrect, it could be a catastrophic nuisance to news outlets and smaller blogs. Without the ability to pull sources from Twitter, outlets will be forced to go the extra step and reach out to the person running the social media account to ask permission. In cases where there are no alternative sources, this could slow progress on a breaking story.
For now, it’s a hiccup that, according to the Electronic Frontier Foundation, could still be appealed, though it’s worth proceeding with caution.
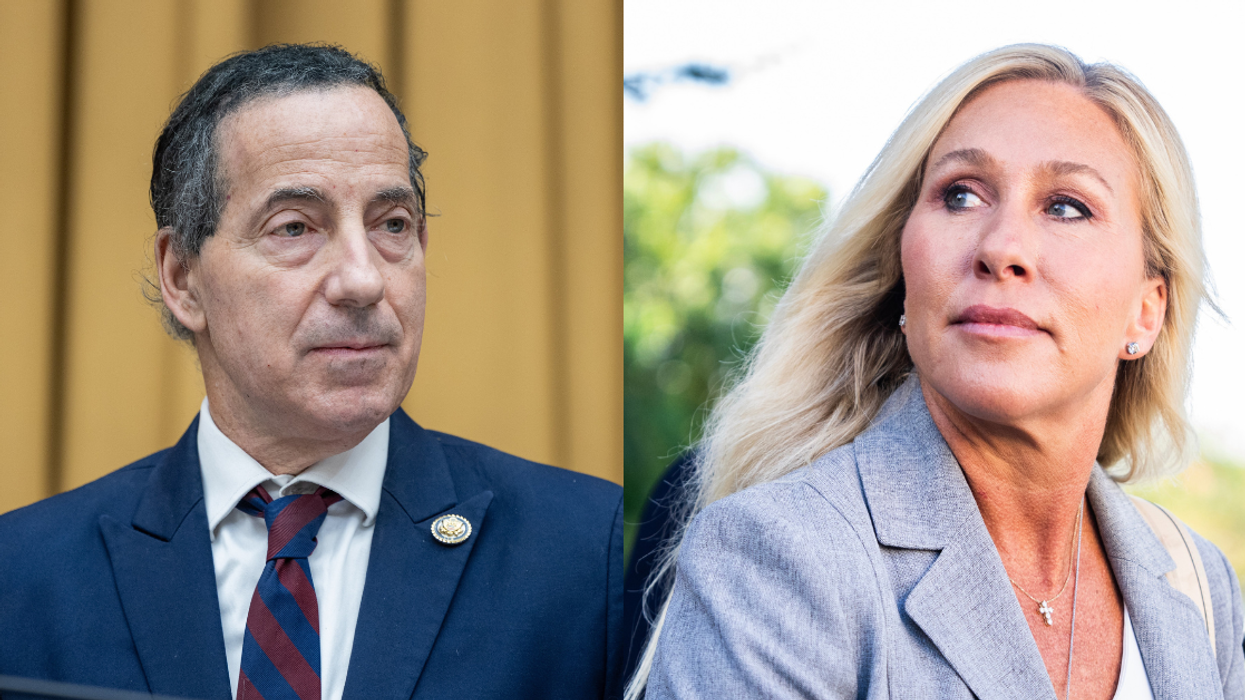







 @TrinityMustache/X
@TrinityMustache/X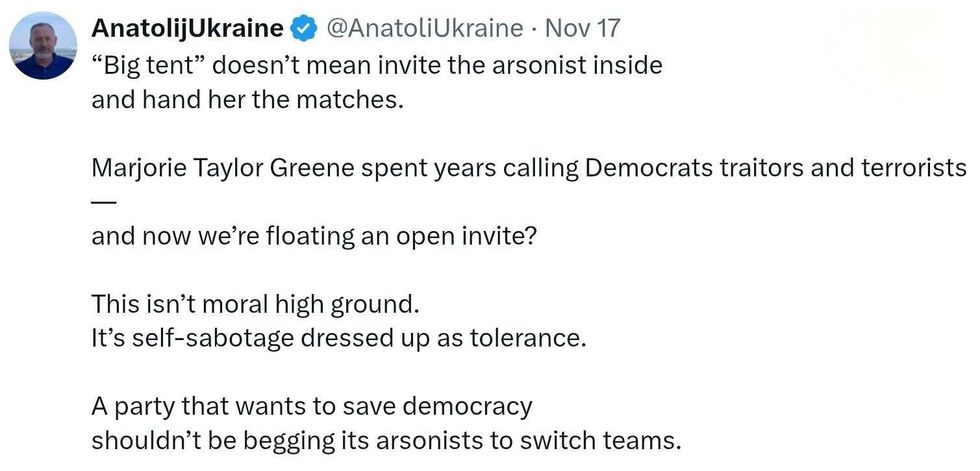 @AnatoliUkraine/X
@AnatoliUkraine/X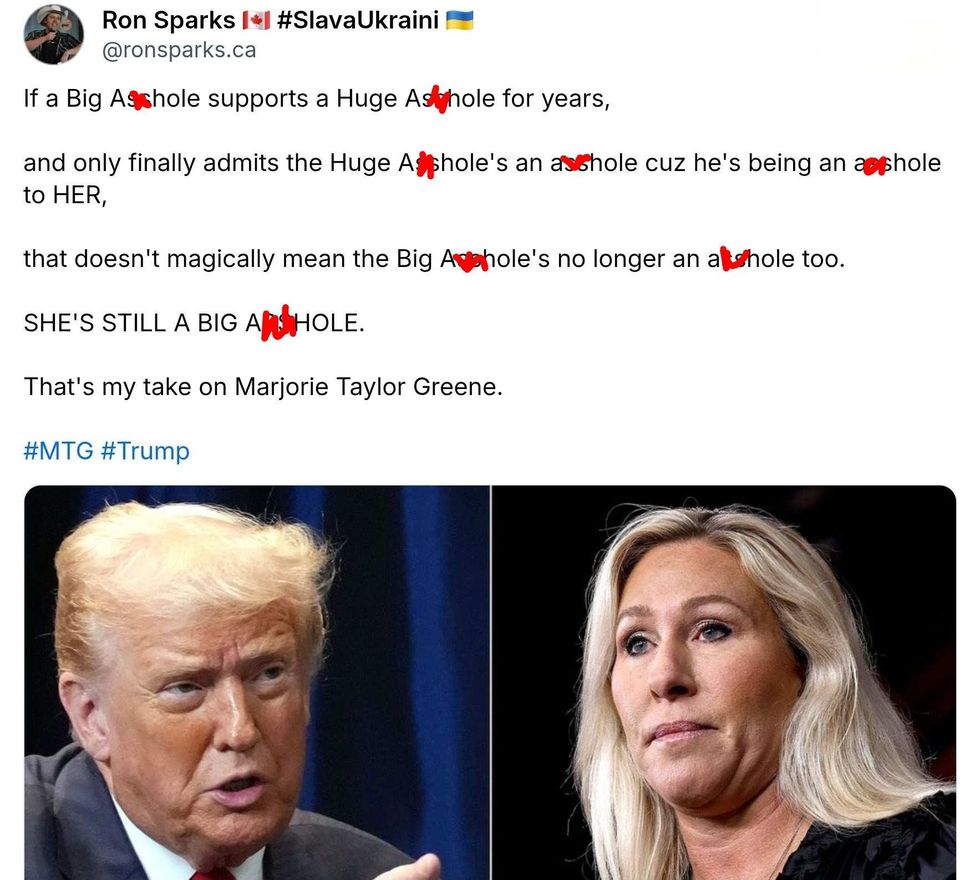 @ronsparks.ca/Bluesky
@ronsparks.ca/Bluesky @sycamoressource/X
@sycamoressource/X @Stephen52534304/X
@Stephen52534304/X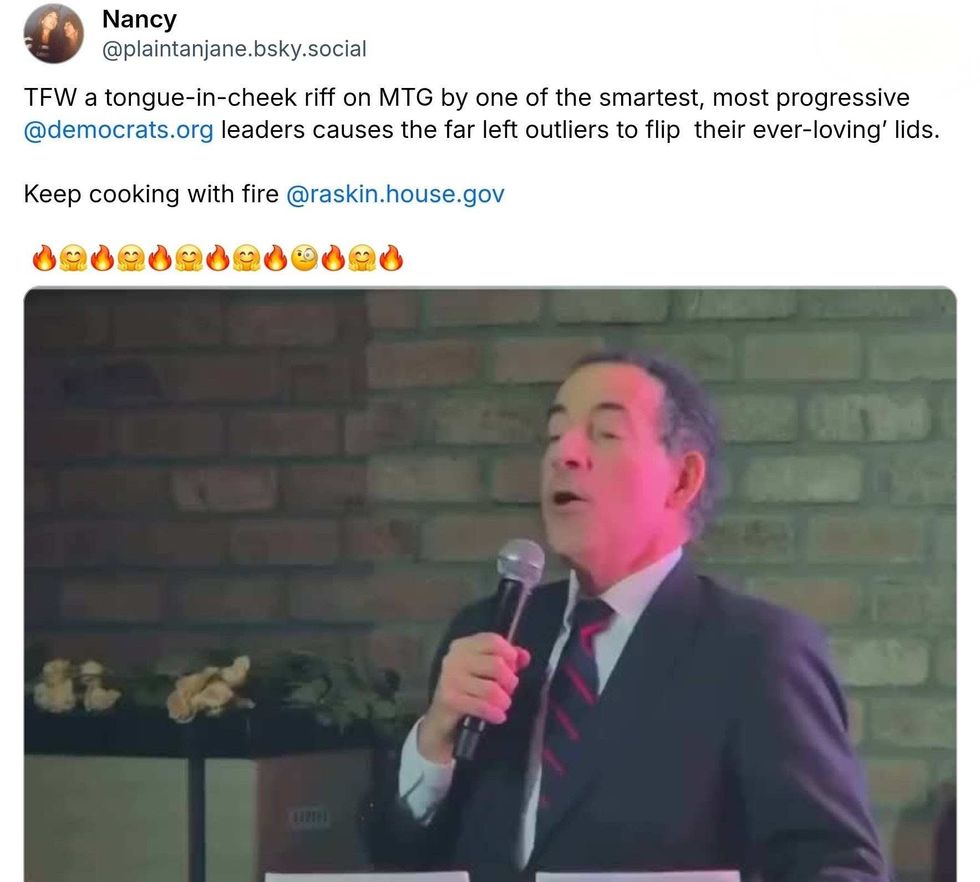 @plaintanjane/Bluesky
@plaintanjane/Bluesky @alycemiller/Bluesky
@alycemiller/Bluesky






 House Oversight Committee
House Oversight Committee @JayShamsX
@JayShamsX


 @ceoofhoesmad/TikTok
@ceoofhoesmad/TikTok @showmeurmoomoo/TikTok
@showmeurmoomoo/TikTok @cablehoe/TikTok
@cablehoe/TikTok @samanthagibson46/TikTok
@samanthagibson46/TikTok @ikranamoktoyu/TikTok
@ikranamoktoyu/TikTok @hopeyoufindyourdad/TikTok
@hopeyoufindyourdad/TikTok @lexytheactress/TikTok
@lexytheactress/TikTok @athenasworld95/TikTok
@athenasworld95/TikTok @kelsibell24/TikTok
@kelsibell24/TikTok @sydneywynder/TikTok
@sydneywynder/TikTok @vickbash/TikTok
@vickbash/TikTok @xp.etros/TikTok
@xp.etros/TikTok