The First of November is referred to as All Saints' Day by the Roman Catholic, Anglican, and Protestant churches. Also known as All Hallows' Day, All Hallows Tide, Hallowmas, Feast of All Saints, and Solemnity of All Saints, the day is a Christian festival that celebrates all saints, known and unknown. It is celebrated on the first Sunday after Pentecost in Eastern Orthodox churches.
The earliest known observance of the holiday was in the early fourth century, and later it was made canon by Pope Boniface IV at the beginning of the seventh century. After Pentecost in 609 A.D., the pope consecrated Rome's Parthenon to the Virgin Mary and all martyrs.
In the eight century, the holy day was moved to November 1 by Pope Gregory III. He sought to assimilate and supersede the autumn pagan Festival of the Dead, also known as Samhain or Feast of Saman (lord of death). Similar integrations happened with Easter and Christmas.
Observances
On this day, as with other Holy Days of Obligation, Catholics are expected to attend Mass, though this requirement is waived by most bishops if the holiday is not on a Sunday. Usually there is a reading of the Beatitudes from Jesus' Sermon on the Mount in the Gospel of Matthew. You may have heard it before; the blessing begins with "Blessed are the poor in spirit, for theirs is the kingdom of heaven."
Every country has different traditions performed on this day. In Spain, Portugal, and Mexico, offerings are made to the dead. People in Belgium, Hungary, and Italy bring flowers to the grave of relatives. It is also a time for cleaning around the graves, weeding, and repairing any damage that occurred in the past year. In many parts of Europe and in Asia, it is customary to leave a lit candle or lantern on top of the grave or tombstone.
The liturgical color on this day is white, and symbols associated with All Saints' Day include a crown, the hand of God, a sheaf of wheat (remnant of pagan harvest festivals), and images of saints.
Please SHARE this with your friends and family.
H/T: Time and Date, Huffington Post, Catholicism.com,


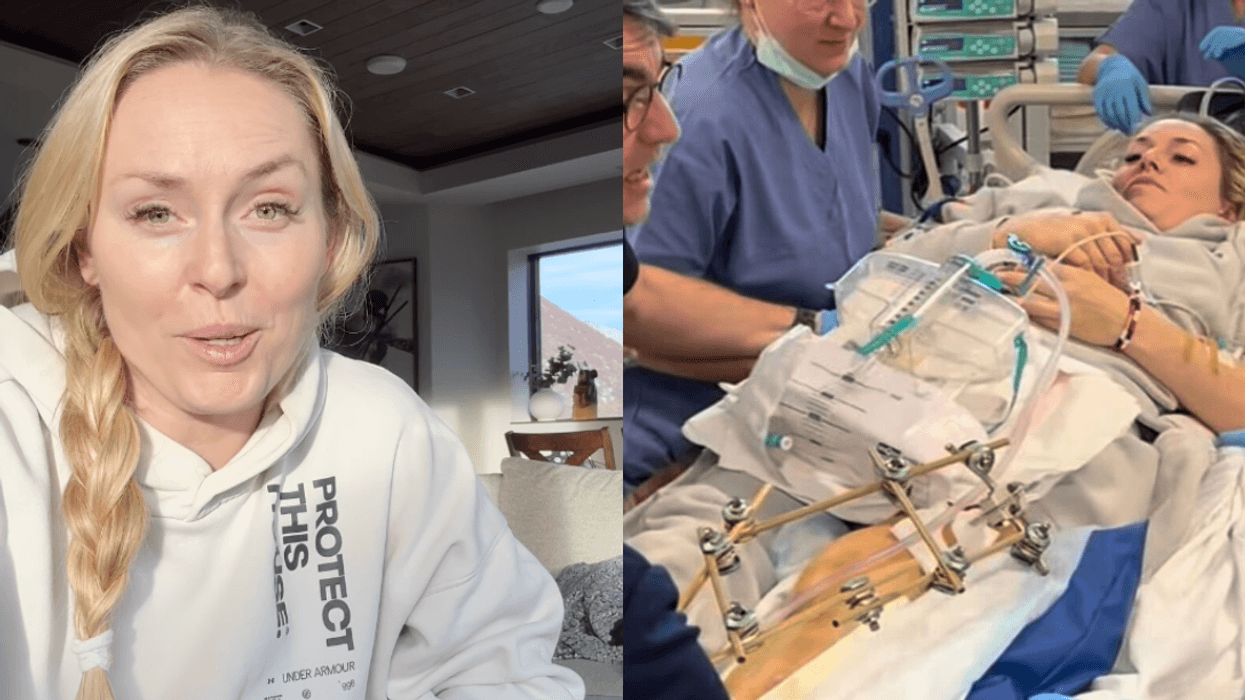




 reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X reply to @elonmusk/X
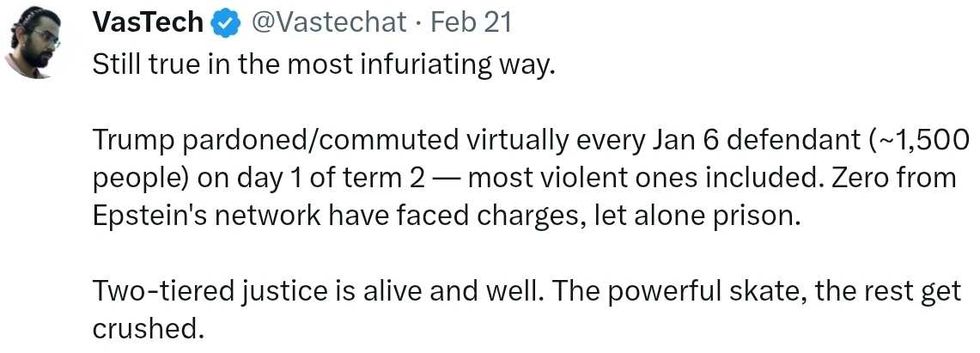
reply to @elonmusk/X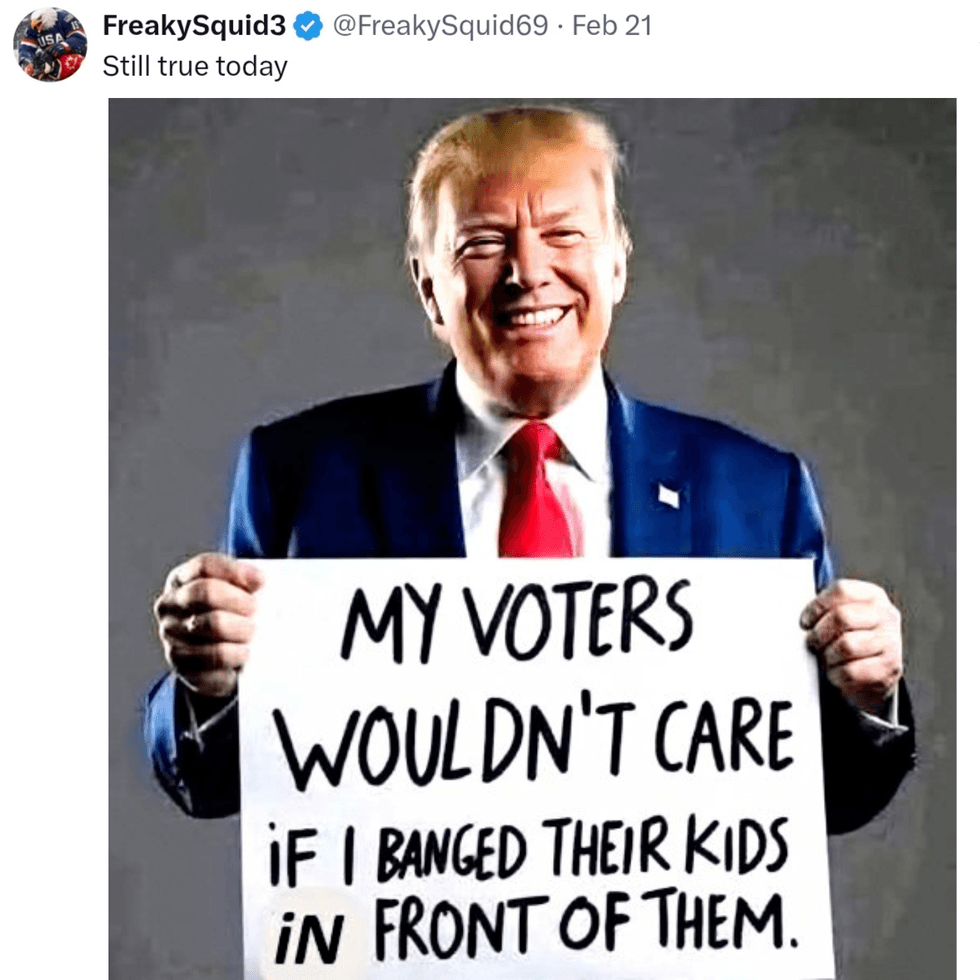 reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X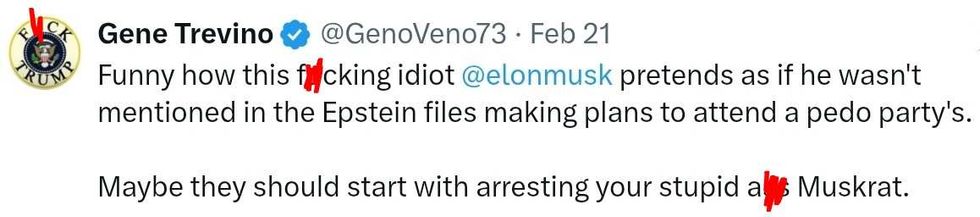 reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X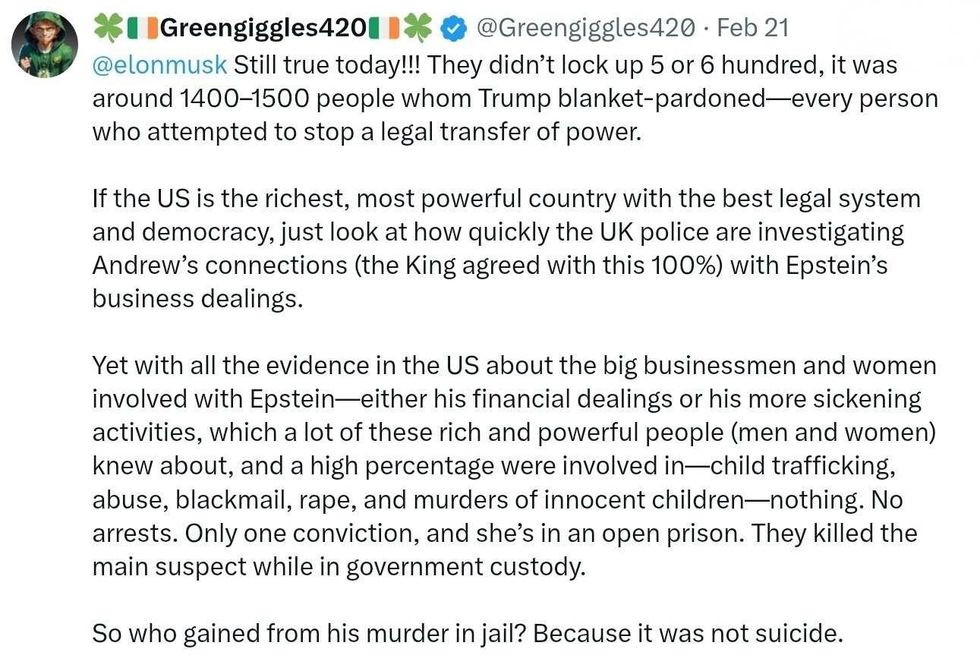 reply to @elonmusk/X
reply to @elonmusk/X








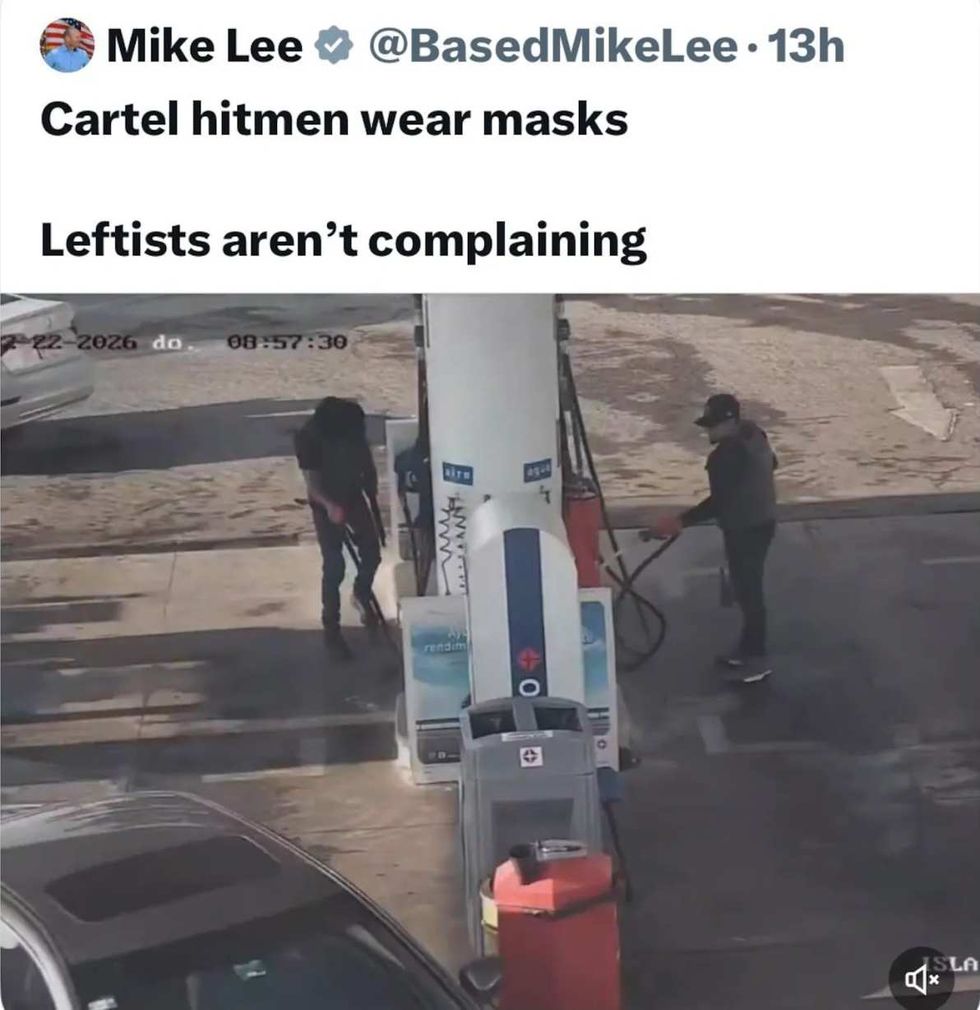 @BasedMikeLee/X
@BasedMikeLee/X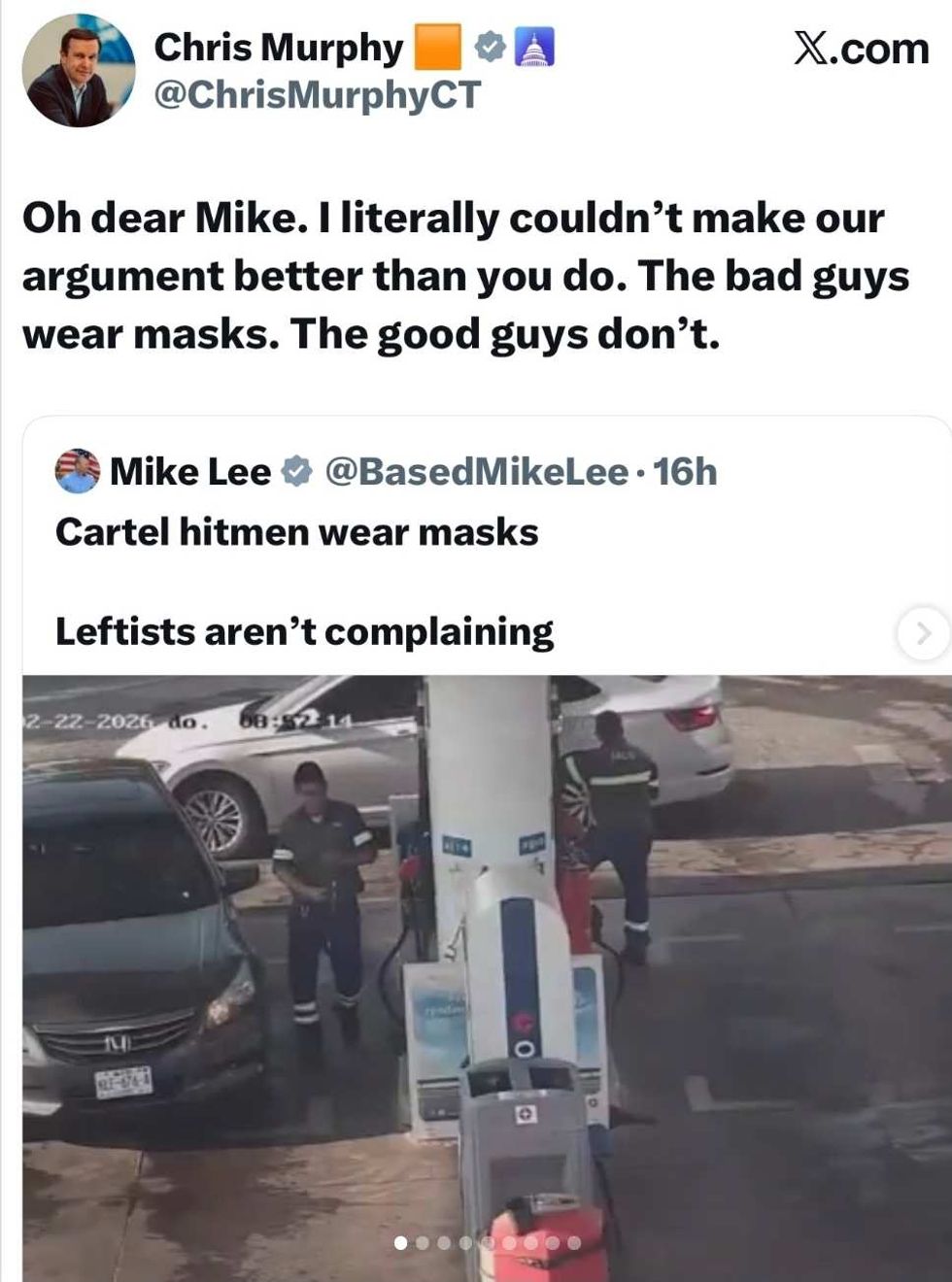 @ChrisMurphyCT/X
@ChrisMurphyCT/X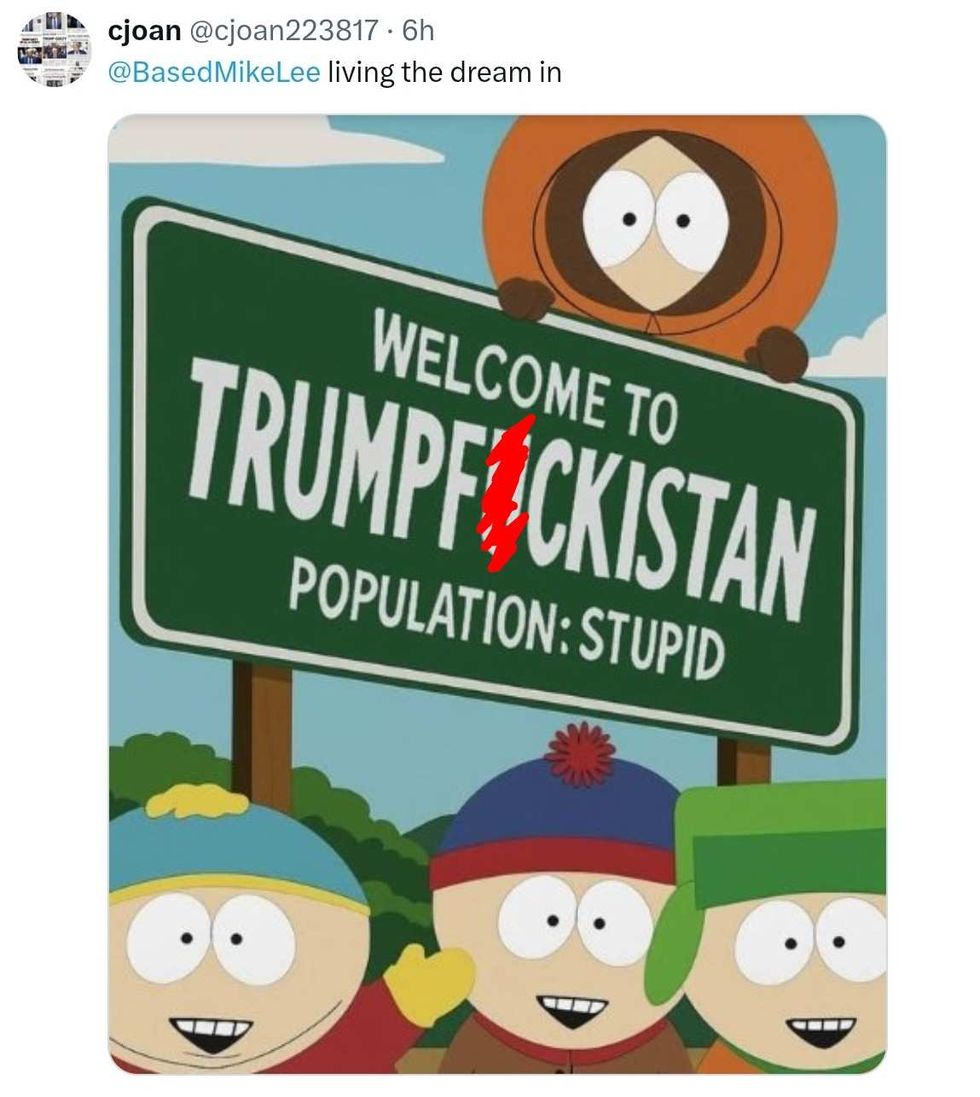 @cjoan223817
@cjoan223817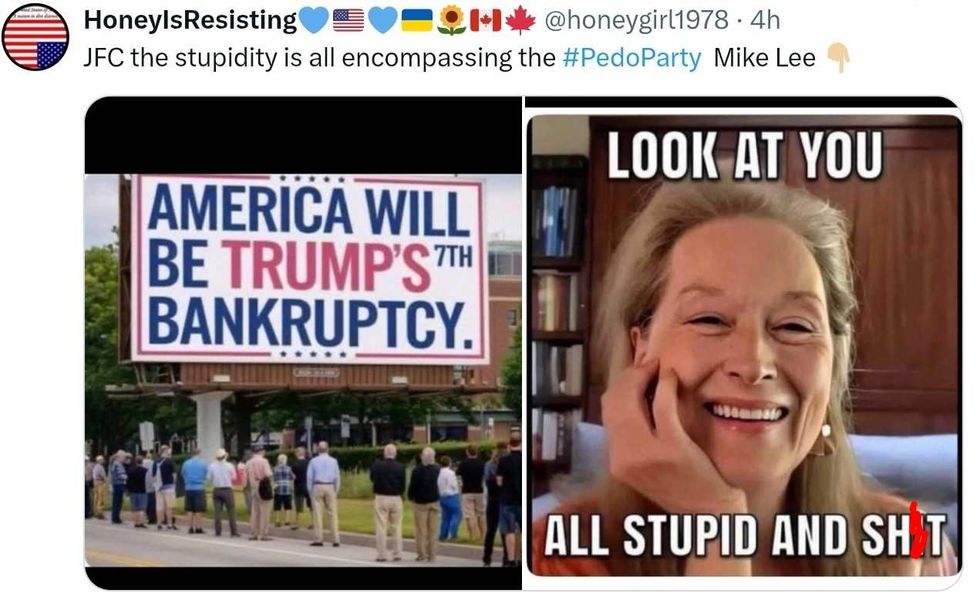

 @wideofthepost/X
@wideofthepost/X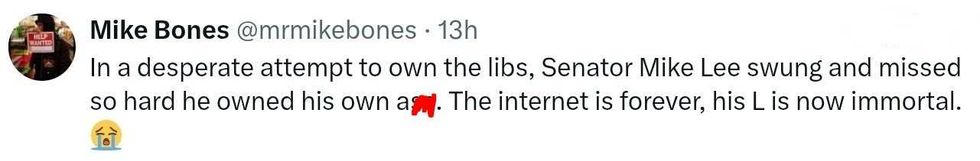 @mrmikebones/X
@mrmikebones/X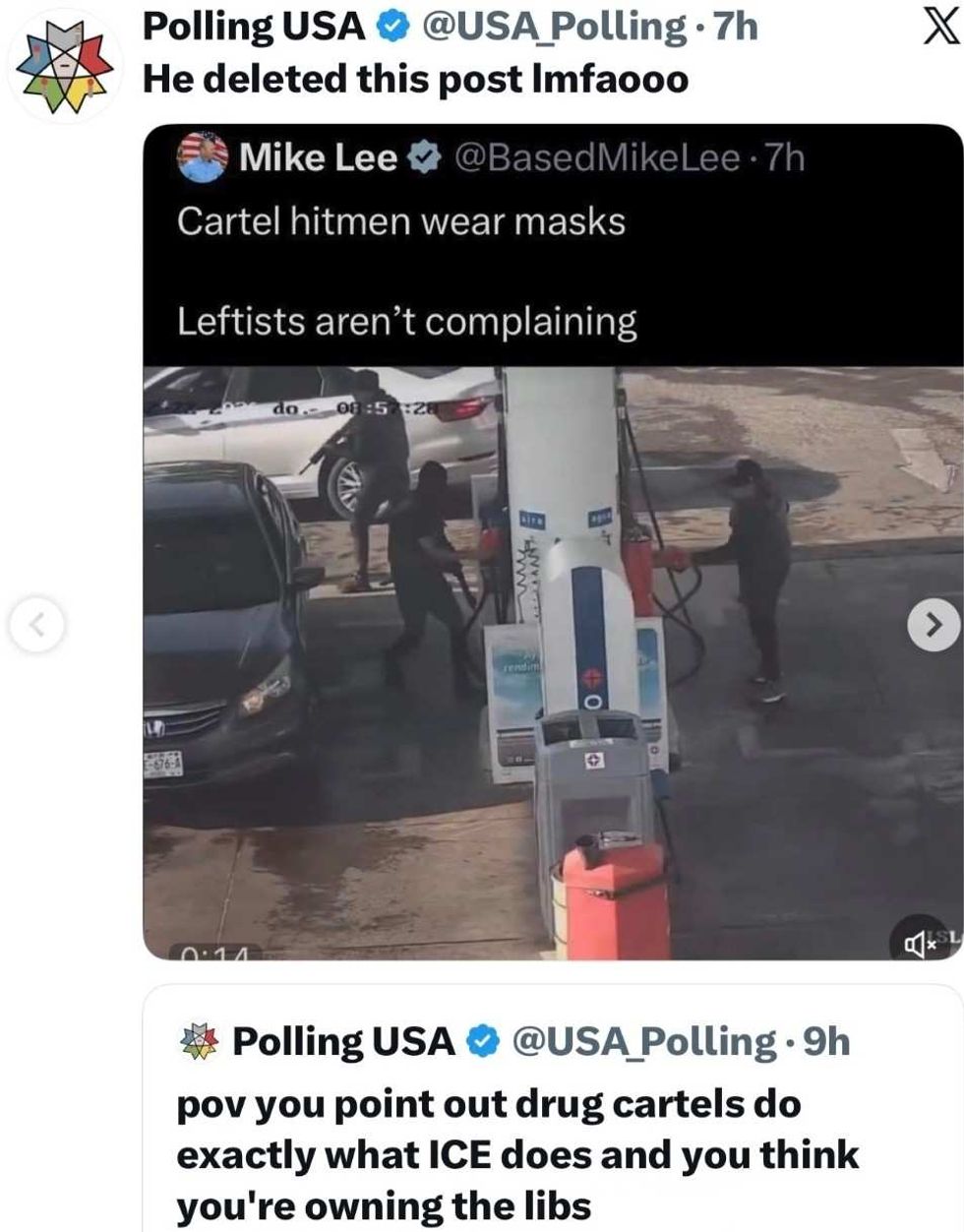 @USA_Polling/X
@USA_Polling/X