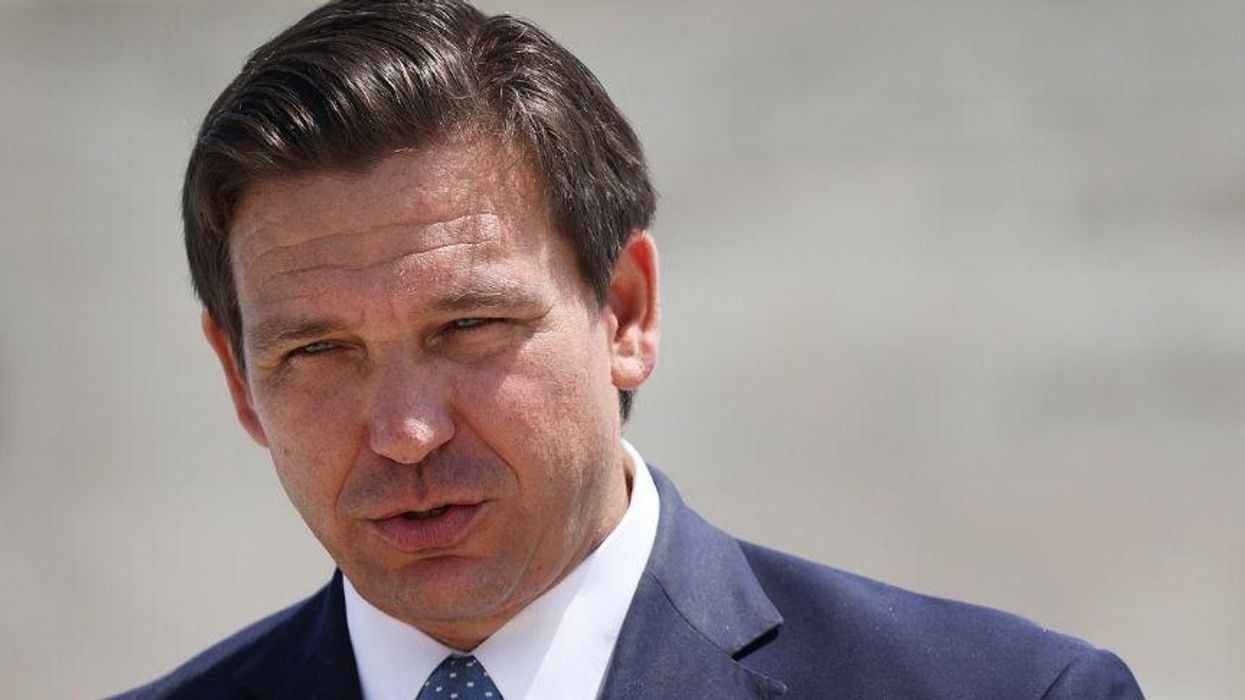
Last week, Florida Governor Ron DeSantis signed into law the most sweeping and restrictive "anti-riot" law in the country, despite his state's having experienced relative calm during last year's Black Lives Matter protests.
DeSantis crowed about the new law at a press conference in Winter Haven, Florida. "If you look at the breadth of this particular piece of legislation, it is the strongest anti-rioting, pro-law enforcement piece of legislation in the country," he said, per the Orlando Sentinel, while surrounded by uniformed deputies and other law enforcement. "There's just nothing even close."
DeSantis intimated that Derek Chauvin might be acquitted for the murder of George Floyd, and that the state was "prepared." Echoing this sentiment, state CFO Jimmy Patronis claimed that Portland, New York and Seattle "burned to the ground" last summer—a hyperbolic statement given that violent protests were limited to small pockets in each of those cities, and the overwhelming majority of protests across the country were peaceful.
Polk County Sheriff Grady Judd, who spoke at the event, trumpeted that the bill would make Florida safe for families and would "guarantee an environment where you can come here and have fun" while holding up pictures of Black families at Disneyland and the beach.
Tellingly, not a single African American was on stage for the crowded signing ceremony. Orlando, where Disneyworld is located, saw only limited unrest last year, and 80 of about 100 arrests on charges of disorderly conduct during the first week of George Floyd protests in 2020 ultimately were dropped. Somewhat bizarrely, during his remarks Judd pivoted to take aim at voter registration, warning "don't register to vote and vote the stupid way they did up north and get what they got."
The new law has been decried by civil rights activists and communities of color as a direct attack upon their right to speech and freedom of assembly. On Wednesday, a nonprofit group called Legacy Entertainment & Arts Foundation filed a lawsuit in federal court to block the law from taking effect, arguing that it violates due process and freedom of speech.
Critics charge that the new law is overly broad and vague, which could lead to emboldened police and anti-protest agitators assaulting peaceful demonstrators. Democratic state Senator Shevrin Jones, (D-West Park) told the Sentinel the new law "undermines every Floridian's constitutional rights, and it is disgusting that the GOP would rather empower vigilantes and silence voices than listen to the majority of Floridians who oppose this dangerous bill. The governor's spectacle is a distraction that will only further disenfranchise Black and brown communities."
The ACLU warned the new law would give police broad discretion over what constitutes a demonstration or a riot. "The bill was purposely designed to embolden the disparate police treatment we have seen over and over again directed towards Black and brown people who are exercising their constitutional right to protest," said Micah Kubic, the executive director of ACLU of Florida. Senator Jones echoed this sentiment.
"You don't want us on the streets. You don't want us to kneel at games. You don't want us to shut down the streets," Jones said. "Our response to injustice is to protest, but your response is to criminalize it when the recourse for us is to turn to the streets to make our voices heard in this unjust system."
Some of the law's most controversial provisions raise risks to those who are assembling peacefully. A gathering of three or more people can now be considered a riot, according to an analysis by Vice. Further, in addition to making blocking any highway a felony offense, the law grants civil liability immunity to anyone who drives through protestors blocking a road. Critics charge that could encourage vigilantes to harm protestors, thinking they cannot be held to account for it. It also denies bail to anyone arrested during a protest until their first court appearance happens, which DeSantis admitted is aimed at keeping people who were arrested from rejoining ongoing protests.
The new bill also creates a whole swath of new crimes including ones called "aggravated rioting" (which carries a whopping 15-year sentence) and a vague crime of "mob intimidation" (defined as two or more people trying to compel someone to "assume, abandon, or maintain a particular viewpoint against his or her will") while protecting memorials, statues and historical properties including Confederate monuments.
Any person who tears down a memorial dedicated to a historical person or event now faces a second-degree felony—which is punishable by up to 15 years in prison. It also penalizes local governments that move to decrease funding for their police departments and makes them liable for damage if elected leaders "tell law enforcement to stand down," according to the governor.
The law's fate in the courts is unclear. Legal experts note that there are several aspects of it that appear to infringe upon speech and assembly in ways that are not narrowly tailored to serve a significant government interest, and there are parts of the law that appear facially overbroad and vague. Federal courts will be weighing in not long from now to determine whether all, part or none of it can withstand constitutional scrutiny.























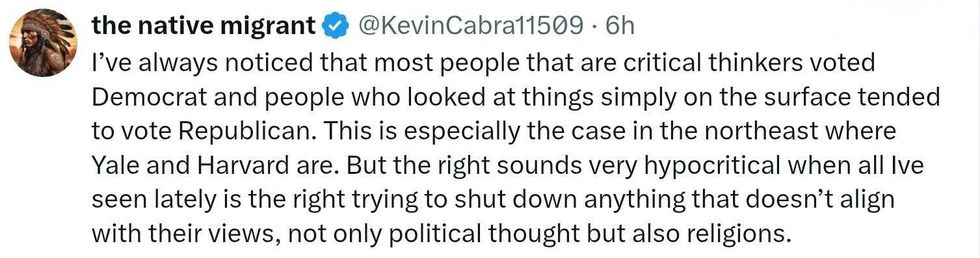 replying to @elonmusk/X
replying to @elonmusk/X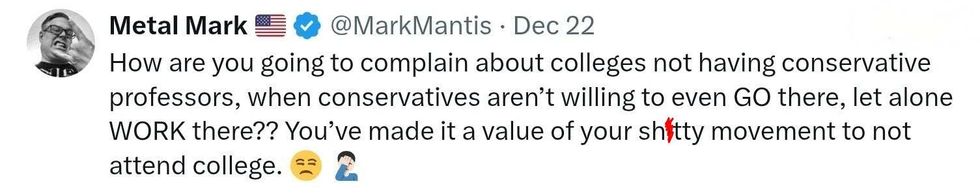 replying to @elonmusk/X
replying to @elonmusk/X replying to @elonmusk/X
replying to @elonmusk/X replying to @elonmusk/X
replying to @elonmusk/X
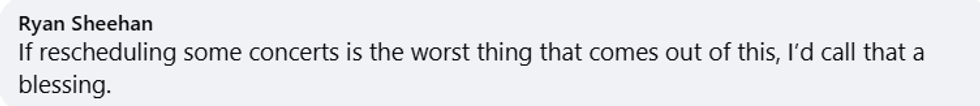 Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook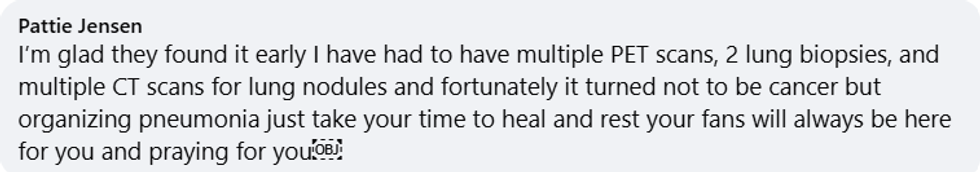 Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook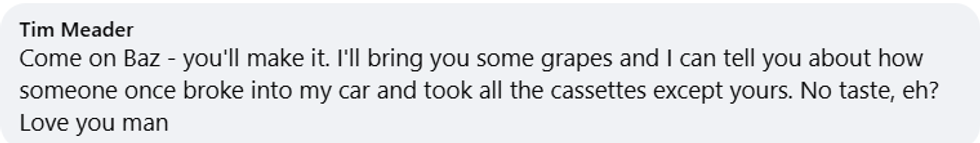 Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook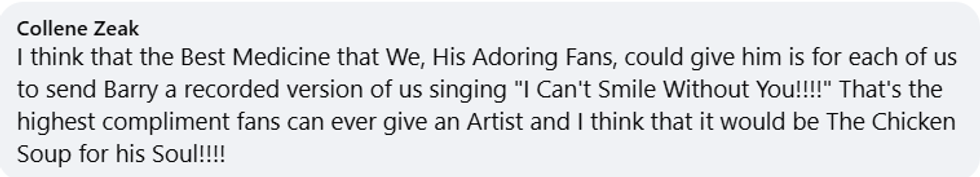 Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook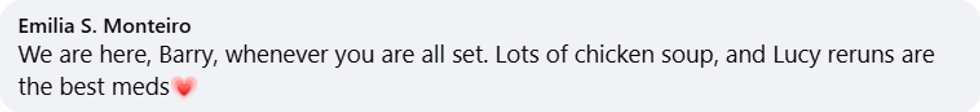 Barry Manilow/Facebook
Barry Manilow/Facebook