According to the generations that precede them, millennials have killed a number of timeless industries: brick-and-mortar stores, diamonds, napkins, and good ole' fashioned conversation to name a few. Next on the executioner's block? The English language. But before anyone gets too worked up about the end of communication as we know it, be aware that millennials aren't just breaking down the way written English is used—they're building a new system on top of it.
Millennials are forming a new grammatical system, wherein misspellings, capitalizations, and incorrect grammar are used to signal previously undetectable nuances like tone, body language, and sarcasm.
The simplest changes are just meant to save time.
In a world of digital communication, the less keystrokes it takes to convey an idea, the better. Millennials are routinely leaving the apostrophes out of contractions like "dont," "cant," and "im," while also shortening phrases like "thank you" and "I don't know" to "ty," "idk," "lol," "bc," and so forth. Chances are, even the least tech savvy individual will have encountered some of those famous text abbreviations.
Though these changes arise out of convenience (or laziness, depending on who you're talking to), linguists know the urge to save some time is essentially the basis for how language evolves, so they're taking a particular interest in these "mutations."
One particularly interesting device Millennials use is "atypical capitalization."
The standard rules of English state that capitalization should be "reserved for proper nouns, people, countries, brands, the first person pronoun, and the first word in a new sentence." Millennials are unbound by these rules, however, and use capitalization to express information that wasn't previously provided. According to Dr. Lauren Fonteyn, an English Linguistics lecturer at University of Manchester who spoke with Mashable:
What we see in millennial spelling is different, but not unruly. Capitals are not necessarily used for people (we know who ed sheeran is, it's Ed Sheeran), or initial words of a text or tweet.
Punctuation (or lack of it) plays an important role as well!
The absence of a period at the end of a sentence typically indicates a neutral tone in "millennial speak," while the grammatically correct full stop to conclude a thought can indicate anger. Two periods ("..") are used to ask for elaboration and an ellipses ("...") is basically an awkward pause. And, mimicking real life, punctuation completely disappears when a millennial is excited:
These quirks of English don't only convey tone; they convey community.
A senior lecturer in Welsh Linguistics, Dr Peredur Webb-Davies, says internet speak is not only helpful in conveying paralinguistic information (body language, tone, etc.), but also imparts a sense of identity in the digital world. Dr. Fonteyn agrees, and pointed out the use of the trademark symbol as an example:
When TM is added to a phrase, it ADDS something you can't do in a regular conversation. I don't think this originates in speech, because I don't think anyone actually says "the point TM." This emphatic method might actually originate in digital language: they're not just indicating prosody from spoken language but they are adding a visual joke to it, TM in Hyperscript.
Many of these changes are both funny and practical.
The ability to convey paralinguistic information isn't just an oddity—it's an advantage informal internet English has over its older, stuffier predecessor. Some researchers believe we're watching the beginnings of a newer, more expressive version of our written word.











 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok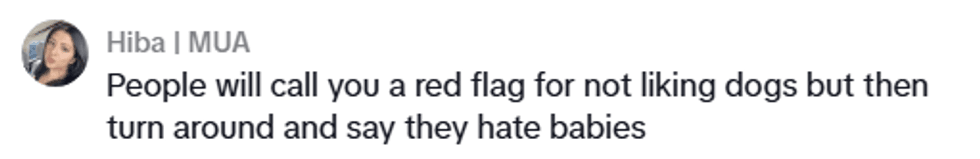 @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok @madswellness/TikTok
@madswellness/TikTok
 @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok @vanellimelli030/TikTok
@vanellimelli030/TikTok
 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok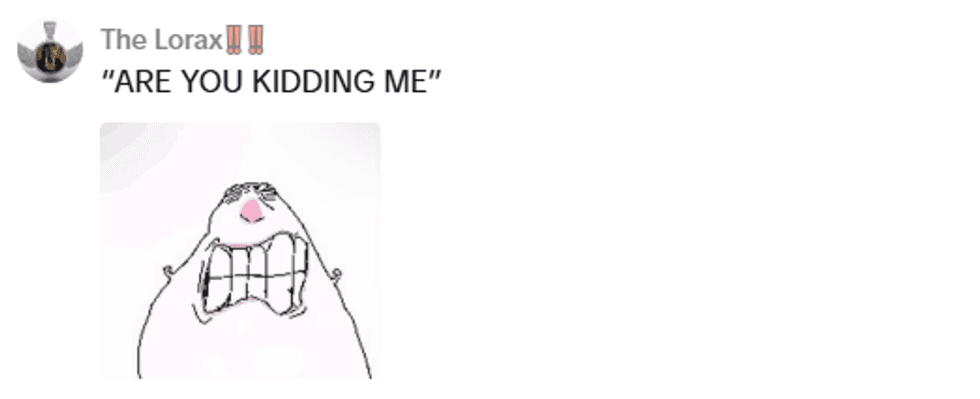 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok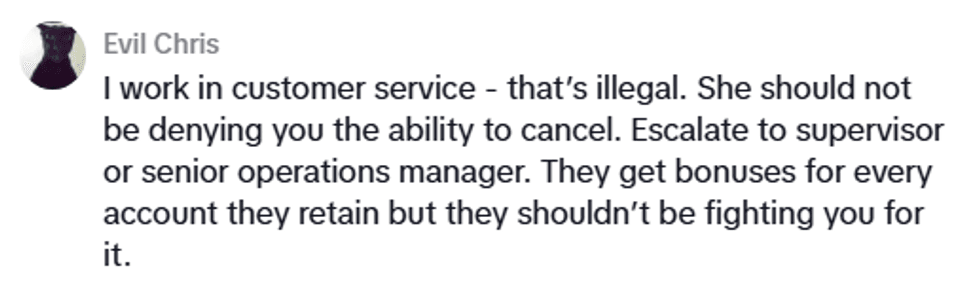 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok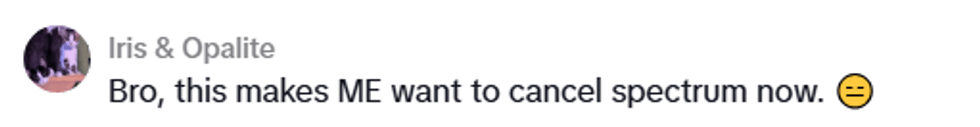 @anissahm15/TikTok
@anissahm15/TikTok
 @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok @hustleb***h/TikTok
@hustleb***h/TikTok